Related Research Articles

Bernard Bailey Kerik is an American consultant and former police officer who was the 40th Commissioner of the New York Police Department from 2000 to 2001. As a convicted felon, he obtained a presidential pardon from President Donald Trump in 2020 for his numerous federal convictions for tax fraud, ethics violations, and criminal false statements.

In American politics, a swing state is any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often referring to presidential elections, by a swing in votes. These states are usually targeted by both major-party campaigns, especially in competitive elections. Meanwhile, the states that regularly lean to a single party are known as "safe states", as it is generally assumed that one candidate has a base of support from which a sufficient share of the electorate can be drawn without significant investment or effort by the campaign.

A push poll is an interactive marketing technique, most commonly employed during political campaigning, in which a person or organization attempts to manipulate or alter prospective voters' views under the guise of conducting an opinion poll. Large numbers of voters are contacted with little effort made to collect and analyze their response data. Instead, the push poll is a form of telemarketing-based propaganda and rumor-mongering masquerading as an opinion poll. Push polls may rely on innuendo, or information gleaned from opposition research on the political opponent of the interests behind the poll.

Jason E. Chaffetz is an American retired politician who served as the U.S. representative for Utah's 3rd congressional district from 2009 until his resignation in 2017. He chaired the Committee on Oversight and Government Reform from 2015 until 2017.
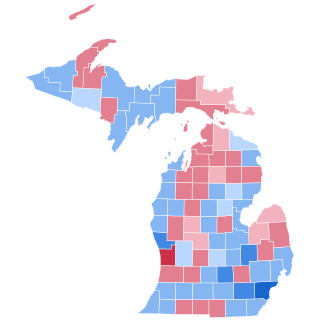
The 2008 United States presidential election in Michigan took place on November 4, 2008. It was part of the 2008 United States presidential election which happened throughout all 50 states and D.C. Voters chose 17 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state and First Lady of the United States Hillary Clinton and Virginia junior senator Tim Kaine, in what was considered one of the biggest political upsets in American history. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote. It was also the sixth and most recent presidential election in U.S. history in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 1944.

Jocelyn Benson is an American academic administrator, attorney, and politician serving as the 43rd Secretary of State of Michigan since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, she is a former dean of Wayne State University Law School, a co-founder of the Military Spouses of Michigan, and a board member of the Ross Initiative in Sports for Equality. Benson is the author of State Secretaries of State: Guardians of the Democratic Process.

Robert E. Mook is an American former political strategist. He was the campaign manager for Hillary Clinton's 2016 presidential campaign.

John Rufus Gifford is an American politician, and diplomat, who has served as Finance Chair of the Harris 2024 presidential campaign since July 2024. He was the chief of protocol of the United States from 2022 to 2023. Between 2013 and 2017, he was the United States Ambassador to Denmark.

The 2016 presidential campaign of Hillary Clinton was announced in a YouTube video on April 12, 2015. Clinton was the 67th United States Secretary of State and served during the first term of the Obama administration, from 2009 to 2013. She was previously a United States Senator from New York from 2001 to 2009, and is the wife of former President Bill Clinton. Hillary Clinton served as First Lady of the United States from 1993 to 2001.
Social media and political communication in the United States refers to how political institutions, politicians, private entities, and the general public use social media platforms to communicate and interact in the United States.

The 2020 United States Senate election in Michigan was held on November 3, 2020, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent Michigan. It was held concurrently with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.

Katherine Marie Walsh is an American Republican political operative who served as White House Deputy Chief of Staff for Implementation in the Donald Trump administration. She also worked with the Trump-aligned 501(c)(4) advocacy organization America First Policies.
In the 2010s, personal data belonging to millions of Facebook users was collected without their consent by British consulting firm Cambridge Analytica, predominantly to be used for political advertising.
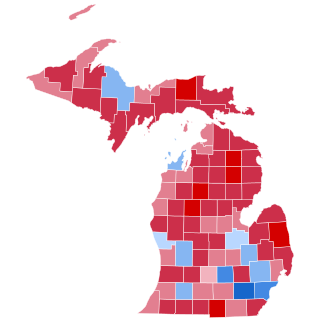
The 2020 United States presidential election in Michigan was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Michigan voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and his running mate, Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana against the Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate, Senator Kamala Harris of California. Michigan had 16 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Minnesota was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Minnesota voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald J. Trump, and running mate Vice President Michael R. Pence against the DFL nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Minnesota has ten electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in North Carolina was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. North Carolina voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state was narrowly won by the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana, against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. North Carolina had 15 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2022 Nevada gubernatorial election took place on November 8, 2022, to elect the governor of Nevada. Incumbent Democratic governor Steve Sisolak lost re-election to a second term, being defeated by Republican nominee, Clark County Sheriff, Joe Lombardo.

This is a list of statewide public opinion polls that have been conducted relating to the 2020 United States presidential election. The persons named in the polls were declared candidates or received media speculation about their possible candidacy.

In the United States, Sanders–Trump voters, also known as Bernie–Trump voters, are Americans who voted for Bernie Sanders in the 2016 or 2020 Democratic Party presidential primaries, but who subsequently voted for Republican Party nominee Donald Trump in the general election. In the 2016 U.S. presidential election, these voters composed an estimated 6%-12% of Sanders supporters.
References
- ↑ Madhani, Aamer (2 May 2014). "White House raises concerns about data discrimination". USA Today . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "Obama Campaign Shared '08 Polling With Silver". BuzzFeed. 5 September 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Issenberg, Sasha (11 September 2012). The Victory Lab: The Secret Science of Winning Campaigns. Crown/Archetype. ISBN 9780307954817 . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Nixon, Ron (14 April 2011). "U.S. Groups Helped Nurture Arab Uprisings". New York Times . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Reid J. Epstein (17 October 2014). "Pols' Picks: Prognosticators Boost View of GOP Senate Chances". Wall Street Journal . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 Javers, Eamon (12 February 2014). "Inside the wacky world of weird data: What's getting crunched". CNBC . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Weichselbaum, Simone (July 16, 2018). "How a 'Sentiment Meter' Helps Cops Understand Their Precincts". Wired.
- ↑ "FRANKLIN BANK FIRES UP SEAHOLM HIGH COMPUTER LAB". thefreelibrary.com. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 "Michael Simon". crainsdetroit.com. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 Serge Grossman; Michael Simon (2008). "And Congress Shall Know the Truth: The Pressing Need for Restructuring Congressional Oversight of Intelligence" (PDF). Harvard Law and Policy Review . 2. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Frayne, James (9 September 2013). Meet the People: Why businesses must engage with public opinion to manage and enhance their reputations. Harriman House. ISBN 978-0857192578 . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Scott, Amy (July 24, 2018). "The tech tool for police accountability that's like "Yelp for cops"". Marketplace.
- ↑ "Quadrangle" (PDF). law.umich.edu. University of Michigan Law School. p. 35. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Varon, Elana (2 October 2012). "Voter Data: What the Candidates Know About You". Mashable . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Fitzpatrick, Jack (1 March 2015). "Giffords's Gun-Control Group Plots Path Forward After Rough 2014 Debut". National Journal . Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ Fitzpatrick, Jack (March 1, 2015). "Giffords's Gun-Control Group Plots Path Forward After Rough 2014 Debut". The Atlantic.
- ↑ "CBS Radio Nets Obama Campaign Vet". Inside Radio. December 23, 2015.
- 1 2 "Elucd, a Community Pollster for Police, Raises $1M Seed Round". Government Technology. January 8, 2018.
- 1 2 Bailey, Jonathan (July 18, 2019). "Survey shows low trust in the South Bend Police Department". ABC57.
- ↑ Shieber, Jonathan (August 21, 2017). "Elucd's polling pushes for greater community accountability for police". TechCrunch.
- ↑ Baker, Al (May 8, 2017). "Updated N.Y.P.D. Anti-Crime System to Ask: 'How We Doing?'". New York Times.
- ↑ "AOC wants to cancel those who worked for Trump. Good luck with that, they say". Politico . Archived from the original on 2023-05-29.