Related Research Articles

Henri de Tonti, also spelled Henri de Tonty, was an Italian-born French military officer, explorer, and voyageur who assisted René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, with North American exploration and colonization from 1678 to 1686. de Tonti was one of the first explorers to navigate and sail the upper Great Lakes. He also sailed the Illinois and the Mississippi, to its mouth and thereupon claimed the length of the Mississippi for Louis XIV of France. He is credited with founding the settlement that would become Peoria, Illinois. De Tonti established the first permanent European settlement in the lower Mississippi valley, known as Poste de Arkansea, making him "The Father of Arkansas".

Cyprien Tanguay was a French Canadian priest and historian.

The Battle of Fort Niagara was a siege late in the French and Indian War, the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War. The British siege of Fort Niagara in July 1759 was part of a campaign to remove French control of the Great Lakes and Ohio Valley regions, making possible a western invasion of the French province of Canada in conjunction with General James Wolfe's invasion to the east.
Marin Boucher, was a pioneer of early New France and one of the most prolific ancestors of French Canada, being the ancestor of most of the Bouchers of North America, particularly in the Province of Quebec, Northern New Brunswick, Ontario and Western Canada. Estimates of the number of families in Canada and the United States descended from Marin Boucher run as high as 350,000, although most of them do not bear the name Boucher today because Marin's line produced more daughters than sons.

Antoine Juchereau Duchesnay was the Seigneur of Beauport, Saint-Denis, Fossambault, Gaudarville, and Saint-Roch-des-Aulnaies. He fought with the Troupes de Marine and after the British Conquest of New France joined the British Army, defending Fort Saint-Jean where he was captured and imprisoned by the Americans in 1775. He represented Buckingham County in the 1st Parliament of Lower Canada and was afterwards appointed a member of the Executive Council of Lower Canada.
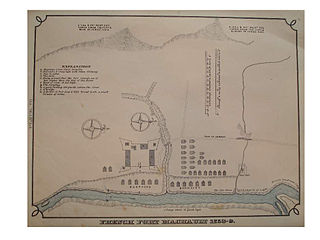
Fort Machault was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort helped the French control these waterways, part of what was known as the Venango Path from Lake Erie to the Ohio River. It was one of four forts designed to protect French access to the Ohio Country and connections between its northern and southern colonies. From north to south the forts were Fort Presque Isle, Fort Le Boeuf, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne. In January 1759 the British launched an expedition to attack Fort Machault, but had to turn back after encountering resistance from French-Allied Native Americans. The fort was abandoned by the French in August 1759, and burned so that the British could not use it. It was replaced by the British in 1760 with Fort Venango.
Jean-Baptiste Bissot, Sieur de Vincennes, was a Canadian soldier, explorer, and friend to the Miami Nation. He spent a number of years at the end of his life as an agent of New France among the Miami.
François-Marie Picoté, sieur de Belestre II was a colonial soldier for both New France and Great Britain.

Pierre Boucher de Boucherville was a French settler, soldier, officer, naturalist, official, governor, and ennobled aristocrat in Nouvelle-France or New France.

The military of New France consisted of a mix of regular soldiers from the French Army and French Navy supported by small local volunteer militia units. Most early troops were sent from France, but localization after the growth of the colony meant that, by the 1690s, many were volunteers from the settlers of New France, and by the 1750s most troops were descendants of the original French inhabitants. Additionally, many of the early troops and officers who were born in France remained in the colony after their service ended, contributing to generational service and a military elite. The French built a series of forts from Newfoundland to Louisiana and others captured from the British during the 1600s to the late 1700s. Some were a mix of military posts and trading forts.
Jacques Goulet was a pioneer settler to Canada who was part of the Percheron immigration movement recruited to colonize the shores of the Saint Laurence River at Québec in New France, a miller and the ancestor of all of the Goulets in North America.
The Battle of La Belle-Famille occurred on July 24, 1759, during the French and Indian War along the Niagara River portage trail. François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery's French relief force for the besieged French garrison at Fort Niagara fell into Eyre Massey's British and Iroquois ambush. This action formed part of the larger Battle of Fort Niagara.
Captain Pierre Pouchot was a French military engineer and officer in the French regular army.
François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery was a colonial military leader in the French province of Canada. Active in the defense of New France during the Seven Years' War, he died of wounds sustained in the 1759 Battle of La Belle-Famille.
Pierre Robineau de Portneuf, was an officer in the colonial regular troops. He was born on August 9, 1708, in Montreal, Quebec, second son of René Robineau de Portneuf and Marguerite Daneau de Muy, He married Marie-Louise Dandonneau Du Sablé on April 22, 1748. He died November 15, 1761, in the shipwreck of the Auguste off Cape Breton Island.
Gaspard-Joseph Chaussegros de Léry, was Louis XV's Chief Engineer of New France. He is recognised as the father of the first truly Canadian architecture. In 2006, the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada designated him a person of national historic importance. It highlighted his contribution to the development of New France through the quality, variety, importance and scope of his work in the fields of military engineering, civil and religious architecture, and urban planning.
Nicolas Paquin was an early pioneer in New France now Quebec, Canada), a carpenter and the ancestor of virtually all of the Paquins in North America.
Louis-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire, also known as Sononchiez by the Iroquois, was a French army officer and interpreter for New France who worked with the Iroquois tribes during the French and Indian Wars in the early 18th century. He helped negotiate the Great Peace of Montreal in 1701 and founded Fort Niagara in 1720.
Philippe-Thomas Chabert de Joncaire, also known as Nitachinon by the Iroquois, was a French army officer and interpreter in New France who established Fort Machault in the 18th century. During his career, he largely served as a diplomat with the indigenous nations rather than as a soldier.
Daniel-Marie Chabert de Joncaire de Clausonne was a French army officer and interpreter in New France who established Fort du Portage near Niagara Falls and fought in the French and Indian War.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gallay, Alan (2015) [1996]. Colonial Wars of North America, 1512-1763. Routledge. p. 409. ISBN 9781317487197.
- 1 2 Zoltvany, Yves F. (1982) [1969]. "Chabert de Joncaire, Louis-Thomas, Sononchiez". Dictionary of Canadian Biography . Vol. 2. University of Toronto/Université Laval.
- 1 2 3 Tanguay, Cyprien (1886). A travers les registres : notes recueillies. Librairie Saint Joseph, Cadieux & Derome. p. 139.
- 1 2 3 4 "Sieur Michel Maray de la Chauvignerie (1704 - 1778)". Genealogy Quebec. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- ↑ Tanguay, Cyprien (1871). Dictionnaire généalogique des familles canadiennes depuis la fondation de la colonie. p. 408.
- ↑ Hickerson, Harold (1985). The Chippewa and Their Neighbors: A Study in Ethnohistory. Ardent Media. p. 44. ISBN 9780829009880.