
Zug, is an affluent municipality and town in Switzerland. The name Zug originates from fishing vocabulary; in the Middle Ages it referred to the right to pull up fishing nets and hence to the right to fish.

Cherbourg-Octeville is a city and former commune situated at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It is a subprefecture of its department, and was officially formed when the commune of Cherbourg absorbed Octeville on 28 February 2000. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Cherbourg-en-Cotentin. The city is a Maritime prefecture and sub-prefecture of la Manche. Due to its union, it is the most populated city in its department with 37,121 inhabitants making it the first city of the department before the Saint-Lô prefecture and the second in the region after Caen.
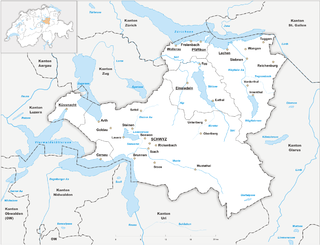
The canton of Schwyz is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centered on and named after the town of Schwyz.

The Eastern Front of World War II was a theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers and co-belligerent Finland against the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.), Poland and other Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It has been known as the Great Patriotic War in the former Soviet Union and modern Russia, while in Germany it was called the Eastern Front, or the German-Soviet War by outside parties.

Lenzburg Castle is a castle located above the old part of the town of Lenzburg in the Canton of Aargau, Switzerland. It ranks among the oldest and most important of Switzerland. The castle stands on the almost circular castle hill, which rises approximately 100 m (330 ft) over the surrounding plain but is only about 250 m (820 ft) in diameter. The oldest parts of the castle date to the 11th century, when the Counts of Lenzburg built it as their seat. The castle, its historical museum and the castle hill with its Neolithic burial grounds are listed as heritage sites of national significance.

Brugg is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Aargau and is the seat of the district of the same name. The city is located at the confluence of the Reuss, Aare, and Limmat, with the Aare flowing through the city's old town. It is located approximately 16 kilometers (9.9 mi) from the cantonal capital of Aarau; 28 kilometers (17 mi) from Zürich; and about 45 kilometers (28 mi) from Basel.

Augusta Raurica is a Roman archaeological site and an open-air museum in Switzerland located on the south bank of the Rhine river about 20 km east of Basel near the villages of Augst and Kaiseraugst. It is the site of the oldest known Roman colony on the Rhine.

Saint-Maurice, or Saint-Maurice d'Agaune, is a small city located in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It is also the capital of the district and of the municipality of Saint-Maurice. The district of Saint-Maurice (district) is composed with 9 municipalities : Collonges, Dorénaz, Evionnaz, Finhaut, Massongex, Salvan, St-Maurice, Vernayaz and Vérossaz. On 1 January 2013, the former municipality of Mex merged into the municipality of Saint-Maurice.

Arbon is a historic and statistic town and a municipality and district capital of the district of Arbon in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
The history of the Swiss Air Force began in 1914 with the establishment of an ad hoc force consisting of a handful of men in outdated and largely civilian aircraft. It was only in the 1930s that an effective air force was established at great cost, capable of inflicting several embarrassing defeats on the Nazi Luftwaffe in the course of an initially vigorous defence of neutral Swiss airspace. The Swiss Air Force as an autonomous military service was created in October 1936. After World War II it was renamed the Swiss Air Force and Anti-Aircraft Command and in 1996 became a separate service independent from the Army, under its present name Schweizer Luftwaffe.
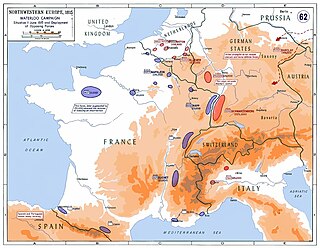
On 1 March 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte escaped from his imprisonment on the isle of Elba, and launched a bid to recover his empire. A confederation of European powers pledged to stop him. During the period known as the Hundred Days Napoleon chose to confront the armies of Prince Blücher and the Duke of Wellington in what has become known as the Waterloo Campaign. He was decisively defeated by the two allied armies at the Battle of Waterloo, which then marched on Paris forcing Napoleon to abdicate for the second time. However Russia, Austria and some of the minor German states also fielded armies against him and all of them also invaded France. Of these other armies the ones engaged in the largest campaigns and saw the most fighting were two Austrian armies: The Army of the Upper Rhine and the Army of Italy.

Franz Brozincevic & Cie (FBW) was a Swiss maker of trucks, motorbuses and trolleybuses, founded by Croatian-born engineer and constructor Franjo (Franz) Brozinčević (1874-1933), active between 1922 and 1985 and based in Wetzikon.

The Swiss National Redoubt was a defensive plan developed by the Swiss government beginning in the 1880s to respond to foreign invasion. In the opening years of the Second World War the plan was expanded and refined to deal with a potential German invasion, that was planned, but never carried out. The term "National Redoubt" primarily refers to the fortifications begun in the 1880s that secured the mountainous central part of Switzerland, providing a defended refuge for a retreating Swiss Army.
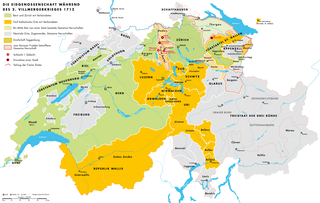
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy, that took place from 12 April until 11 August 1712. On the one hand there were the Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint Gall, on the other the Protestant cantons of Bern and Zürich as well as the abbatial subjects of Toggenburg. The conflict was simultaneously a religious war, a war for the hegemony within the Confederacy and an uprising of subjects. The war ended in a Protestant victory and toppled the balance of political power within the Confederacy.

The Berna L275/10 is a truck model manufactured by the Swiss company Berna from 1937 onwards. The Berna L275 / 10, military designation "Lastw gl 1.5t 4x2", has a total weight of 2200 kg, a structure with cabin and bridge as well as an on-board voltage of 6 V. The 6-cylinder petrol engine with 3600 cm³ produces a power of 66 kW (90 hp).

The GMC AC 454 is a truck model that the GMC manufactured from 1940 on.

The APE 4.80 is a passenger trailer wagon and was built by the Swiss manufacturer Gebrüder Moser + Cie and Ramseier & Jenzer + Cie, both in Bern, for the Zugerland Verkehrsbetriebe (ZVB).

The Saurer 5 DUK is a bus of the Swiss manufacturer Adolph Saurer AG, from Arbon.

































