
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant.

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4,500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

An underground power station is a type of hydroelectric power station constructed by excavating the major components from rock, rather than the more common surface-based construction methods.

Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Incorporated is a Japanese electric utility holding company servicing Japan's Kantō region, Yamanashi Prefecture, and the eastern portion of Shizuoka Prefecture. This area includes Tokyo. Its headquarters are located in Uchisaiwaicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo, and international branch offices exist in Washington, D.C., and London. It is a founding member of strategic consortiums related to energy innovation and research; such as JINED, INCJ and MAI.
Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power is a subsidiary of the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). It operates large nuclear and hydroelectric plants in South Korea, which are responsible for about 27 percent of the country's electric power.

The Tokuyama Dam is an embankment dam near Ibigawa, Ibi District, Gifu Prefecture in Japan. The dam was completed in 2008 and will support a 153 MW hydroelectric power station that is expected to be fully operational in 2015. Currently, Unit 1 at 23 MW was commissioned in May 2014. The dam was originally intended to withhold the upper reservoir of a 400 MW pumped-storage power station until a design change in 2004. The dam is also intended for flood control and water supply. It is the largest dam by structural volume in Japan and withholds the country's largest reservoir by volume as well.

The Hatanagi-I is a dam on the Ōi River in Aoi-ku, Shizuoka, Shizuoka Prefecture on the island of Honshū, Japan. With a height of 125 metres (410 ft), it is the tallest hollow-core concrete gravity dam in the world. It has a hydroelectric power generating station owned by the Chubu Electric Power Company. It supports a 137 megawatts (184,000 hp) pumped-storage hydroelectric power station.

Hydroelectricity is, as of 2019, the second-largest renewable source of energy in both generation and nominal capacity in the United States. In 2021, hydroelectric power produced 31.5% of the total renewable electricity, and 6.3% of the total U.S. electricity.

India is 5th globally for installed hydroelectric power capacity. As of 31 March 2020, India's installed utility-scale hydroelectric capacity was 46,000 MW, or 12.3% of its total utility power generation capacity. Additional smaller hydroelectric power units with a total capacity of 4,683 MW have been installed. India's hydroelectric power potential is estimated at 148,700 MW at 60% load factor. In the fiscal year 2019–20, the total hydroelectric power generated in India was 156 TWh with an average capacity factor of 38.71%.

The Kannagawa Hydropower Plant (神流川発電所) is an under construction pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant near Minamiaiki in Nagano Prefecture and Ueno in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. The power plant utilizes the Minamiaiki River along with an upper and lower reservoir created by two dams, the upper Minamiaiki Dam and the lower Ueno Dam. The power station in between the two dams will contain six 470 megawatts (630,000 hp) pump-generators for a total installed capacity of 2,820 megawatts (3,780,000 hp). Unit 1 commenced commercial operation in 2005 and Unit 2 in 2012. When completed, the plant will have the second-largest pumped-storage power capacity in the world.
The Lianghekou Dam is a clay-core rockfill Embankment dam currently in operation on the Yalong River, a tributary of Yangtze River, in Yajiang County, Sichuan Province, China. The dam is located at the confluence of the Yalong, Xianshui and Qingda Rivers. The 295 m (968 ft) tall dam is the highest embankment dam in the country and support a 3,000 MW power station. Studies for the dam were completed between 2005 and 2009 with preliminary construction beginning that year. Major works on the dam officially began in October 2014. The first two generators were commissioned in September 2021 and the final unit was put in service in March 2022. With the reservoir's relatively large active capacity with respect to the river's annual flow, it can regulate the river flow across multiple years and increase the downstream hydroelectric power stations' output by smoothing out river flow peaks and troughs.
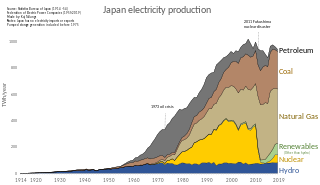
The electric power industry in Japan covers the generation, transmission, distribution, and sale of electric energy in Japan. Japan consumed approximately 918 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity in 2014. Before the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, about a quarter of electricity in the country was generated by nuclear power. In the following years, most nuclear power plants have been on hold, being replaced mostly by coal and natural gas. Solar power is a growing source of electricity, and Japan has the third largest solar installed capacity with about 50 GW as of 2017. Japan's electricity production is characterized by a diverse energy mix, including nuclear, fossil fuels, renewable energy, and hydroelectric power.
Hydroelectricity is the second most important renewable energy source after solar energy in Japan with an installed capacity of 50.0 gigawatt (GW) as of 2019. According to the International Hydropower Association Japan was the world's sixth largest producer of hydroelectricity in 2020. Most of Japanese hydroelectric power plants are pumped-storage plants. Conventional hydropower plants account for about 20 GW out of the total installed capacity as of 2007.

Hydroelectricity is currently China's largest renewable energy source and the second overall after coal. According to the International Hydropower Association, China is the worlds largest producer of hydroelectricity as of 2021. China's installed hydroelectric capacity in 2021 was 390.9 GW, including 36.4 GW of pumped storage hydroelectricity capacity, up from 233 GW in 2011. That year, hydropower generated 1,300 TWh of power, an increase of 68 TWh over 2018 when hydropower generated 1,232 TWh of power, accounting for roughly 18% of China's total electricity generation.

The Okawachi Pumped Storage Power Station is a large pumped-storage hydroelectric power station in Kamikawa Town in the Kanzaki District of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. With a total installed capacity of 1,280 megawatts (1,720,000 hp), it is one of the largest pumped-storage power stations in Japan. The facility is run by the Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO). The power plant started operation in October 1992 and all four units were commissioned by June 1995.

The Shimogo Pumped Storage Power Station is a large pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant in Shimogō, Minamiaizu, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. With an installed capacity of 1,000 megawatts (1,300,000 hp), the system is one of the largest pumped-storage power stations in Japan.

The Imaichi Pumped Storage Power Station is a large pumped-storage hydroelectric power station in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. With a total installed capacity of 1,050 megawatts (1,410,000 hp), it is one of the largest pumped-storage power stations in Japan. The facility is run by the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO). The power plant started operation in July 1988 with a capacity of 350 MW. The other two units entered operation in December 1991. The plant is one of the many large scale pure pumped-storage plants built in Japan since the 1970s to compensate for the increased penetration of base-load nuclear power and peak load from cooling and air-conditioning.















