
Mantophasmatidae is a family of carnivorous wingless insects within the order Notoptera, which was discovered in Africa in 2001. Originally, the group was regarded as an order in its own right, and named Mantophasmatodea, but, using recent evidence indicating a sister group relationship with Grylloblattidae, Arillo and Engel have combined the two groups into a single order, Notoptera.

Pachydactylus is a genus of insectivorous geckos, lizards in the family Gekkonidae. The genus is endemic to Africa, and member species are commonly known as thick-toed geckos. The genus also displays rich speciation, having 57 distinct species identified when compared to other closely related gecko genera like Rhoptropus, most of which have emerged since 35Ma. It has been suggested that the reason for this rich speciation not from adaptive radiation nor nonadaptive radiation, but that the genus represents a clade somewhere between the two drivers of speciation. P. bibronii geckos have been used by NASA as animal models for experimentation.

Namaqualand is an arid region of Namibia and South Africa, extending along the west coast over 1,000 km (600 mi) and covering a total area of 440,000 km2 (170,000 sq mi). It is divided by the lower course of the Orange River into two portions – Little Namaqualand to the south and Great Namaqualand to the north.

Bulbinella is a genus of plants in the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Asphodeloideae, first described as a genus in 1843. Many species are endemic to Cape Province in western South Africa, confined to the winter rainfall area. Other species are endemic to New Zealand, where they are most common in the central Otago region which enjoys a similar climate to the Cape Region of South Africa.

The Richtersveld is a desert landscape characterised by rugged kloofs and high mountains, situated in the north-western corner of South Africa’s Northern Cape province. It is full of changing scenery from flat, sandy, coastal plains, to craggy sharp mountains of volcanic rock and the lushness of the Orange River, which forms the border with neighboring Namibia. The area ranges in altitude from sea level, to 1,377 m (4,518 ft) at Cornellberg. Located in the north-eastern side of the Northern Cape province in South Africa, the Richtersveld is regarded as the only arid biodiversity hotspot on earth and the majority of the area is inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List due to its cultural values.

Pachypodium namaquanum, also known as halfmens or elephants trunk, is a succulent plant of Southern Africa. The genus name Pachypodium is from the Greek for 'thick foot', an allusion to its swollen base, while the species name namaquanum is a reference to Namaqualand.
Crassothonna clavifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in Namibia. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Aloidendron pillansii, formerly Aloe pillansii, the giant quiver tree or bastard quiver tree, is a large, branching species of succulent plant indigenous to southern Africa. It is regarded as critically endangered.
Dicranocara is a genus of Scarabaeidae or scarab beetles in the superfamily Scarabaeoidea. Dicranocara is endemic to the Richtersveld National Park. Three species are known, D. deschodti Frolov and Scholtz, D. tatasensis Deschodt and Scholtz and D. inexpectata Deschodt and Scholtz. Only D. tatasensis occurs south of the Orange River.

ǀAi-ǀAis is a Namibian holiday resort with hot mineral springs in the bed of the Fish River. It is situated in Southern Namibia's ǁKaras Region at the base of the Great Karas Mountains, 128 kilometres (80 mi) west of Karasburg and 224 kilometres (139 mi) south-west of Keetmanshoop.

The ǀAi-ǀAis/Richtersveld Transfrontier Park is a peace park straddling the border between South Africa and Namibia. It was formed in 2003 by combining the Namibian ǀAi-ǀAis Hot Springs Game Park and the South African Richtersveld National Park. Most of the South African part of the park forms part of the buffer zone of the Richtersveld Cultural and Botanical Landscape World Heritage Site, which measures 5,920 square kilometres (2,290 sq mi). The Fish River Canyon is located in the park, the largest canyon in Africa. A Memorandum of Understanding was signed on 17 August 2003 by the presidents of South Africa and Namibia, which formalized the establishment of the park. |Ai-|Ais means ‘burning water’, after the hot springs of the same name.
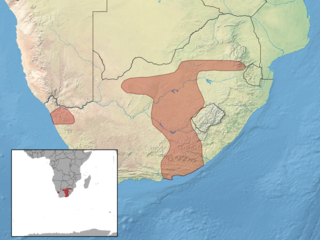
Acontias gracilicauda, the slendertail lance skink or thin-tailed legless skink, is a species of skink. It is found in the Republic of South Africa and Lesotho. Acontias namaquensis was formerly included in this species as a subspecies, but is now recognized as a distinct species.

Aloe ser. Mitriformes is a taxonomic series within the genus Aloe, comprising several closely related species of Southern African rambling aloe. These typically multi-branched sprawling aloe species have rigid fleshy leaves and slender pedicels about the length of the perianth, each being roughly 40 mm long. The stems tend to sprawl along the ground, with the ends densely leafed and upturned.
Amaryllis paradisicola is a species of bulbous perennial plant from South Africa.

Kuboes is a town in Richtersveld Local Municipality in the Northern Cape province of South Africa.
The Richtersveld katydid is a species of katydid that is endemic to the Richtersveld National Park in South Africa. It occurs in semi-arid habitats of the Karoo biotope. It is threatened by livestock grazing and climate change.

Meyerophytum is a genus of succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to the arid region of the Namaqualand and Richtersveld, in the far north-west of South Africa.

Hadogenes is a genus of large African scorpions found from South Africa up to Tanzania.

Conophytum hammeri is a small, endangered, South African species of succulent plant, of the genus Conophytum.

Kuboesphasma is a genus of insects in the family Mantophasmatidae. It is a monotypic genus consisting of the species Kuboesphasma compactum.
















