This section of the timeline of United States history concerns events from 1820 to 1859.

The Southern Review is a quarterly literary magazine that was established by Robert Penn Warren in 1935 at the behest of Charles W. Pipkin and funded by Huey Long as a part of his investment in Louisiana State University. It publishes fiction, poetry, critical essays, and excerpts from novels in progress by established and emerging writers and includes reproductions of visual art. The Southern Review continues to follow Warren's articulation of the mission when he said that it gives "writers decent company between the covers, and [concentrates] editorial authority sufficiently for the journal to have its own distinctive character and quality".
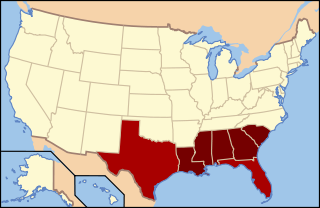
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on plantations and slavery. After the American Civil War ended in 1865, the region suffered economic hardship and was a major site of racial tension during and after the Reconstruction era. Before 1945, the Deep South was often referred to as the "Cotton States" since cotton was the primary cash crop for economic production. The civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s helped usher in a new era, sometimes referred to as the New South. The Deep South is part of the highly-religious, socially conservative Bible Belt and is currently a Republican Party stronghold. It is contrasted with the Mid-South and Tidewater region, as well as the Upper South and the border states.

A literary magazine is a periodical devoted to literature in a broad sense. Literary magazines usually publish short stories, poetry, and essays, along with literary criticism, book reviews, biographical profiles of authors, interviews and letters. Literary magazines are often called literary journals, or little magazines, terms intended to contrast them with larger, commercial magazines.

The National Medical Association (NMA) is the largest and oldest organization representing African American physicians and their patients in the United States. As a 501(c)(3) national professional and scientific organization, the NMA represents the interests of over 30,000 African American physicians and their patients, with nearly 112 affiliated societies throughout the nation and U.S. territories. Through its membership, professional growth, community health education, advocacy, research, and collaborations with public and private organizations, the organization is dedicated to enhancing the quality of health among minorities and underprivileged people. Throughout its history, the NMA has primarily focused on health issues related to African Americans and medically underserved populations. However, its principles, goals, initiatives, and philosophy encompass all ethnic groups
Conceived in no spirit of racial exclusiveness, fostering no ethnic antagonism, but born of the exigencies of the American environment, the National Medical Association has for its object the banding together for mutual cooperation and helpfulness, the men and women of African descent who are legally and honorably engaged in the practice of the cognate professions of medicine, surgery, pharmacy and dentistry.
— C.V. Roman, M.D. NMA Founding Member and First Editor of the Journal of the National Medical Association (NMA) 1908

Southern United States literature consists of American literature written about the Southern United States or by writers from the region. Literature written about the American South first began during the colonial era, and developed significantly during and after the period of slavery in the United States. Traditional historiography of Southern United States literature emphasized a unifying history of the region; the significance of family in the South's culture, a sense of community and the role of the individual, justice, the dominance of Christianity and the positive and negative impacts of religion, racial tensions, social class and the usage of local dialects. However, in recent decades, the scholarship of the New Southern Studies has decentralized these conventional tropes in favor of a more geographically, politically, and ideologically expansive "South" or "Souths".
Indigenous people lived in what is now Texas more than 10,000 years ago, as evidenced by the discovery of the remains of prehistoric Leanderthal Lady. In 1519, the arrival of the first Spanish conquistadors in the region of North America now known as Texas found the region occupied by numerous Native American tribes. The name Texas derives from táyshaʼ, a word in the Caddoan language of the Hasinai, which means "friends" or "allies." In the recorded history of what is now the U.S. state of Texas, all or parts of Texas have been claimed by six countries: France, Spain, Mexico, the Republic of Texas, the Confederacy during the Civil War, and the United States of America.
The New York University Law Review is a bimonthly general law review covering legal scholarship in all areas, including legal theory and policy, environmental law, legal history, and international law. The journal was established in 1924 as a collaborative effort between law students and members of the local bar. Its first editor-in-chief was Paul D. Kaufman. Between 1924 and 1950, it was at various times known as the Annual Review of the Law School of New York University and the New York University Law Quarterly Review before obtaining its current name in 1950.

The University of Hawaiʻi Press is a university press that is part of the University of Hawaiʻi.

This is a selected bibliography of the main scholarly books and articles of Reconstruction, the period after the American Civil War, 1863–1877.
The African Studies Review is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering African studies. The journal also publishes book and film reviews.
The AMWA Journal is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal and the official publication of the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA). The journal "aims to be the authoritative, comprehensive source of information about knowledge, skills, and opportunities in the field of medical communication worldwide." The current editor is Jim Cozzarin.
Hispania is a peer-reviewed academic journal and the official journal of the American Association of Teachers of Spanish and Portuguese. It is published quarterly by the AATSP and covers Spanish and Portuguese literature, linguistics, and pedagogy. Hispania publishes in literature, linguistics, and pedagogy having to do with Portuguese- and Spanish-speaking communities, as well as book/media reviews, which are subdivided into Pan-Hispanic/Luso-Brazilian Literary and Cultural Studies, linguistics, language, media, and fiction and film.

Annals of Science is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the history of science and technology. It is published by Taylor & Francis and was established in 1936. The founding editor-in-chief was the Canadian historian of science Harcourt Brown.

Warren Ralph Eubanks Jr. is an American author, essayist, journalist, professor, and public speaker. His work focuses on race, identity, and the culture and literature of the American South. As of May 2021, he was a Radcliffe Institute fellow at Harvard University.

The American Genealogist is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal which focuses on genealogy and family history. It was established by Donald Lines Jacobus in 1922 as the New Haven Genealogical Magazine. In July 1932 it was renamed The American Genealogist and New Haven Genealogical Magazine and the last part of the title was dropped in 1937, giving the journal its current title. All editors have been fellows of the American Society of Genealogists.
The Leadership Quarterly is a bimonthly peer-reviewed multidisciplinary social science journal. It is dedicated to the scientific study of leadership. The journal has a broad focus and publishers papers from various fields of social science as well as of biological science. The journal also publishes methodological advances.

The Black Belt in the American South refers to the social history, especially concerning slavery and black workers, of the geological region known as the Black Belt. The geology emphasizes the highly fertile black soil. Historically, the black belt economy was based on cotton plantations – along with some tobacco plantation areas along the Virginia-North Carolina border. The valuable land was largely controlled by rich whites, and worked by very poor, primarily black slaves who in many counties constituted a majority of the population. Generally the term is applied to a larger region than that defined by its geology.
Arkansas Review: A Journal of Delta Studies is an interdisciplinary humanities journal that focuses on the seven states of the Mississippi River Delta. Each issue of the journal contains fiction, nonfiction, poetic, and visual art works which offer different perspectives on the Delta region. The journal is assembled and published through the Department of English, Philosophy, and World Languages at Arkansas State University in Jonesboro, Arkansas under the direction of Marcus Tribbett.

Richard Beale Davis was an American academic who specialized in the history of the Southern United States, with a focus on its literature and intellectual history. His works include the 1978 book Intellectual Life in the Colonial South, which was awarded the National Book Award for history and several other accolades. He taught at the University of Virginia, University of South Carolina, and University of Tennessee, among other places.












