
Janet is a high-speed network for the UK research and education community provided by Jisc, a not-for-profit company set up to provide computing support for education. It serves 18 million users and is the busiest National Research and Education Network in Europe by volume of data carried. Previously, Janet was a private, UK-government funded organisation, which provided the JANET computer network and related collaborative services to UK research and education.
The National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET) was a program of coordinated, evolving projects sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF) from 1985 to 1995 to promote advanced research and education networking in the United States. The program created several nationwide backbone computer networks in support of these initiatives. Initially created to link researchers to the NSF-funded supercomputing centers, through further public funding and private industry partnerships it developed into a major part of the Internet backbone.

Internet2 is a not-for-profit United States computer networking consortium led by members from the research and education communities, industry, and government. The Internet2 consortium administrative headquarters are located in Ann Arbor, Michigan, with offices in Washington, D.C., and Emeryville, California.
CARNET is the national research and education network of Croatia. It is funded from the government budget and it operates from offices in Zagreb and five other cities.
PIONIER is the Polish national research and education network created to provide high-speed Internet access and to conduct network-based research. Most of the government founded higher education organisations and all of metropolitan area networks in Poland are connected to the PIONIER network, and are members of the PIONIER Consortium. The previous versions of the Polish academic computer network were called POL-34 and POL-155.

Abilene Network was a high-performance backbone network created by the Internet2 community in the late 1990s. In 2007 the Abilene Network was retired and the upgraded network became known as the "Internet2 Network".

AARNet provides Internet services to the Australian education and research communities and their research partners.
The China Education and Research Network is the first nationwide education and research computer network in China. The CERNET project is funded by the Chinese government and directly managed by the Chinese Ministry of Education. It is constructed and operated by Tsinghua University and the other leading Chinese universities.
The Corporation for Education Network Initiatives in California is a nonprofit corporation formed in 1997 to provide high-performance, high-bandwidth networking services to California universities and research institutions. Through this corporation, representatives from all of California's K-20 public education combine their networking resources toward the operation, deployment, and maintenance of the California Research and Education Network, or CalREN. Today, CalREN operates over 8,000 miles of fiber optic cable and serves more than 20 million users.
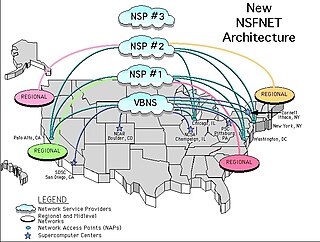
The very high-speed Backbone Network Service (vBNS) came on line in April 1995 as part of a National Science Foundation (NSF) sponsored project to provide high-speed interconnection between NSF-sponsored supercomputing centers and select access points in the United States. The network was engineered and operated by MCI Telecommunications under a cooperative agreement with the NSF.

Internet in Russia, or Russian Internet, and sometimes Runet, is the part of the Internet that is related to Russia. As of 2015, Internet access in Russia is available to businesses and home users in various forms, including dial-up, cable, DSL, FTTH, mobile, wireless and satellite.

CANARIE is the not-for-profit organisation which operates the national backbone network of Canada's national research and education network (NREN). The organisation receives the majority of its funding from the Government of Canada. It supports the development of research software tools; provides cloud resources for startups and small businesses; provides access and identity management services; and supports the development of policies, infrastructure and tools for research data management.
Delivery of Advanced Network Technology to Europe (DANTE) is a not-for-profit company that plans, builds and operates the consecutive generations of the backbone network that interconnects the national research and education networks (NRENs) in Europe. The organisation is based in Cambridge, United Kingdom and was formed in 1993 as a limited liability company owned by Réseaux Associés pour la Recherche Européenne (RARE). Ownership was transferred to a number of NRENs and government agencies in 1994.

Merit Network, Inc., is a nonprofit member-governed organization providing high-performance computer networking and related services to educational, government, health care, and nonprofit organizations, primarily in Michigan. Created in 1966, Merit operates the longest running regional computer network in the United States.

Broadband is a term normally considered to be synonymous with a high-speed connection to the internet. Suitability for certain applications, or technically a certain quality of service, is often assumed. For instance, low round trip delay would normally be assumed to be well under 150ms and suitable for Voice over IP, online gaming, financial trading especially arbitrage, virtual private networks and other latency-sensitive applications. This would rule out satellite Internet as inherently high-latency. In some applications, utility-grade reliability or security are often also assumed or defined as requirements. There is no single definition of broadband and official plans may refer to any or none of these criteria.
The Ohio Academic Resources Network (OARnet) is a state-funded IT organization that provides member organizations with intrastate networking, virtualization and cloud computing solutions, advanced videoconferencing, connections to regional and international research networks and the commodity Internet, colocation services and emergency web-hosting.
The Academic Scientific Research Computer Network of Armenia (ASNET-AM) is the national research and education network (NREN) of Armenia. ASNET-AM was created in 1994. The structure and policy of ASNET-AM operation was developed and realized by the Institute for Informatics and Automation Problems of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia.
GARR is the Italian national computer network for universities and research. The main objective of GARR is to design and manage a very high-performance network infrastructure that delivers advanced services to the Italian academic and scientific community. The GARR network is connected to other national research and education networks in Europe and the world, is an integral part of the global Internet, and thereby promotes the exchange and collaboration between researchers, teachers, and students worldwide.

The Research and Educational Networking Association of Moldova (RENAM) is the national research and education networking organisation (NREN) of Moldova. RENAM was incorporated in June 1999 as an association under Moldovan law. It is a member of TERENA.

ACOnet is the name of the national research and education network in Austria. The ACONET association promotes the development and use of that network. ACOnet is not managed and operated by ACONET, but by a unit in the Computing Centre of the University of Vienna that also operates the Vienna Internet Exchange. The University of Vienna represents ACOnet internationally, for example as a member of TERENA and as a participant in the project that funds the European backbone network GÉANT.










