
Sphaerium is a genus of very small freshwater clams, aquatic bivalve molluscs in the family Sphaeriidae, known as the fingernail clams. The small clams in this genus are unusual in that many of them, such as Sphaerium corneum, can climb around underwater on aquatic plants, using their long and strong foot.

Monochamus is a genus of longhorn beetles found throughout the world. They are commonly known as sawyer beetles or sawyers, as their larvae bore into dead or dying trees, especially conifers such as pines. They are the type genus of the Monochamini, a tribe in the huge long-horned beetle subfamily Lamiinae, but typically included in the Lamiini today.

Stuhlmann's starling is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is found in Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. Their length is usually around 19 cm, and they feed on seed, grain, arthropods and larvae.
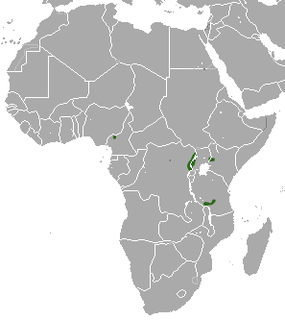
Stuhlmann's golden mole is a species of mammal in the family Chrysochloridae. It is found in Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forest, subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland, Mediterranean-type shrubby vegetation, subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland, subtropical or tropical high-altitude grassland, arable land, and pastureland.
Chrysochloris is a genus of mammal in the family Chrysochloridae. It contains the following species:
The eastcoast lampeye is a species of fish in the family Poeciliidae. It is endemic to coastal Kenya and Tanzania, where found in brackish water, mangrove swamps, pools, lagoons and river deltas. It reaches up to 5 cm (2.0 in) in total length. This fish was described by Ernst Ahl as Haplochilichthys stuhlmanni with the type locality given as Tanganyika Territory. The specific name honours the co-leader of the German East Africa Expedition (1889-1892) on which type was collected, Franz Ludwig Stuhlmann (1863-1928) of the German Colonial Service.
Tropodiaptomus stuhlmanni is a species of calanoid copepod in the family Diaptomidae.

Monochamus scutellatus, commonly known as the white-spotted sawyer or spruce sawyer or spruce bug, is a common wood-boring beetle found throughout North America. It is a species native to North America.

Monochamus dubius is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Charles Joseph Gahan in 1894. It is known from India, Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam, Taiwan, and China.

Monochamus subfasciatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1873. It is recorded from Japan where it infests Japanese red pine and is a vector of the nematode Bursaphelenchus doui.
Monochamus adamitus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1857. It is known from Tanzania, Sierra Leone, Angola, Ghana, Mozambique, the Ivory Coast, Senegal, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, and Zimbabwe.

Monochamus clamator, the spotted pine sawyer, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by John Lawrence LeConte in 1852.

Monochamus galloprovincialis, the pine sawyer beetle, also referred to as the black pine sawyer beetle, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Olivier in 1795, originally under the genus Cerambyx. It has a wide distribution, occurring naturally throughout Europe and the Caucasus. It has also been introduced into the Canary Islands. It serves as a vector for the parasitic nematode species Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and also acts as a host to the parasitoid wasp species Dolichomitus tuberculatus.

Monochamus irrorator is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Chevrolat in 1855, originally spelled as "Monohammus" irrorator. It is known from the Republic of the Congo and Nigeria.
Monochamus leuconotus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Francis Polkinghorne Pascoe in 1869, originally under the genus Anthores. It is known from Tanzania, Cameroon, Malawi, Kenya, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Angola, and Zimbabwe. It feeds on Coffea arabica.

Monochamus maculosus, the spotted pine sawyer, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It is known from Canada and the United States, and was formerly known as Monochamus mutator.
Monochamus ruspator is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1781, originally under the genus Lamia. It has a wide distribution throughout Africa.

Monochamus sartor is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1787, originally under the genus Lamia. It is known from throughout Europe, as well as in Kazakhstan, Mongolia, North Korea and South Korea. It is rated by the IUCN as Least Concern.

The Stuhlmann's elephant shrew is a species of elephant shrew that lives in the forests and savannas of Africa. It was discovered in 1893 and declared a new species. In the 1960s, however, it was downgraded to a subspecies of checkered sengi. In 2018, following genetic tests, scientists re-evaluated the mammal as a full species again.

Laevicaulis stuhlmanni is a species of terrestrial, nocturnal slug in the family Veronicellidae. It is native to parts of tropical Africa.













