Related Research Articles
In the United States, school colors are the colors chosen by a school to represent it on uniforms and other items of identification. Most schools have two colors, which are usually chosen to avoid conflicts with other schools with which the school competes in sports and other activities. The colors are often worn to build morale among the teachers and pupils, and as an expression of school spirit.

The flame shoulder is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1761. It is distributed throughout the Palearctic from Ireland in the west to Siberia then Korea and Japan in the east.

The setaceous Hebrew character is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found in the Palearctic ecozone. It is a common species throughout Europe and North Asia and Central Asia, South Asia, China, Japan and Korea. It is also found in North America, from coast to coast across Canada and the northern United States to western Alaska. It occurs in the Rocky Mountains from Montana to southern Arizona and New Mexico. In the east, it ranges from Maine to North Carolina. It has recently been recorded from Tennessee.

Graphium sarpedon, the common bluebottle or blue triangle in Australia, is a species of swallowtail butterfly, that is found in South and Southeast Asia, as well as eastern Australia. There are approximately sixteen subspecies with differing geographical distributions.

Euskelosaurus browni is a semi-bipedal plateosaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur from the early Triassic of South Africa and Lesotho. Fossils have only been recovered from the lower Elliot Formation in South Africa and Lesotho, and in one locality in Zimbabwe.

Galidiinae is a subfamily of carnivorans that is restricted to Madagascar and includes six species classified into four genera. Together with the three other species of indigenous Malagasy carnivorans, including the fossa, they are currently classified in the family Eupleridae within the suborder Feliformia. Galidiinae are the smallest of the Malagasy carnivorans, generally weighing about 600 to 900 g. They are agile, short-legged animals with long, bushy tails.

The Mexican big-eared bat is a species of vesper bat endemic to Mexico. They are nocturnal and insectivorous. Their very large ears are located across their foreheads, and when captured, the bats are observed to curl their ears in a protective manner. The adults are usually brown colored, while the juveniles are usually a smokey brown color. They have small noses.

The European ratsnake or leopard snake, is a species of nonvenomous colubrid snake endemic to Europe, Asia Minor, and the Caucasus.

Lampropeltis zonata, or the California mountain kingsnake, is a species of nonvenomous colubrid snake, which is endemic to North America. It is a coral snake mimic, having a similar pattern consisting of red, black, and yellow on its body, but the snake is completely harmless. Five subspecies are recognized in the U.S., including the nominotypical subspecies, with two subspecies recognized in Mexico.

Deltote bankiana, the silver barred, is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in the Palearctic.

Nepita is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae described by Moore in 1860. Its only species, Nepita conferta, the footman moth, was first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It can be found in India and Sri Lanka.
Nephelomys meridensis, also known as the Mérida oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in cloud forest in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida of western Venezuela at elevations from 1100 to 4000 m. It is solitary, nocturnal and terrestrial, and has a varied diet.
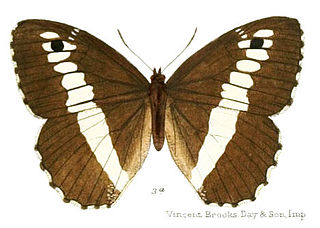
Aulocera is a genus in the subfamily Satyrinae of the brush-footed butterfly family, Nymphalidae. Commonly referred to as banded satyrs, species of the genus Aulocera are endemic to the Himalayas and associated mountain ranges.

Leucania loreyi, the cosmopolitan, false army worm or nightfeeding rice armyworm, is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in most of African countries, the Indo-Australian subtropics and tropics of India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, the eastern Palearctic ecozone and the Near East and Middle East. The species was first described by Philogène Auguste Joseph Duponchel in 1827.

Hyblaea constellata is a moth in the family Hyblaeidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, south-east Asia, including China, Japan, Taiwan, Myanmar and Thailand. It is also found in Queensland, Australia.
Migoplastis correcta is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Francis Walker in 1865. It is found in Sri Lanka.
Amphitorna olga is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Swinhoe in 1894. It is found in north-eastern India and China.
Hemiphruda mecasa is a moth in the family Drepanidae and the only species in the genus Hemiphruda. It was described by Swinhoe in 1894. It is found in India.
Eupterote acesta is a moth in the family Eupterotidae. It was described by Charles Swinhoe in 1894. It is found in Thailand and India.
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Monoprista nudobia". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum. Retrieved April 21, 2018.
- ↑ "The Annals and Magazine of Natural History: Including Zoology, Botany, and Geology, 1894". forgottenbooks.com.[ permanent dead link ]
| This article on a moth of the subfamily Drepaninae is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |