Related Research Articles

Triceratops is an extinct genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one of the last-known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name Triceratops, which literally means 'three-horned face', is derived from the Greek words trí- meaning 'three', kéras meaning 'horn', and ṓps meaning 'face'.

Devil's club or devil's walking stick is a large understory shrub native to the arboreal rainforests of the Pacific Northwest, but also disjunct on islands in Lake Superior. It is noted for its large palmate leaves and erect, woody stems covered in noxious and irritating spines. It is also known as Alaskan ginseng and similar names, although it is not a true ginseng.

The thorny devil, also known commonly as the mountain devil, thorny lizard, thorny dragon, and moloch, is a species of lizard in the family Agamidae. The species is endemic to Australia. It is the sole species in the genus Moloch. It grows up to 21 cm (8.3 in) in total length, with females generally larger than males.
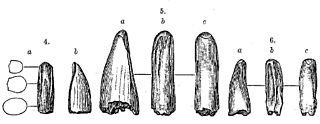
Aublysodon is a genus of carnivorous dinosaurs known only from the Judith River Formation in Montana, which has been dated to the late Campanian age of the late Cretaceous period. The only currently recognized species, Aublysodon mirandus, was named by paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1868. It is now considered dubious, because the type specimen consists only of an isolated premaxillary (front) tooth. Although this specimen is now lost, similar teeth have been found in many US states, western Canada, and Asia. These teeth almost certainly belong to juvenile tyrannosaurine tyrannosaurids, but most have not been identified to species level. However, it is likely that the type tooth belongs to one of the species in the genus Daspletosaurus, which was present in contemporary formations, and which matches specific details of the original tooth. The synapomorphies alleged to distinguish the Aublysodontinae, especially lack of serrations on premaxillary teeth could have been caused by tooth wear in life, postmortem abrasion, or digestion. Most other "aublysodontine"-type teeth may be from ontogenetic stages or sexual morphs of other tyrannosaurids.

The timber rattlesnake, canebrake rattlesnake or banded rattlesnake is a species of venomous pit viper endemic to eastern North America. This is the only rattlesnake species in most of the populous northeastern United States and is second only to its cousins to the west, the prairie rattlesnake, as the most northerly distributed venomous snake in North America. No subspecies are currently recognized.
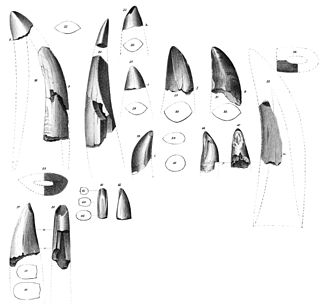
Deinodon is a dubious tyrannosaurid dinosaur genus containing a single species, Deinodon horridus. D. horridus is known only from a set of teeth found in the Late Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana and named by paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1856. These were the first tyrannosaurid remains to be described and had been collected by Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden. The teeth of Deinodon were slightly heterodont, and the holotype of Aublysodon can probably be assigned to Deinodon.
Horridus is a fictional superheroine created by Erik Larsen for his Image Comics series, The Savage Dragon.

Argosarchus is a monotypic genus in the family Phasmatidae containing the single species Argosarchus horridus, or the New Zealand bristly stick insect, a stick insect endemic to New Zealand. The name "horridus" means bristly in Latin, likely referring to its spiny thorax.

Acanthosicyos horridus is an unusual melon that is endemic to the Namib desert. In English it is known as Nara, butter-nuts, or butterpips; in one of the Khoisan languages it is locally called ǃnaras or ǃnara.

Encephalartos horridus, the Eastern Cape blue cycad, is a small, low-growing cycad up to 0.9 m (3.0 ft) high and 0.9 m (3.0 ft) wide. It is a native of Eastern Cape Province, South Africa, and found in arid shrublands, most commonly on ridges and slopes with shallow soils. The species is particularly known for its distinctly blue-gray leaves, although the degree of coloration can vary significantly. The species name horridus is Latin for 'bristly', after the plant's stiff, spiny leaflets.
Horridus may refer to:
Horrilysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Morimopsini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae. It was described by Lacordaire in 1869.
Monoxenus is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Nothophantes, the horrid ground-weaver, is a critically endangered monotypic genus of European dwarf spiders containing the single species, Nothophantes horridus. It was first described by P. Merrett & R. A. Stevens in 1995, and has only been found in an area of Plymouth smaller than 1 square kilometre (0.39 sq mi). The name comes from the Ancient Greek νόθος, meaning "spurious", and hyphantes, meaning "weaver". The species name comes from the Latin horridus, meaning "bristly".
Monoxenus bicristatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1939.
Monoxenus elongatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1939.
Monoxenus spinosus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1939.
Monoxenus tridentatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1903 and is known from Cameroon.
Monoxenus bispinosus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Karl Jordan in 1894, originally under the genus Apomempsis. It is known from Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and the Central African Republic.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Monoxenus horridus. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.