South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although most of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography.

The Vaal River is the largest tributary of the Orange River in South Africa. The river has its source near Breyten in Mpumalanga province, east of Johannesburg and about 30 kilometres (19 mi) north of Ermelo and only about 240 kilometres (150 mi) from the Indian Ocean. It then flows westwards to its conjunction with the Orange River southwest of Kimberley in the Northern Cape. It is 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) long, and forms the border between Mpumalanga, Gauteng and North West Province on its north bank, and the Free State on its south.

KwaZulu-Natal is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu and Natal Province were merged. It is located in the southeast of the country, enjoying a long shoreline beside the Indian Ocean and sharing borders with three other provinces and the countries of Mozambique, Eswatini and Lesotho. Its capital is Pietermaritzburg and its largest city is Durban. It is the 2nd most populous province in South Africa, with slightly fewer residents than Gauteng.

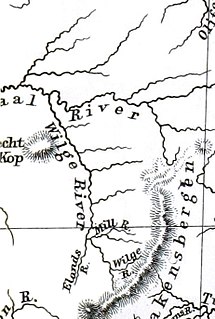
The Drakensberg is the name given to the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation in this region – 2,000 to 3,482 metres. It is located in South Africa and Lesotho.

The Tugela River is the largest river in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. It is one of the most important rivers of the country.

Maloti-Drakensberg Park was established on 11 June 2001 by linking the Sehlabathebe National Park in the Kingdom of Lesotho and the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. The highest peak is Thaba Ntlenyana rising to 3.482 m.

Winterton is a small town situated on the banks of the Tugela River in the foothills of the Drakensberg mountains, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1905 as Springfield when the Natal Government built a weir across the Little Tugela River. The town later changed its name to Winterton in honour the secretary for agriculture, HD Winter. Winterton is a small town with only a primary school. It is close to the Second Boer War battle sites of Battle of Vaal Krantz and Spioenkop.

Harrismith is a large town in the Free State province of South Africa. It was named for Sir Harry Smith, a 19th-century British governor of the Cape Colony. It is situated by the Wilge River, alongside the N3 highway, about midway between Johannesburg, about 300 km to the north-west, and Durban to the southeast. The town is located at the junction of the N5 highway, which continues westward towards the provincial capital Bloemfontein, some 340 km to the south-west. This important crossroads in South Africa's land trade routes is surrounded by mesas and buttes. It is located at the base of one of these called Platberg.

The Highveld is the portion of the South African inland plateau which has an altitude above roughly 1500 m, but below 2100 m, thus excluding the Lesotho mountain regions to the south-east of the Highveld. It is home to some of the country's most important commercial farming areas, as well as its largest concentration of metropolitan centres, especially the Gauteng conurbation, which accommodates one-third of South Africa's population.

The Maloti Mountains are a mountain range of the highlands of the Kingdom of Lesotho. They extend for about 100 km into the Free State. The Maloti Range is part of the Drakensberg system that includes ranges across large areas of South Africa. “Maloti” is also the plural for Loti, the currency of the Kingdom of Lesotho. The range forms the northern portion of the boundary between the Butha-Buthe District in Lesotho and South Africa’s Free State.

The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateau downward in the direction of the oceans that surround Southern Africa on three sides. While it lies predominantly within the borders of South Africa, in the east it extends northwards to form the border between Mozambique and Zimbabwe, continuing on beyond the Zambezi River valley to form the Muchinga Escarpment in eastern Zambia. In the west, it continues northwards into Namibia and Angola.

The Amphitheatre is one of the geographical features of the Northern Drakensberg, South Africa, and is widely regarded as one of the most impressive cliff faces on earth. The cliff face of the Amphitheatre is roughly three times the size of the total combined area of all the cliff faces in Yosemite's famous El Capitan, and more than 10 times the size of El Capitan's most famous face. It is part of the Royal Natal National Park.

The Mooi River is a river in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. It rises in the Mkomazi Nature Reserve in the Drakensberg Mountains, and empties into the Tugela River near Muden. The town of Mooi River lies on the river.

The uKhahlamba-Drakensberg Park is in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa, covering 2,428.13 km2 (938 sq mi) of area. The park includes Royal Natal National Park, a provincial park, and covers part of the Drakensberg, the highest mountain range in Southern Africa.

The Bushman's River is an east to north-easterly flowing tributary of the Tugela River, in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. It rises in the Drakensberg Mountain range, with its upper catchment in the Giant's Castle Game Reserve, north of the Giant's Castle promontory. It feeds the Wagendrift Dam and then flows past the town of Estcourt to join the Tugela River near the town of Weenen.

The border between Lesotho and South Africa is 909 kilometres (565 mi) long and forms a complete loop, as Lesotho is an enclave entirely surrounded by South Africa. The border follows the Caledon River, the drainage divide of the Drakensberg mountains, the Tele River, the Orange River, the Makhaleng River, and a series of hills joining the Makhaleng back to the Caledon.