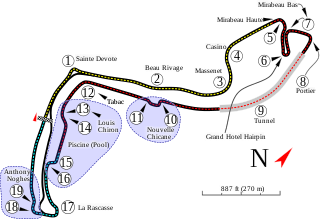
The Monaco Grand Prix is a Formula One motor racing event held annually on the Circuit de Monaco, in late May or early June. Run since 1929, it is widely considered to be one of the most important and prestigious automobile races in the world, and is one of the races—along with the Indianapolis 500 and the 24 Hours of Le Mans—that form the Triple Crown of Motorsport. It is the only Grand Prix that does not adhere to the FIA's mandated 305-kilometre (190-mile) minimum race distance for F1 races.

Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is a semi-enclave bordered by France to the north, east and west. The principality is home to 38,682 residents, of whom 9,486 are Monégasque nationals; it is widely recognised as one of the wealthiest and most expensive places in the world. The official language of the principality is French. In addition, Monégasque, English and Italian are spoken and understood by many residents.

Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. The name comes from the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, where the primary developer of the method, physicist Stanislaw Ulam, was inspired by his uncle's gambling habits.

Monte Carlo is officially an administrative area of Monaco, specifically the ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is located. Informally, the name also refers to a larger district, the Monte Carlo Quarter, which besides Monte Carlo/Spélugues also includes the wards of La Rousse/Saint Roman, Larvotto/Bas Moulins and Saint Michel. The permanent population of the ward of Monte Carlo is about 3,500, while that of the quarter is about 15,000. Monaco has four traditional quarters. From west to east they are: Fontvieille, Monaco-Ville, La Condamine, and Monte Carlo.

Louis II was Prince of Monaco from 26 June 1922 to 9 May 1949.

Nicholas Constantine Metropolis was a Greek-American physicist.
In computing, a Monte Carlo algorithm is a randomized algorithm whose output may be incorrect with a certain probability. Two examples of such algorithms are the Karger–Stein algorithm and the Monte Carlo algorithm for minimum feedback arc set.
A casino is a facility that houses and accommodates certain types of gambling activities.

The Lancia Montecarlo is a Pininfarina-designed mid-engined sports car produced by Lancia in Italy from 1975 to 1981.

Monte Carlo or Bust! is a 1969 epic Comedy film, also known by its American title, Those Daring Young Men in Their Jaunty Jalopies. A co-production of the United Kingdom, France and Italy, the story is based on the Monte Carlo Rally – first raced in 1911 – and the film, set in the 1920s, recalls this general era. A lavish all-star film, it is the story of an epic car rally across Europe that involves a lot of eccentric characters from all over the world who will stop at nothing to win.

Marco Piccinini is a Monegasque sport personality, businessman, and politician.

The Monte Carlo Casino, officially named Casino de Monte-Carlo, is a gambling and entertainment complex located in Monaco. It includes a casino, the Opéra de Monte-Carlo, and the office of Les Ballets de Monte-Carlo.

Carlo Vanzina was an Italian film director, producer and screenwriter.

Patrick Mimran is a contemporary French multimedia artist, composer, and the former CEO of Lamborghini. He is most widely known for Lamborghini's turn-around in the early 1980s and his art exhibit, "The Billboard Project".

Pierre Rainier Stefano Casiraghi is the younger son and youngest of three children of Caroline, Princess of Hanover, and her second husband, Stefano Casiraghi. He is the maternal-line grandson of Rainier III, Prince of Monaco, and American actress Grace Kelly. Casiraghi is eighth in the line of succession to the Monegasque throne, following his twin cousins Hereditary Prince Jacques and Princess Gabriella, his mother, his brother Andrea, nephews Alexandre and Maximilian Casiraghi and niece India Casiraghi.

24 Hours of a Woman's Life, also known as Affair in Monte Carlo, is a 1952 British romantic drama film directed by Victor Saville and starring Merle Oberon, Richard Todd and Leo Genn. It is loosely based on the 1927 novella by Stefan Zweig. Produced by ABPC, it was shot at the company's Elstree Studios and on location in Monaco. The film's sets were designed by the art director Terence Verity.
In computer science, Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) is a heuristic search algorithm for some kinds of decision processes, most notably those employed in software that plays board games. In that context MCTS is used to solve the game tree.

Montecarlo Gran Casinò is a 1987 Italian comedy film directed by Carlo Vanzina.
"George and Alfred" is a short story by P. G. Wodehouse and a Mr. Mulliner story. It was published in Playboy magazine in the US in January 1967. The story was also included in the 1966 collection Plum Pie.













