Related Research Articles

The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for 1,375 kilometres (854 mi), into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. It is the 11th longest river in Canada. The river's annual discharge at its mouth is 112 cubic kilometres (27 cu mi) or 3,550 cubic metres per second (125,000 cu ft/s), and it discharges 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean.

The Chilko River is a 75-kilometre-long (47 mi) river in the Chilcotin District of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, flowing northeast from Chilko Lake to the Chilcotin River. Its main tributary is the Taseko River.

The Pitt River in British Columbia, Canada is a large tributary of the Fraser River, entering it a few miles upstream from New Westminster and about 25 km ESE of Downtown Vancouver. The river, which begins in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Coast Mountains, is in two sections above and below Pitt Lake and flows on a generally southernly course. Pitt Lake and the lower Pitt River are tidal in nature as the Fraser's mouth is only a few miles downstream from their confluence.

The Rocky Mountain Trench, also known as the Valley of a Thousand Peaks or simply the Trench, is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The Trench is both visually and cartographically a striking physiographic feature extending approximately 1,600 km (1,000 mi) from Flathead Lake, Montana to the Liard River, just south of the British Columbia–Yukon border near Watson Lake, Yukon. The trench bottom is 3–16 km (1.9–9.9 mi) wide and is 600–900 m (2,000–3,000 ft) above sea level. The general orientation of the Trench is an almost straight 150/330° geographic north vector and has become convenient as a visual guide for aviators heading north or south.

The Klinaklini River is one of the major rivers of the Pacific Ranges section of the Coast Mountains in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It originates in the Pantheon Range and empties into the head of Knight Inlet.

The West Road River or Blackwater River or Tiyakoh is an important tributary of the Fraser River, flowing generally north-eastward from the northern slopes of the Ilgachuz Range and across the Fraser Plateau in the Chilcotin region of central British Columbia, Canada. With only one major tributary, the Nazko River, its confluence with the Fraser is approximately 40 km northwest of Quesnel. It forms the division between the Chilcotin Plateau (S) and the Nechako Plateau (N), which are subdivisions of the Fraser Plateau.
The Taseko River or Desiqox in the original Chilcotin, is a tributary of British Columbia's Chilko River, a tributary of the Chilcotin River which joins the Fraser near the city of Williams Lake.
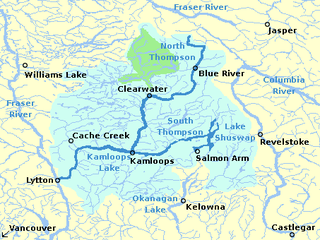
The South Thompson River is the southern branch of the Thompson River, the largest tributary of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It originates at the outlet of Little Shuswap Lake at the town of Chase and flows approximately 58 kilometres (36 mi) southwest and west through a wide valley to Kamloops where it joins the North Thompson River to form the main stem Thompson River.

The Robson Valley is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia, comprising the section of the Rocky Mountain Trench that lies southeast of the city of Prince George following the Fraser River to the Yellowhead Pass. The name is derived from Mount Robson, which stands near the entrance to the Yellowhead Pass. Communities in the Robson Valley include the settlements of Dome Creek, Crescent Spur, Dunster, and Tête Jaune Cache, with larger population concentrations in the villages of McBride and Valemount. On a map, the Robson Valley is located immediately south of the elbow in the boundary between Alberta and British Columbia. Transportation corridors through the Robson Valley include the Canadian National Railway lines, and Highways 16 and 5.

The Doré River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia.
The Nahatlatch River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It originates in the Lillooet Ranges of the Coast Mountains and empties into the Fraser River in the Fraser Canyon, north of Boston Bar.
The Seton River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The name is relatively new, and encompasses what had formerly been the Seton Portage River or Portage Creek and Seton Creek.
The McGregor River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia.

The Cariboo River is a tributary of the Quesnel River, one of the main tributaries of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows through the Cariboo region of the British Columbia Interior, southeast of Prince George. Above Cariboo Lake it was formerly known as the Swamp River. The name was adopted, and replaced the former names, in 1936 in association with Cariboo Lake.
The Baezaeko River is a tributary of the West Road River, one of the main tributaries of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows through the Fraser Plateau to the West Road River.

The Raush River is a tributary of the Fraser River in British Columbia, Canada. It drains a watershed of approximately 100,000 hectares on the eastern flanks of the Cariboo Mountains, a sub-range of the Columbia Mountains. The river joins the Fraser near the community of Dunster in the Robson Valley. The river's name is the result of a transcription error; it was originally called the Rivière au Shuswap, this was recorded on some maps as R.auSh., which then became Raush on official maps. Its source is the Raush Glacier, and major tributary creeks include Black Martin and Quanstrom.

The Goat River is a tributary of the Fraser River in British Columbia, Canada. Starting in the northern reaches of the Cariboo Mountains, it flows eastward and northeastward to join the Fraser near the settlement of Crescent Spur in the Robson Valley. Including its main tributary, the Milk River, its watershed covers 66,468 hectares. Other major tributaries for the river include McLeod, North Star, Whitehorse, Quartz, Diggings and Kendall creeks.
The McLennan River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Robson Valley region of British Columbia. The river was named after an engineer on one of the Canadian Pacific Railway surveys in the 1870s.
The McKale River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The river was named in 1913 by surveyor J.A. Walker, after James McKale, a timber cruiser at McBride
The Raft River is a tributary of the North Thompson River, one of the main tributaries of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows through the Shuswap Highland region southeast of Wells Gray Provincial Park. Most of the Raft River's watershed lies outside the boundaries of Wells Gray, except for some of the headwaters of the West Raft River tributary.
References
- ↑ Derived using topographic maps and TopoQuest.
- 1 2 Elevation derived from ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model, using GeoLocator, and BCGNIS coordinates.
- ↑ "Morkill River". BC Geographical Names.
- 1 2 "Archived Hydrometric Data Search". Water Survey of Canada. Archived from the original on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 4 August 2013. Search for Station 08KA013 Morkill River below Hellroaring Creek
- ↑ Akrigg, GPV; Helen B. Akrigg (1998). British Columbia place names . Vancouver, B.C.: UBC Press. p. 180. ISBN 9780774806367.
- ↑ "Morkill RMZ". Robson Valley Land and Resource Management Plan. Integrated Land Management Bureau - Province of British Columbia. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.