
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is an astronomical facility operated since 1998 by the European Southern Observatory, located on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each equipped with a primary mirror that measures 8.2 meters in diameter. These optical telescopes, named Antu, Kueyen, Melipal, and Yepun, are generally used separately but can be combined to achieve a very high angular resolution. The VLT array is also complemented by four movable Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) with 1.8-meter apertures.

Subaru Telescope is the 8.2-metre (320 in) telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, located at the Mauna Kea Observatory on Hawaii. It is named after the open star cluster known in English as the Pleiades. It had the largest monolithic primary mirror in the world from its commissioning until the Large Binocular Telescope opened in 2005.

The W. M. Keck Observatory is an astronomical observatory with two telescopes at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have 10 m (33 ft) aperture primary mirrors, and, when completed in 1993 and 1996, they were the largest optical reflecting telescopes in the world. They are currently the third and fourth largest.

Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments.

The Gemini Observatory comprises two 8.1-metre (26.6 ft) telescopes, Gemini North and Gemini South, situated in Hawaii and Chile, respectively. These twin telescopes offer extensive coverage of the northern and southern skies and rank among the most advanced optical/infrared telescopes available to astronomers. (See List of largest optical reflecting telescopes).

The Apache Point Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in the Sacramento Mountains in Sunspot, New Mexico, United States, approximately 18 miles (29 km) south of Cloudcroft. The observatory is operated by New Mexico State University (NMSU) and owned by the Astrophysical Research Consortium (ARC). Access to the telescopes and buildings is private and restricted.

The National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) was the United States national observatory for ground-based nighttime ultraviolet-optical-infrared (OUVIR) astronomy. The National Science Foundation (NSF) funded NOAO to provide forefront astronomical research facilities for US astronomers. Professional astronomers from any country in the world could apply to use the telescopes operated by NOAO under the NSF's "open skies" policy.
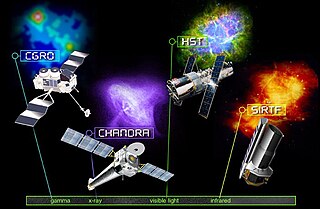
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.

The Galileo National Telescope, is a 3.58-meter Italian telescope, located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The TNG is operated by the "Fundación Galileo Galilei, Fundación Canaria", a non-profit institution, on behalf of the Italian National Institute of Astrophysics (INAF). The telescope saw first light in 1998 and is named after the Italian Renaissance astronomer Galileo Galilei.

The Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) is located near the summit of Mauna Kea mountain on Hawaii's Big Island at an altitude of 4,204 meters, part of the Mauna Kea Observatory. Operational since 1979, the telescope is a Prime Focus/Cassegrain configuration with a usable aperture diameter of 3.58 metres (11.7 ft).

The NASA Infrared Telescope Facility is a 3-meter (9.8 ft) telescope optimized for use in infrared astronomy and located at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii. It was first built to support the Voyager missions and is now the US national facility for infrared astronomy, providing continued support to planetary, solar neighborhood, and deep space applications. The IRTF is operated by the University of Hawaii under a cooperative agreement with NASA. According to the IRTF's time allocation rules, at least 50% of the observing time is devoted to planetary science.

The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) is a high-altitude astronomy station located in Hanle, India and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. Situated in the Western Himalayas at an elevation of 4,500 meters (14,764 ft), the IAO is one of the world's highest located sites for optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes. It is currently the tenth highest optical telescope in the world. It is India's first dark-sky preserve.

The Calar Alto Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in Almería province in Spain on Calar Alto, a 2,168-meter-high (7,113 ft) mountain in the Sierra de Los Filabres subrange of the Sierra Nevada.

The Vainu Bappu Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. It is located at Kavalur in the Javadi Hills, near Vaniyambadi in Tirupathur district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is 200 km south-west of Chennai and 175 km south-east of Bangalore.

The Physical Research Laboratory is a National Research Institute for space and allied sciences, supported mainly by Department of Space, Government of India. This research laboratory has ongoing research programmes in astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences and aeronomy, planetary and geosciences, Earth sciences, Solar System studies and theoretical physics. It also manages the Udaipur Solar Observatory and Mount Abu InfraRed Observatory. The PRL is located in Ahmedabad.

IUCAA Girawali Observatory is an optical astronomy observatory run by the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, India. The Observatory is located about 80 km from Pune, off the Pune Nashik Highway in Girawali.

Integral field spectrographs (IFS) combine spectrographic and imaging capabilities in the optical or infrared wavelength domains (0.32 μm – 24 μm) to get from a single exposure spatially resolved spectra in a bi-dimensional region. The name originates from the fact that the measurements result from integrating the light on multiple sub-regions of the field. Developed at first for the study of astronomical objects, this technique is now also used in many other fields, such bio-medical science and Earth remote sensing. Integral field spectrography is part of the broader category of snapshot hyperspectral imaging techniques, itself a part of hyperspectral imaging.
The National Large Solar Telescope (NLST) is a Gregorian multi-purpose open telescope proposed to be built in Merak village in Ladakh in India and aims to study the sun's microscopic structure.

Origins Space Telescope (Origins) is a concept study for a far-infrared survey space telescope mission. A preliminary concept in pre-formulation, it was presented to the United States Decadal Survey in 2019 for a possible selection to NASA's large strategic science missions. Origins would provide an array of new tools for studying star formation and the energetics and physical state of the interstellar medium within the Milky Way using infrared radiation and new spectroscopic capabilities.



















