
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to space science:

Siding Spring Observatory near Coonabarabran, New South Wales, Australia, part of the Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics (RSAA) at the Australian National University (ANU), incorporates the Anglo-Australian Telescope along with a collection of other telescopes owned by the Australian National University, the University of New South Wales, and other institutions. The observatory is situated 1,165 metres (3,822 ft) above sea level in the Warrumbungle National Park on Mount Woorat, also known as Siding Spring Mountain. Siding Spring Observatory is owned by the Australian National University (ANU) and is part of the Mount Stromlo and Siding Spring Observatories research school.

Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO) is a radio astronomy observatory located near Big Pine, California (US) in Owens Valley. It lies east of the Sierra Nevada, approximately 350 kilometers north of Los Angeles and 20 kilometers southeast of Bishop. It was established in 1956, and is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The Owens Valley Solar Array portion of the observatory has been operated by New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) since 1997.

The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) is a high-altitude astronomy station located in Hanle, India and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. Situated in the Western Himalayas at an elevation of 4,500 meters (14,764 ft), the IAO is one of the world's highest located sites for optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes. It is currently the tenth-highest optical telescope in the world.

The Astronomical Observatory of Belogradchik or Belogradchik Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Institute of Astronomy of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. It is located near the town of Belogradchik in northwestern Bulgaria, at the foot of the Western Balkan Mountains. The other observatory operated by the same institute is the Rozhen Observatory.

The Vainu Bappu Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. It is located at Kavalur in the Javadi Hills, near Vaniyambadi in Tirupathur district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is 200 km south-west of Chennai and 175 km south-east of Bangalore.

Tuorla Observatory is the Department of Astronomy at the University of Turku, southwest Finland. It is the largest astronomical research institute in Finland. Together with the Space Research Laboratory at the Physics Department of the University of Turku, it forms the Väisälä Institute of Space Physics and Astronomy (VISPA).

IUCAA Girawali Observatory is an optical astronomy observatory run by the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, India. The Observatory is located about 80 km from Pune, off the Pune Nashik Highway in Girawali.
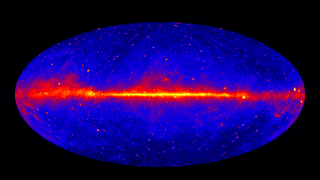
Gamma-ray astronomy is a subfield of astronomy where scientists observe and study celestial objects and phenomena in outer space which emit cosmic electromagnetic radiation in the form of gamma rays, i.e. photons with the highest energies at the very shortest wavelengths. Radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.

The Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences is a scientific institute headquartered at the Ondřejov Observatory, roughly 35 km southeast of Prague, Czech Republic.
The National Large Solar Telescope (NLST) is a Gregorian multi-purpose open telescope proposed in 2010 to be built in Merak village in Ladakh in India and aims to study the sun's microscopic structure.

Devasthal is an observatory in the district of Nainital, Kumaon, India. The literal meaning of the place is "abode of god". The observatory is situated in the Kumaon Himalayas at an altitude of 2450 meters. Devasthal peak is an emerging optical astronomical site for Indian telescopes. Currently, a 130-cm optical telescope is working at the site. The sites are managed by the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A*, at the center of the Milky Way.
Multi-messenger astronomy is the coordinated observation and interpretation of multiple signals received from the same astronomical event. Many types of cosmological events involve complex interactions between a variety of astrophysical processes, each of which may independently emit signals of a characteristic "messenger" type: electromagnetic radiation, gravitational waves, neutrinos, and cosmic rays. When received on Earth, identifying that disparate observations were generated by the same source can allow for improved reconstruction or a better understanding of the event, and reveals more information about the source.

The 3.6m DevasthalOptical Telescope is a clear-aperture Ritchey–Chrétien telescope built by Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) and is located at the Devasthal Observatory site near Nainital, Kumaon, India. ARIES operates another 1.3m telescope at the same location. The telescope was activated remotely on 31 March 2016 by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Belgian Prime Minister Charles Michel from Brussels. The telescope optics were built in collaboration with the Belgian firm Advanced Mechanical and Optical System (AMOS).

Iranian National Observatory (INO) is an Iranian astronomical observatory inaugurated in 2021. It has reported the capture of its first light on 15 October 2022 upon the commissioning of INO340, a home-grown optical telescope with a primary mirror of 3.4 m, making it by far the country's largest astronomical research facility.

Skinakas Observatory is an astronomical observatory located on the eponymous peak of Psiloritis, on the island of Crete, Greece. It is equipped with a 1.3 m modified Ritchey–Chrétien telescope and another 1 m Ritchey–Chrétien, a 0.6 m Cassegrain telescope and a 0.3 m Schmidt–Cassegrain. The telescopes are operated by the University of Crete and the Foundation for Research & Technology – Hellas.
The International Liquid Mirror Telescope is a 4-meter telescope in Uttarakhand, India. It is the first liquid-mirror telescope for astronomy in Asia and the largest liquid-mirror telescope in Asia.
Dipankar Banerjee is an Indian solar physicist. He is a senior Professor of Solar Physics at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (Bangalore) and currently serves as the director of the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology. Prior to this, he served as the director of the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES).




















