
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night.

The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~50 miles (80 km) west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twenty-eight 25-meter radio telescopes deployed in a Y-shaped array and all the equipment, instrumentation, and computing power to function as an interferometer. Each of the massive telescopes is mounted on double parallel railroad tracks, so the radius and density of the array can be transformed to adjust the balance between its angular resolution and its surface brightness sensitivity. Astronomers using the VLA have made key observations of black holes and protoplanetary disks around young stars, discovered magnetic filaments and traced complex gas motions at the Milky Way's center, probed the Universe's cosmological parameters, and provided new knowledge about the physical mechanisms that produce radio emission.

The Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) is a radio telescope operated by CSIRO at the Paul Wild Observatory, twenty five kilometres (16 mi) west of the town of Narrabri in New South Wales, Australia.

The Paul Wild Observatory, also known as the Narrabri Observatory and Culgoora Observatory, is an astronomical research facility located about 24 km west of Narrabri, New South Wales, Australia. It is the home of the Australia Telescope Compact Array, and the Culgoora Solar Observatory.

The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO), located in Hanle near Leh in Ladakh, India, has one of the world's highest located sites for optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes. It is operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore. It is currently the ninth highest optical telescope in the world, situated at an elevation of 4,500 meters (14,764 ft).

Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR) also known as Satpura National Park is located in the Hoshangabad District of Madhya Pradesh in India. Its name is derived from the Satpura range. It covers an area of 524 km2 (202 sq mi). Satpura National Park, along with the adjoining Bori and Pachmarhi wildlife sanctuaries, provides 2,200 km2 (850 sq mi) of unique central Indian highland ecosystem. It was set up in 1981.

The Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory is an American astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO); it is their largest field installation outside of their main site in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is located near Amado, Arizona on the summit, a ridge and at the foot of Mount Hopkins.

IACT stands for Imaging AtmosphericCherenkov Telescope or Technique. It is a device or method to detect very-high-energy gamma ray photons in the photon energy range of 50 GeV to 50 TeV.

VERITAS is a major ground-based gamma-ray observatory with an array of four 12 meter optical reflectors for gamma-ray astronomy in the GeV – TeV photon energy range. VERITAS uses the Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope technique to observe gamma rays that cause particle showers in Earth's atmosphere that are known as extensive air showers. The VERITAS array is located at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory, in southern Arizona, United States. The VERITAS reflector design is similar to the earlier Whipple 10-meter gamma-ray telescope, located at the same site, but is larger in size and has a longer focal length for better control of optical aberrations. VERITAS consists of an array of imaging telescopes deployed to view atmospheric Cherenkov showers from multiple locations to give the highest sensitivity in the 100 GeV – 10 TeV band. This very high energy observatory, completed in 2007, effectively complements the Large Area Telescope (LAT) of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope due to its larger collection area as well as coverage in a higher energy band.

A telescope is an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, by using glass lenses. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy.

Tourism in Madhya Pradesh has been an attraction of India because of its location in the centre of the country. Madhya Pradesh has won Best Tourism State National award for 3 consecutive years i.e. 2017, 2016 and 2015.

The Green Bank Interferometer (GBI) is a former radio astronomy telescope located at Green Bank, West Virginia (USA) and operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO). It included three on-site radio telescopes of 85-foot (26m) diameter, designated 85-1, 85-3, and 85-2 and a portable telescope.

The Cherenkov Telescope Array or CTA is a multinational, worldwide project to build a new generation of ground-based gamma-ray instrument in the energy range extending from some tens of GeV to about 300 TeV. It is proposed as an open observatory and will consist of two arrays of Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes (IACTs), a first array at the Northern Hemisphere with emphasis on the study of extragalactic objects at the lowest possible energies, and a second array at the Southern Hemisphere, which is to cover the full energy range and concentrate on galactic sources. The physics program of CTA goes beyond high energy astrophysics into cosmology and fundamental physics.
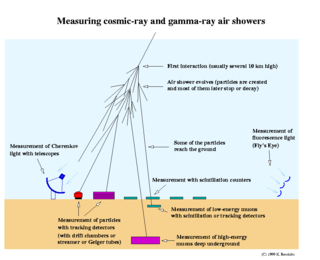
A cosmic-ray observatory is a scientific installation built to detect high-energy-particles coming from space called cosmic rays. This typically includes photons, electrons, protons, and some heavier nuclei, as well as antimatter particles. About 90% of cosmic rays are protons, 9% are alpha particles, and the remaining ~1% are other particles.
Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT) also known as Insight is a Chinese X-ray space observatory, launched on June 15, 2017 to observe black holes, neutron stars, active galactic nuclei and other phenomena based on their X-ray and gamma-ray emissions. It is based on the JianBing 3 imagery reconnaissance satellite series platform.

Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) is a leading research institute in Nainital, Uttarakhand which specializes in Astronomy, Solar Physics, Astrophysics and Atmospheric Sciences. It is an autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, the institute is situated at Manora Peak, about 9 km from Nainital, a popular hill station.
Fenton Hill Observatory is an astronomical research facility operated by Los Alamos National Laboratory in the Jemez Mountains of New Mexico, about 35 miles (56 km) west of Los Alamos. The site is home to several astronomical experiments and observatories spanning 30 acres (120,000 m2). It is also known as Technical Area 57 (TA-57) and is located at an elevation of 8,700 feet (2,700 m) in a region shielded from light pollution. Los Alamos National Laboratory has a use agreement with the Forest Service for the 30 acres (120,000 m2), which is located near Fenton Lake State Park.

The OVRO 40 meter Telescope is a radio telescope at the Owens Valley Radio Observatory near Big Pine, California, US. It is owned and operated by Caltech. The telescope is easily visible from the section of US highway 395 just north of Big Pine.

Major Atmospheric Cerenkov Experiment Telescope (MACE) is an Imaging Atmospheric Cerenkov telescope (IACT) located near Hanle, Ladakh, India. It is the highest and second largest Cerenkov telescope in the world. It was built by Electronics Corporation of India, Hyderabad, for the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre and was assembled at the campus of Indian Astronomical Observatory at Hanle. It was originally scheduled to become operational by 2016, but plans were pushed back to begin operations in 2020. It will be remotely operated and will run on solar power.

















