Bari is an administrative region (gobol) in northeastern Somalia that consists of six districts: Qandala, Iskushuban, Aluula, Bosaso, Bandarbeyla, and Qardho. The port city of Bosaso is the capital of the region and the largest city in Bari. The region is part of the autonomous Somali state of Puntland.

Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda. Although there is no verifiable evidence of its earliest volcanic activity, geologists estimate that Mount Elgon is at least 24 million years old, making it the oldest extinct volcano in East Africa. The mountain's name originates from its Maasai name, “Ol Doinyo Ilgoon”.
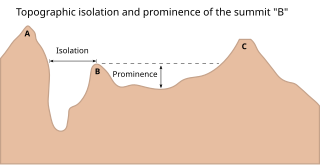
In topography, prominence or relative height measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the parent peak is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria.

Mount Nebo is the southernmost and highest mountain in the Wasatch Range of Utah, in the United States, and the centerpiece of the Mount Nebo Wilderness, inside the Uinta National Forest. It is named after the biblical Mount Nebo in Jordan, overlooking Israel from the east of the Jordan River, which is said to be the place of Moses' death.

Jabal Al-Mebraḥ, also known by the name Jabal Yibir, is a 1,527 m (5,010 ft) tall mountain in the Emirate of Fujairah, the U.A.E.

Mount Tahat is the highest mountain in Algeria. It sits at an elevation of 2,908 metres. Other sources indicate an elevation of 3,003 metres (9,852 ft). Tahat is also the highest peak in the Hoggar Mountains. Its nearest city is Tamanrasset which is located 56 kilometres (35 mi) to the south.
Mount Shimbiris is the highest peak of Somalia and Somaliland. It has an elevation of 2,460 metres (8,071 ft) above sea level. It is located in the Ogo Mountains range in the Sanaag region. SRTM data shows that its often-quoted elevation of 2,416 metres (7,927 ft) is slightly low.

Cal Madow is a mountain range in Somaliland. It stretches across an area between the east of Sanaag to the Bari regions of Somaliland. Its peak sits at almost 2,500 m (8,200 ft) in Shimbiris, northwest of Erigavo. Cal Madow was a tourist destination in the late 1980s. The local population of the Sanaag region is primarily responsible for preserving the habitat, which continues to face the risk of deforestation.
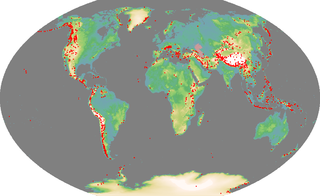
An ultra-prominent peak, or ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,524 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and thus do not achieve enough topographic prominence.

Mount Guna is a mountain and shield volcano located near the cities of Nefas Mewcha and Debre Tabor, in the northern Amhara Region of Ethiopia. It is the highest point in the South Gondar Zone, with an elevation of 4,120 metres (13,517 ft) above sea level.

Mount Hanang is a mountain in northern Tanzania. The peak has an elevation of 3,420 m above sea level. Hanang is located in Manyara Region's Hanang District. It is the fourth-highest mountain in Tanzania, if the three peaks of Kilimanjaro are counted as one mountain.
Saramati is a peak rising above the surrounding peaks at the mountainous border of the Indian state of Nagaland and the Naga Self-Administered Zone of the Sagaing Region of Myanmar. It is located near the village of Thanamir in the Kiphire District of Nagaland. it draws huge tourist to this tribal heritage rich state and is popularly known as the Crown of Nagaland.

The Golis Mountains are a mountain range in Somaliland. Also known as Qar Golis, they cut through the Togdheer region, and end near the Gan Libah.

Mount Loolmalasin or Loolmalassin is a mountain located in the Ngorongoro District of the Arusha Region, Tanzania. It has a peak elevation of 3,682 metres (12,080 ft) above sea level. It is, after Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Meru, the third-highest mountain in Tanzania if Kilimanjaro's three peaks are considered to be one mountain. The Mountain is located entirely within Nainokanoka ward. The volcano is located in the geographic area of the Crater Highlands and is an extinct volcano that last erupted in the pleistocene. Mount Loolmalasin is the second tallest mountain in Arusha Region and the highest point in Ngorongoro District. The mountain also is the source of Simiyu River, which flows west to Lake Victoria in Simiyu Region.
Buuraha Habeeno is a mountain in the Cal Miskaad mountain range, Somalia.

Somaliland is an unrecognised sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, internationally considered to be part of Somalia.
Somaliland is located in the East African sub-continent between the equator and the Gulf of Aden. The country occupies an area of approximately 176,120 square kilometres (68,000 sq mi). The climate is mostly hot and desertlike; it is largely arid with some semi-arid regions.
Mount Smith is a mountain located in the South West Ethiopia Peoples' Region, Ethiopia. Mount Smith is an ultra-prominent peak in the Central Ethiopian Highlands and is the 46th highest in Africa. It has an elevation in 2,560 m.