Related Research Articles

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

Queen Mary Land or the Queen Mary Coast is the portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between Cape Filchner, in 91° 54' E, and Cape Hordern, at 100° 30' E. It is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory.

The Framnes Mountains is a group of Antarctic mountain ranges in Mac. Robertson Land, to the south of the Mawson Coast. The range is surrounded by, and largely covered by, an ice sheet.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.
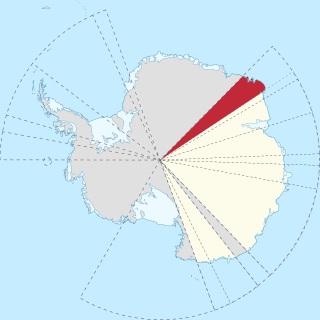
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
Mount Lawrence is a peak, 1,230 metres (4,040 ft) high, just north of Mount Coates in the David Range of the Framnes Mountains, Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from air photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for J. Lawrence, a diesel mechanic at Mawson Station in 1959.

The David Range (67°54′S62°30′E is a mountain range that extends for 26 kilometres in the Framnes Mountains of Mac.Robertson Land in Antarctica. The range is surrounded by, and largely covered by, an ice sheet. Only the peaks are visible.
Cape Hordern is an ice-free cape, overlain by morainic drift, at the northwest end of the Bunger Hills in Antarctica. It was probably sighted from Watson Bluff by A.L. Kennedy and other members of the Western Base Party of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition under Mawson, 1911–1914, who charted the west wall of what appeared to be two small islands lying north of Cape Hoadley in about 100°35′E. It was named "Hordern Island" by Mawson for Sir Samuel Hordern of Sydney, a patron of the expedition. It was renamed Cape Hordern by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) following correlation of Kennedy's map with the US-ACAN map of 1955 compiled from aerial photographs taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47.
Lawson Nunatak is a small tooth-like nunatak lying 2 nautical miles (4 km) southeast of Branson Nunatak in the Masson Range of the Framnes Mountains of Antarctica. The feature was fixed by intersection from trigonometrical stations by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions in 1968. It was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for E. J. Lawson, a diesel mechanic at Mawson Station, who assisted with the survey work in 1967.

The Western Base Party was a successful exploration party of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition. The eight-man Western Party was deposited by the SY Aurora on the Shackleton Ice Shelf at Queen Mary Land. The leader of the team was Frank Wild and the party included the geologist Charles Hoadley.
Kirkby Head is a sheer coastal outcrop on Tange Promontory in Enderby Land, Antarctica, which is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Continental ice reaches almost to the top on its southern side. It is located at the east side of the entrance to Alasheyev Bight.
Mount Coates is a peak, 1,280 metres (4,200 ft) high, just south of Mount Lawrence in the David Range of the Framnes Mountains. It was discovered and named in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Mawson.
Jennings Bluff is a dark, flat-topped outcrop in the Nicholas Range of Antarctica, 10 nautical miles (19 km) north of Mount Storegutt. It rises about 100 metres (330 ft) above the general ice level and has a steep eastern side, backing to an ice scarp in the west. The bluff was discovered by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition, 1929–31, under Mawson. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from aerial photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, and called Brattstabben. It was photographed from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions aircraft in 1956 and remapped, and was renamed by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia in 1961 for Noel Durrent Jennings, an assistant diesel mechanic at Mawson Station in 1960.
The Playfair Mountains are a group of mountains between Swann Glacier and Squires Glacier in southeast Palmer Land, Antarctica.
Smith Peaks is a group of peaks standing close south of Mount Hordern in the David Range of the Framnes Mountains. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37. Remapped by ANARE, 1957–60, and named by Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for F.A. Smith, diesel mechanic at Mawson Station, 1957.
Falla Bluff is a prominent rocky coastal bluff at the head of Utstikkar Bay. It was discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Mawson and named by him for R.A. Falla, ornithologist with the expedition.
Mount Humble is, at 1,450 metres (4,760 ft), the highest mountain in the Raggatt Mountains of Antarctica, standing 16 miles (26 km) south of the isolated mountain Mount Sibiryakov. It was plotted from air photos taken by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions in 1956, and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for John Edmund Humble, a cosmic ray physicist at Mawson Station in 1960.
Relay Hills is a group of low, ice-covered hills, mainly conical in shape, between Mount Edgell and Kinnear Mountains in western Antarctic Peninsula. First roughly surveyed from the ground by British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE), 1936–37. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), November 1947. Resurveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), November 1958. The name, applied by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC), arose because both the BGLE and the FIDS sledging parties had to relay their loads through this area to the head of Prospect Glacier.
Mount Keyser is a mountain 3 nautical miles (6 km) east of Mount Ryder, in the eastern part of the Tula Mountains in Enderby Land, Antarctica. It was plotted from air photos taken from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions aircraft in 1957, and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for D.O. Keyser, a radio officer at Mawson Station in 1961.
Landmark Point is a rocky point lying 1 kilometre (0.5 nmi) southeast of Safety Island, on the coast of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica. It was mapped from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions surveys and air photos, 1956–66, and was so named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia because it is almost due south from Auster Rookery and affords an excellent landmark if approaching the rookery along the coast from Mawson Station.
References
- ↑ "Hordern, Mount". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2012-06-25.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Hordern, Mount". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Hordern, Mount". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.