
Mount Monadnock, or Grand Monadnock, is a mountain in the New England state of New Hampshire, known for being featured in the writings of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Henry David Thoreau. It is the most prominent mountain peak in southern New Hampshire and is the highest point in Cheshire County. It is located 62 miles (100 km) northwest of Boston and 38 miles (61 km) southwest of Concord, within the towns of Jaffrey and Dublin, New Hampshire. At 3,165 feet (965 m), Mount Monadnock is nearly 1,000 feet (305 m) higher than any other mountain peak within 30 miles (48 km) and rises 2,000 feet (610 m) above the surrounding landscape.
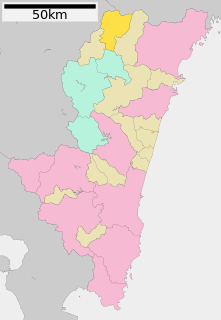
Takachiho is a town in Nishiusuki District, Miyazaki Prefecture, Japan.

Mount Bierstadt is a high mountain summit of the Chicago Peaks in the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The 14,065-foot (4,287 m) fourteener is located in the Mount Evans Wilderness of Pike National Forest, 9.4 miles (15.1 km) south by east of the Town of Georgetown in Clear Creek County, Colorado, United States. It was named in honor of Albert Bierstadt, the American landscape painter who made the first recorded summit of the mountain in 1863.

100 Famous Japanese Mountains is a book composed in 1964 by mountaineer and author Kyūya Fukada. The list became famous when Crown Prince Naruhito took note of it. The list has been the topic of NHK documentaries, and other hiking books.

Mount Takao is a mountain in the city of Hachiōji, Tokyo, Japan. It is protected within Meiji no Mori Takao Quasi-National Park.

Mount Poroshiri or sometimes Mount Horoshiri is located in the Hidaka Mountains, Hokkaidō, Japan. Its name was derived from a phonetic kanji transcription of the Ainu words for "great mountain", poro-shiri. It is the highest mountain in the Hidaka range, and is one of the 100 famous mountains in Japan.

Mount Tomuraushi is located in Daisetsuzan National Park, Hokkaidō, Japan. Its name was derived from the Ainu words for "place with many flowers" or "place with many water stains". It is one of the 100 famous mountains in Japan.

Mount Rishiri is a quaternary stratovolcano located off the coast of Hokkaidō, Japan in the Sea of Japan. The extinct volcano rises out of the sea forming Rishiri Island. Because its cone shape resembles Mount Fuji it is sometimes referred to as Rishiri Fuji. It is one of the 100 famous mountains in Japan.

Mount Kumotori stands at the boundary of Tokyo, Saitama, and Yamanashi Prefectures on the island of Honshū, Japan. With an elevation of 2,017 metres (6,617 ft), its summit is the highest point in Tokyo. It separates the Okutama Mountains and the Okuchichibu Mountains. While it marks the end of the Ishione (石尾根) mountain ridge that begins near the JR Okutama Station, the highest mountain ridge in Tokyo, its remote location amongst a group of mountains from both mountain ranges makes access difficult.

Mount Ishizuchi is a 1,982-metre-high (6,503 ft) mountain on the border of Saijō and Kumakōgen, in Ehime, Japan. This mountain is one of the 100 famous mountains in Japan. It is the highest mountain in Western Japan and the island of Shikoku.

Mount Iwaki is a stratovolcano located in western Aomori Prefecture, Tohoku, Japan. It is also referred to as Tsugaru-Fuji due to its shape. The mountain is listed as one of the 100 Famous Japanese Mountains in a 1964 book by mountaineer/author Kyūya Fukada. The mountain and its surroundings are located within the borders of Tsugaru Quasi-National Park.

Mount Tanigawa is a 1,977m mountain on the border of Gunma Prefecture and Niigata Prefecture in Japan.

Mount Ena is a mountain peak of the Kiso Mountains range in the Chūbu region of Japan.

Mt. Shirouma is a peak in the Hida Mountains range of the Japanese Alps, located in Nagano Prefecture and Toyama Prefecture, central Honshu, Japan.

Mount Hayachine is the highest mountain in the Kitakami Range, located in the Tōhoku region of northern Honshū, Japan. With an elevation of 1,917 m (6,289 ft), it is the second highest in Iwate Prefecture after Mount Iwate. Mount Hayachine is mentioned in 100 Famous Japanese Mountains, a book written in 1964 by Kyūya Fukada. The mountain is on the borders of the municipalities of Hanamaki, Tōno, and Miyako, east of the prefectural capital of Morioka.

Mount Iwate is a stratovolcano complex in the Ōu Mountains of western Iwate Prefecture, in the Tōhoku region of northern Honshū, Japan. With an elevation of 2,038 metres (6,686 ft), it is the highest in Iwate Prefecture. It is included as one of the 100 famous mountains in Japan, a book composed in 1964 by mountaineer and author Kyūya Fukada. The mountain is on the borders of the municipalities of Hachimantai, Takizawa, and Shizukuishi, west of the prefectural capital of Morioka. Much of the mountain is within the borders of the Towada-Hachimantai National Park. The mountain is also referred to as the "Nanbu Fuji" for its resemblance to Mount Fuji.

Mount Karasuba is a mountain of modest height on the border of the cities Minamibōsō and Kamogawa in Chiba Prefecture, Japan, reaching an elevation of 266.6 m (875 ft). It is one of the mountains of the Mineoka Mountain District of the Bōsō Hill Range. The kanji for Mount Karasuba, 烏 and 場, mean 'crow' and 'place' respectively. The mountain became a popular hiking destination after the construction of a hiking trail in 1975. The trail features three viewing platforms that offer views of the Pacific Ocean, surrounding hills, and nearby cities.

Mount Kanmuri, also known as Mount Yoshiwa Kanmuri, is a mountain located in the Yoshiwa District of Hatsukaichi, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. "Kanmuri" is a common name for mountains in Japan; Hiroshima Prefecture has six mountains by this name alone, hence the modifier "Yoshiwa".

Mount Saga is a mountain located on the border of Futtsu and Kyonan, Chiba Prefecture. Mount Saga has an elevation of 315.5 m (1,035 ft) and is one of the peaks of the Mineoka Mountain District of the Bōsō Hill Range.

Mount Yamato Katsuragi or simply Mount Katsuragi is a mountain in the Kongō Range straddling the prefectural border between Chihayaakasaka, Osaka and Gose, Nara in Japan. The peak elevation is 959.2 metres (3,147 ft). The mountain is located along the Gose Line of the Kintetsu Railway.






























