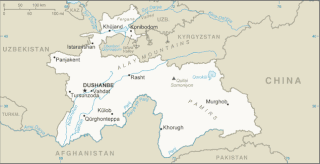
Tajikistan is nestled between Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan to the north and west, China to the east, and Afghanistan to the south. Mountains cover 93 percent of Tajikistan's surface area. The two principal ranges, the Pamir Mountains and the Alay Mountains, give rise to many glacier-fed streams and rivers, which have been used to irrigate farmlands since ancient times. Central Asia's other major mountain range, the Tian Shan, skirts northern Tajikistan. Mountainous terrain separates Tajikistan's two population centers, which are in the lowlands of the southern and northern sections of the country. Especially in areas of intensive agricultural and industrial activity, the Soviet Union's natural resource utilization policies left independent Tajikistan with a legacy of environmental problems.

The Bernese Alps are a mountain range of the Alps located in western Switzerland. Although the name suggests that they are located in the Berner Oberland region of the canton of Bern, portions of the Bernese Alps are in the adjacent cantons of Valais, Fribourg and Vaud, the latter being usually named Fribourg Alps and Vaud Alps respectively. The highest mountain in the range, the Finsteraarhorn, is also the highest point in the canton of Bern.

The Linth is a Swiss river that rises near the village of Linthal in the mountains of the canton of Glarus, and eventually flows into the Obersee section of Lake Zurich. It is about 50 kilometres (31 mi) in length.

The Tian Shan, also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the "Mountains of God/Heaven", is a large system of mountain ranges in Central Asia. The highest peak is at the Jengish Chokusu at 7,439 metres (24,406 ft) high. Its lowest point is at the Turpan Depression, which is 154 m (505 ft) below sea level.

The Alay or Alai Range is a mountain range that extends from the Tien Shan mountain range in Kyrgyzstan west into Tajikistan. It is part of the Pamir-Alay mountain system. The range runs approximately east to west. Its highest summit is Pik Tandykul, reaching 5544 m. It forms the southern border of the Fergana Valley, and in the south it falls steeply to the Alay Valley. The southern slopes of the range drain into the Kyzylsuu or Vakhsh River, a tributary of the Amu Darya. The streams that drain the northern slopes of the range are tributaries of the Syr Darya, and empty into the Fergana Valley to the north of the range. Pik Skobeleva, 5,051 metres (16,572 ft), is also a well-known summit. European route E007: Tashkent – Kokand – Andijan – Osh – Irkeshtam crosses the range by the Taldyk Pass. The range is also traversed by Pamir highway.

The Ili River is a river in Northwest China and Southeastern Kazakhstan. It flows from the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to the Almaty Region in Kazakhstan.
The Reedy Glacier is a major glacier in Antarctica, over 100 nautical miles long and 6 to 12 nautical miles wide, descending from the polar plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf between the Michigan Plateau and Wisconsin Range in the Transantarctic Mountains. It marks the limits of the Queen Maud Mountains on the west and the Horlick Mountains on the east.
Lillie Glacier is a large glacier in Antarctica, about 100 nautical miles long and 10 nautical miles wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue.

The Zarafshon is a river in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan in Central Asia. Its name, "spreader of gold" in Persian, refers to the presence of gold-bearing sands in the upper reaches of the river. To the ancient Greeks it was known as the Polytimetus. It was also formerly known as Sughd River. The river is 877 kilometres (545 mi) long and has a basin area of 17,700 square kilometres (6,800 sq mi).

The Trans-Alay or Trans-Alai Range is the northernmost range of the Pamir Mountain System. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, the range has been divided between Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan.
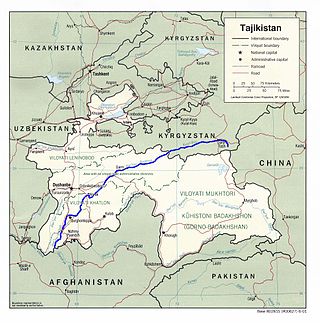
The Vakhsh, also known as the Surkhob in north-central Tajikistan and as the Kyzyl-Suu in Kyrgyzstan, is a Central Asian river and one of the main rivers of Tajikistan. It is a tributary of the Amu Darya river.

The Vanj is a river in east Tajikistan. It is a right tributary of the Panj in Vanj District, north-western Gorno-Badakhshan. The river is 103 kilometres (64 mi) long and has a basin area of 2,070 square kilometres (800 sq mi). It flows southwest between the Darvoz Range to the north and the Vanj Range to the south, joining the Panj on the border with Afghanistan. The Vanj valley is broader and more fertile than other valleys feeding the Panj. Vanj town is about 20 km upstream from the Panj. At the head of the valley, beyond the village of Po-i-Mazar, the river turns southeast and is fed by the Geographical Society Glacier near Independence Peak. Beyond the head of the valley are the Academy of Sciences Range and the Fedchenko Glacier.

The Vanch-Yakh Glacier is a large glacier in the Yazgulem Range, Pamir Mountains, of north-central Gorno-Badakhshan province, Tajikistan. The glacier is long and narrow, currently extending for 77 kilometres (48 mi) and covering over 700 square kilometres (270 sq mi). It is the longest glacier in the world outside of the polar regions. The maximum thickness of the glacier is 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), and the volume of the glacier and its dozens of tributaries is estimated at 144 cubic kilometres (35 cu mi)—about a third of the volume of Lake Erie.

The Suru River is a tributary of the Indus River that flows largely through the Kargil district of Ladakh, India into Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan. The Suru Valley is coextensive with the Kargil tehsil, with the town of Kargil situated on its banks. The river enters the Kharmang District of Gilgit-Baltistan, coursing a brief length before joining the Indus near Marol.

Daroot-Korgon is a village in the western Alay Valley of Osh Region, Kyrgyzstan. It is the capital of Chong-Alay District. Its population was 6,421 in 2021. It is about 90 km west of Sary-Tash on the river Kyzyl-Suu. To the north is a route to Osh via the Tengizbay pass, used by Russian explorers before the construction of the road though Sary-Tash.
The Qizilsu or Kyzylsu is a river that rises on the southern slopes of the Vakhsh Range in the north-east of Tajikistan's Khatlon Region and runs south-west until joining the Panj on the border with Afghanistan. The river is 230 kilometres (140 mi) long and has a basin area of 8,630 square kilometres (3,330 sq mi). It merges with the Yakhsu (Akhshu) as a major left tributary south of the town of Kulob. It irrigates the cotton-growing Qizilsu Valley between Kulob and Panj in the south-east of Khatlon Province. It is not the Kyzyl-Suu River that rises in Kyrgyzstan and flows through Tajikistan as Surkhob, then Vakhsh, following a course north-west of Qizilsu.

The Alai Valley is a broad, dry valley running east–west across most of southern Osh Region of Kyrgyzstan in Central Asia.
The Sokh is a river in Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan. It takes its rise at the joint of the north slopes of Alay Mountains and Turkestan Range and ends in Ferghana Valley. The Sokh is a left tributary of the Syr Darya. Currently it is largely used for irrigation. The length of the river is 124 kilometres (77 mi) with a catchment area of 3,510 square kilometres (1,360 sq mi), and average yearly discharge of 42.1 cubic metres per second (1,490 cu ft/s). The maximum discharge is 58.9 m3/s (2,080 cu ft/s). Sokh is full-flowing in June-August, and it falls in September. Overall, 276 glaciers covering a total area of 258.7 square kilometres (99.9 sq mi) are in the river catchment. Its largest tributary is the Kojashkan.

The Zarafshan Range, formerly the Zeravshan Range, is a mountain range in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, part of the Pamir-Alay mountains. Almost all of the range belongs to the drainage basins of the Zarafshan River.















