Psychophysiology is the branch of psychology that is concerned with the physiological bases of psychological processes. While psychophysiology was a general broad field of research in the 1960s and 1970s, it has now become quite specialized, and has branched into subspecializations such as social psychophysiology, cardiovascular psychophysiology, cognitive psychophysiology, and cognitive neuroscience.
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases. Physicians who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Rheumatologists deal mainly with immune-mediated disorders of the musculoskeletal system, soft tissues, autoimmune diseases, vasculitides, and heritable connective tissue disorders.

PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintains the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval.
The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) is one of the institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorder is an umbrella term for conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints and/or connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology. The term "rheumatism", however, does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions.

The human musculoskeletal system is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body.
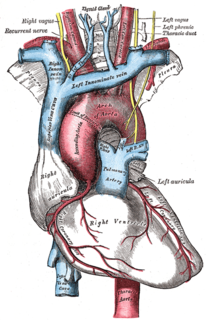
The aortic body is one of several small clusters of peripheral chemoreceptors known as glomus cells, baroreceptors, and supporting cells located along the aortic arch.
Enteroglucagon is a peptide hormone derived from preproglucagon. It is a gastrointestinal hormone, secreted from mucosal cells primarily of the colon and terminal ileum. It consists of 37 amino acids. Enteroglucagon is released when fats and glucose are present in the small intestine; which decrease the motility to allow sufficient time for these nutrients to be absorbed.

In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4-S4). A sacral plexopathy is a disorder affecting the nerves of the sacral plexus, usually caused by trauma, nerve compression, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of motor control, and sensory deficits.
Cardiovascular physiology is the study of the cardiovascular system, specifically addressing the physiology of the heart ("cardio") and blood vessels ("vascular").

Calgranulin is an S100 calcium-binding protein that is expressed in multiple cell types, including renal epithelial cells and neutrophils.

Cell physiology is the biological study about the activities that take place in a cell to keep it alive. This includes, among animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms. The term "physiology" refers to all the normal functions that take place in a living organism. All of these activities in the cell could be counted as following ; nutrition, environmental response, cell growth, cell division, reproduction and differentiation. The differences among the animal cell, plant cell and microorganisms shows the essential functional similarity even though those cells have different structures. Absorption of water by roots, production of food in the leaves, and growth of shoots towards light are examples of plant physiology. The heterotrophic metabolism of food derived from plants and animals and the use of movement to obtain nutrients are characteristic of animal physiology.

CFU-GM is a colony forming unit. It is derived from CFU-GEMM.
Right atrial pressure (RAP) is the blood pressure in the right atrium of the heart. RAP reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump the blood into the arterial system. RAP is often nearly identical to central venous pressure (CVP), although the two terms are not identical, as a pressure differential can sometimes exist between the venae cavae and the right atrium. CVP and RAP can differ when venous tone is altered. This can be graphically depicted as changes in the slope of the venous return plotted against right atrial pressure.
Following Maurice de Montmollin, the French distinguished generally two major trends in ergonomics:
Abnormality refers to any deviation from the normal, the noun form of the adjective abnormal.









