
The Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as soon after birth as possible. In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated. Adults who do not have tuberculosis and have not been previously immunized, but are frequently exposed, may be immunized, as well. BCG also has some effectiveness against Buruli ulcer infection and other nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Additionally, it is sometimes used as part of the treatment of bladder cancer.

Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.
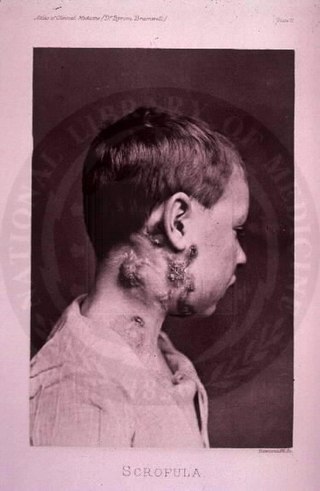
The disease mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis, also known as scrofula and historically as king's evil, involves a lymphadenitis of the cervical (neck) lymph nodes associated with tuberculosis as well as nontuberculous (atypical) mycobacteria.
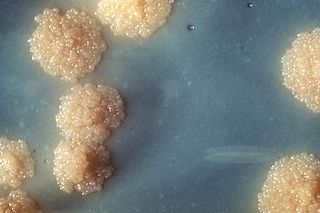
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, M. tuberculosis can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen, or fluorescent stains such as auramine are used instead to identify M. tuberculosis with a microscope. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the tuberculin skin test, acid-fast stain, culture, and polymerase chain reaction.

Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer that contains high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.

Mycobacterium bovis is a slow-growing aerobic bacterium and the causative agent of tuberculosis in cattle. It is related to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium which causes tuberculosis in humans. M. bovis can jump the species barrier and cause tuberculosis-like infection in humans and other mammals.
Paratuberculosis is a contagious, chronic and sometimes fatal infection that primarily affects the small intestine of ruminants. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Infections normally affect ruminants, but have also been seen in a variety of nonruminant species, including rabbits, foxes, and birds. Horses, dogs, and nonhuman primates have been infected experimentally. Paratuberculosis is found worldwide, with some states in Australia being the only areas proven to be free of the disease. At least in Canada, the signs of BJD usually start when cattle are four to seven years of age, and then usually only are diagnosed in one animal at a time. Cattle "with signs of Johne’s disease shed billions of bacteria through their manure and serve as a major source of infection for future calves."

Buruli ulcer is an infectious disease characterized by the development of painless open wounds. The disease is limited to certain areas of the world, most cases occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia. The first sign of infection is a small painless nodule or area of swelling, typically on the arms or legs. The nodule grows larger over days to weeks, eventually forming an open ulcer. Deep ulcers can cause scarring of muscles and tendons, resulting in permanent disability.
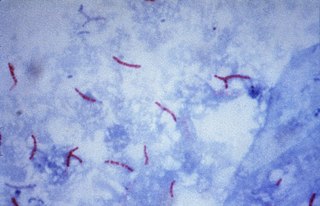
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain, also known as the acid-fast stain, is a bacteriological staining technique used in cytopathology and microbiology to identify acid-fast bacteria under microscopy, particularly members of the Mycobacterium genus. This staining method was initially introduced by Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915) and subsequently modified by the German bacteriologists Franz Ziehl (1859–1926) and Friedrich Neelsen (1854–1898) during the late 19th century.

Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenitis is a form of tuberculosis infection occurring outside of the lungs. In general, it describes tuberculosis infection of the lymph nodes, leading to lymphadenopathy. When cervical lymph nodes are affected, it is commonly referred to as "Scrofula." A majority of tuberculosis infections affect the lungs, and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis infections account for the remainder; these most commonly involve the lymphatic system. Although the cervical region is most commonly affected, tuberculous lymphadenitis can occur all around the body, including the axillary and inguinal regions.

Miliary tuberculosis is a form of tuberculosis that is characterized by a wide dissemination into the human body and by the tiny size of the lesions (1–5 mm). Its name comes from a distinctive pattern seen on a chest radiograph of many tiny spots distributed throughout the lung fields with the appearance similar to millet seeds—thus the term "miliary" tuberculosis. Miliary TB may infect any number of organs, including the lungs, liver, and spleen. Miliary tuberculosis is present in about 2% of all reported cases of tuberculosis and accounts for up to 20% of all extra-pulmonary tuberculosis cases.
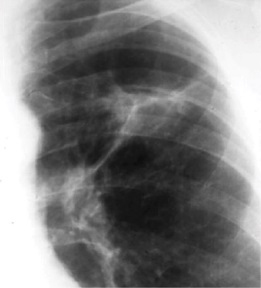
Ghon's complex is a lesion seen in the lung that is caused by tuberculosis. The lesions consist of a Ghon focus along with pulmonary lymphadenopathy within a nearby pulmonary lymph node. A Ghon's complex retains viable bacteria, making them sources of long-term infection, which may reactivate and trigger secondary tuberculosis later in life.
Mycobacterium africanum is a species of Mycobacterium that is most commonly found in West African countries, where it is estimated to cause up to 40% of pulmonary tuberculosis. The symptoms of infection resemble those of M. tuberculosis.
Mycobacterium bohemicum is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium caprae is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycobacterium and a member of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. The species is named after the caprines, the organisms from which M. caprae was first isolated. Prior to 2003, the species was referred to as Mycobacterium tuberculosis subsp. caprae. It is also synonymous with the name Mycobacterium bovis subsp. caprae.
Mycobacterium canettii, a novel pathogenic taxon of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC), was first reported in 1969 by the French microbiologist Georges Canetti, for whom the organism has been named. It formed smooth and shiny colonies, which is highly exceptional for the MTBC. It was described in detail in 1997 on the isolation of a new strain from a 2-year-old Somali patient with lymphadenitis. It did not differ from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the biochemical tests and in its 16S rRNA sequence. It had shorter generation time than clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis and presented a unique, characteristic phenolic glycolipid and lipo-oligosaccharide. In 1998, Pfyffer described abdominal lymphatic TB in a 56-year-old Swiss man with HIV infection who lived in Kenya. Tuberculosis caused by M. canettii appears to be an emerging disease in the Horn of Africa. A history of a stay to the region should induce the clinician to consider this organism promptly even if the clinical features of TB caused by M. canettii are not specific. The natural reservoir, host range, and mode of transmission of the organism are still unknown.
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is a genetically related group of Mycobacterium species that can cause tuberculosis in humans or other animals.

Extrapulmonary tuberculosis is tuberculosis (TB) within a location in the body other than the lungs. It accounts for an increasing fraction of active cases, from 20 to 40% according to published reports, and causes other kinds of TB. These are collectively denoted as "extrapulmonary tuberculosis". Extrapulmonary TB occurs more commonly in immunosuppressed persons and young children. In those with HIV, this occurs in more than 50% of cases. Notable extrapulmonary infection sites include the pleura, the central nervous system, the lymphatic system, the genitourinary system, and the bones and joints, among others.

Abdominal tuberculosis is a type of extrapulmonary tuberculosis which involves the abdominal organs such as intestines, peritoneum and abdominal lymph nodes. It can either occur in isolation or along with a primary focus in patients with disseminated tuberculosis.












