
The mullets or grey mullets are a family (Mugilidae) of ray-finned fish found worldwide in coastal temperate and tropical waters, and some species in fresh water. Mullets have served as an important source of food in Mediterranean Europe since Roman times. The family includes about 78 species in 20 genera.

Myxosporea is a class of microscopic parasites, belonging to the Myxozoa clade within Cnidaria. They have a complex life cycle which comprises vegetative forms in two hosts, an aquatic invertebrate and an ectothermic vertebrate, usually a fish. Each host releases a different type of spore. The two forms of spore are so different that until relatively recently they were treated as belonging to different classes within the Myxozoa.

Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany a century ago, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe, the United States, South Africa, Canada and other countries. In the 1980s, M. cerebralis was found to require a tubificid oligochaete to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules.

Myxobolus is a genus of myxozoa that includes important parasites of fish like Myxobolus cerebralis. The genus is polyphyletic, with members scattered throughout the myxozoa. Some stages of Myxobolus species were previously thought to be different organisms entirely, but are now united in this group.

The flathead grey mullet is an important food fish species in the mullet family Mugilidae. It is found in coastal tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. Its length is typically 30 to 75 centimetres. It is known with numerous English names, including the flathead mullet, striped mullet, black mullet, bully mullet, common mullet, grey mullet, sea mullet and mullet, among others.

Lagunas de Mejía National Sanctuary is a protected area on the coastal plain of Peru, in Islay Province, Arequipa, in the mouth of the Tambo River. It is a sanctuary for migratory and resident birds, and was designated a Ramsar site in 1992.

Pantanos de Villa Wildlife Refuge is a protected area of marshes located in the district of Chorrillos, within the city of Lima, Peru with an extension of 263.27 hectares (2.63 km2).

The smallest organisms found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of organism size, including volume, mass, height, length, or genome size.

Meavy is a small village, civil parish and former manor in the English county of Devon. Meavy forms part of the district of West Devon. It lies a mile or so east of Yelverton. The River Meavy runs near the village. For administrative purposes the parish is grouped with the parishes of Sheepstor and Walkhampton to form Burrator Parish Council, and for electoral purposes it is grouped with the same two parishes to form Burrator Ward.

The Missolonghi-Aitoliko lagoons complex is located in the north part of the Gulf of Patras in the central west coast of Greece. It is one of the most important Mediterranean lagoons. It is a shallow area of 150 km2, extended between the Acheloos and Evinos rivers. It is protected by the Ramsar Convention and it is also included in the Natura 2000 network.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.

Cavisomidae are a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.
Diplosentidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Heterophyes heterophyes was discovered by Theodor Maximaillian Bilharz in 1851. This parasite was found during an autopsy of an Egyptian mummy. H. heterophyes is found in the Middle East, West Europe and Africa. They use different species to complete their complex lifestyle. Humans and other mammals are the definitive host, first intermediate host are snails, and second intermediate are fish. Mammals that come in contact with the parasite are dogs, humans, and cats. Snails that are affected by this parasite are the Cerithideopsilla conica. Fish that come in contact with this parasite are Mugil cephalus, Tilapia milotica, Aphanius fasciatus, and Acanthgobius sp. Humans and mammals will come in contact with this parasite by the consumption of contaminated or raw fish. This parasite is one of the smallest endoparasite to infect humans. It can cause intestinal infection called heterophyiasis.

Kudoa is a genus of Myxozoa and the only genus recognized within the monotypic family Kudoidae. There are approximately 100 species of Kudoa all of which parasitize on marine and estuarine fish. Kudoa are most commonly known and studied for the negative effects the genus has on commercial fishing and aquaculture industries.
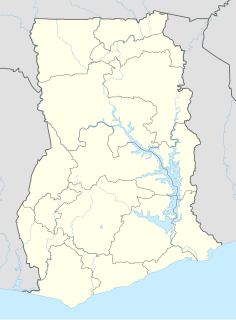
The Sakumo Ramsar Site also known as the Sakumo Lagoon is a wetland of international importance. It covers an area of 1,400 hectares and is situated along the coastal road between Accra and Tema in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. It is about 3 km (1.9 mi) west of Tema. Activities ongoing within the Ramsar Site include farming, fishing, recreation, urban and industrial development.

Beymelek Lagoon is a lagoon on the Mediterranean coast, which is used as a fishery, in Antalya Province, southwestern Turkey. It is named after the village of Beymelek, which is located to the west of the water body. It is situated in Demre ilçe (district) of Antalya Province at 36°16′N30°03′E.
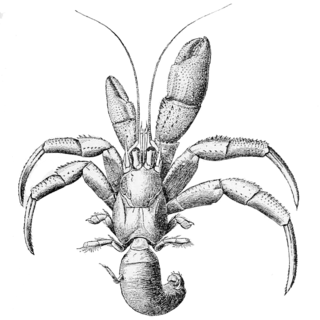
Pagurus acadianus, the Acadian hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab in the family Paguridae. It is found in Western Atlantic Ocean.
Tetraonchus is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Tetraonchidae.
















