
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the nature of the particles that constitute matter and radiation. Although the word particle can refer to various types of very small objects, particle physics usually investigates the irreducibly smallest detectable particles and the fundamental interactions necessary to explain their behaviour.

The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN, is a European research organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, the organization is based in a northwest suburb of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border and has 23 member states. Israel is the only non-European country granted full membership. CERN is an official United Nations Observer.

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundreds of universities and laboratories, as well as more than 100 countries. It lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference and as deep as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva.

High-energy nuclear physics studies the behavior of nuclear matter in energy regimes typical of high-energy physics. The primary focus of this field is the study of heavy-ion collisions, as compared to lighter atoms in other particle accelerators. At sufficient collision energies, these types of collisions are theorized to produce the quark–gluon plasma. In peripheral nuclear collisions at high energies one expects to obtain information on the electromagnetic production of leptons and mesons that are not accessible in electron–positron colliders due to their much smaller luminosities.
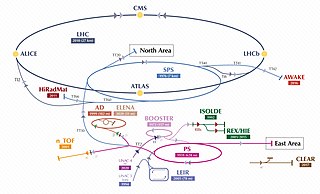
The Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) is a particle accelerator of the synchrotron type at CERN. It is housed in a circular tunnel, 6.9 kilometres (4.3 mi) in circumference, straddling the border of France and Switzerland near Geneva, Switzerland.

The ISOLDE Radioactive Ion Beam Facility, is an on-line isotope separator facility located at heart of the CERN accelerator complex on the Franco-Swiss border. The name of the facility is an acronym for Isotope Separator On Line DEvice. Created in 1964, the ISOLDE facility started delivering radioactive ion beams to users in 1967. Originally located at the SynchroCyclotron accelerator, the facility has been upgraded several times most notably in 1992 when the whole facility was moved to be connected to CERN's ProtonSynchroton Booster (PSB). Entering its 6th decade of existence, ISOLDE is currently the oldest facility still in operation at CERN. From the first pioneering isotope separation on-line (ISOL) beams to the latest technical advances allowing for the production of the most exotic species, ISOLDE benefits a wide range of physics communities with applications covering nuclear, atomic, molecular and solid-state physics, but also biophysics and astrophysics, as well as high-precision experiments looking for physics beyond the Standard Model. The facility is operated by the ISOLDE Collaboration, comprising CERN and fifteen (mostly) European countries. As of 2019, more than 800 experimentalists around the world are coming to ISOLDE to perform typically 45 different experiments per year.

ALICE is one of eight detector experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. The other seven are: ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, LHCf, MoEDAL and FASER.

The Proton Synchrotron is a particle accelerator at CERN. It is CERN's first synchrotron, beginning its operation in 1959. For a brief period the PS was the world's highest energy particle accelerator. It has since served as a pre-accelerator for the Intersecting Storage Rings (ISR) and the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS), and is currently part of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) accelerator complex. In addition to protons, PS has accelerated alpha particles, oxygen and sulfur nuclei, electrons, positrons, and antiprotons.
The High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider is an upgrade to the Large Hadron Collider, operated by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), located at the French-Swiss border near Geneva. From 2011 to 2020, the project was led by Lucio Rossi. In 2020 the lead role was taken up by Oliver Brüning.

The Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB) is the first and smallest circular proton accelerator in the accelerator chain at the CERN injection complex, which also provides beams to the Large Hadron Collider. It contains four superimposed rings with a radius of 25 meters, which receive protons with an energy of 50 MeV from the linear accelerator Linac4 and accelerate them up to 1.4 GeV, ready to be injected into the Proton Synchrotron (PS). Before the PSB was built in 1972, Linac 1 injected directly into the Proton Synchrotron, but the increased injection energy provided by the booster allowed for more protons to be injected into the PS and a higher luminosity at the end of the accelerator chain.

Quark–gluon plasma or QGP is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal and chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word plasma signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan-Boltzmann format governed by fourth power of temperature and many practically mass free quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions near chemical (yield) equilibrium with their colour charge open for a new state of matter to be referred to as QGP.

NA61/SHINE is a particle physics experiment at the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). The experiment studies the hadronic final states produced in interactions of various beam particles with a variety of fixed nuclear targets at the SPS energies.
Strangeness production in relativistic heavy ion collisions is a signature and a diagnostic tool of quark–gluon plasma (QGP) formation and properties. Unlike up and down quarks, from which everyday matter is made, heavier quark flavors such as strangeness and charm typically approach chemical equilibrium in a dynamic evolution process. QGP is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal (kinetic) and not necessarily chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word plasma signals that color charged particles are able to move in the volume occupied by the plasma. The abundance of strange quarks is formed in pair-production processes in collisions between constituents of the plasma, creating the chemical abundance equilibrium. The dominant mechanism of production involves gluons only present when matter has become a quark–gluon plasma. When quark–gluon plasma disassembles into hadrons in a breakup process, the high availability of strange antiquarks helps to produce antimatter containing multiple strange quarks, which is otherwise rarely made. Similar considerations are at present made for the heavier charm flavor, which is made at the beginning of the collision process in the first interactions and is only abundant in the high-energy environments of CERN's Large Hadron Collider.

The NA49 experiment was a particle physics experiment that investigated the properties of quark–gluon plasma. It took place in the North Area of the Super Proton Synchrotron at CERN from 1991-2002. It used a large-acceptance hadron detector to investigate reactions induced by the collision of various heavy ions on targets made of a variety of elements.

The CERN hadron Linacs are linear accelerators that accelerate beams of hadrons from a standstill to be used by the larger circular accelerators at the facility.
The NA35 experiment was a particle physics experiment that took place in the North Area of the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) at CERN. It used a streamer chamber with comprehensive hadronic and electromagnetic calorimetry. This experiment was used to observe the properties of nucleus-nucleus collisions at 60 and 200 GeV/nucleon, to understand the degree of stopping and thermalization, determine the energy densities achievable in those conditions, and to measure other related properties and quantities.

Paolo Giubellino is an experimental particle physicist working on High-Energy Nuclear Collisions. Currently he is the joint Scientific Managing Director of the Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research (FAIR) and the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research (GSI) and Professor at the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Technische Universität Darmstadt.
Sanja Damjanović ; born June 5, 1972 in Nikšić is a physicist from Montenegro and minister of science in the government of Montenegro since 2016.
Hans Joachim Specht is a German experimental particle and nuclear physicist and university professor at the Heidelberg University.










