Related Research Articles

Closed captioning (CC) is a form of subtitling, a process of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information, where the viewer is given the choice of whether the text is displayed. Closed captions are typically used as a transcription of the audio portion of a program as it occurs, sometimes including descriptions of non-speech elements. Other uses have included providing a textual alternative language translation of a presentation's primary audio language that is usually burned-in to the video and unselectable.
NAPLPS is a graphics language for use originally with videotex and teletext services. NAPLPS was developed from the Telidon system developed in Canada, with a small number of additions from AT&T Corporation. The basics of NAPLPS were later used as the basis for several other microcomputer-based graphics systems.

Telidon was a videotex/teletext service developed by the Canadian Communications Research Centre (CRC) during the late 1970s and supported by commercial enterprises led by Infomart in the early 1980s. Most work on the system ended after 1985, having failed to build critical mass.

Color television or colour television is a television transmission technology that includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improves on the monochrome or black-and-white television technology, which displays the image in shades of gray (grayscale). Television broadcasting stations and networks in most parts of the world upgraded from black-and-white to color transmission between the 1960s and the 1980s. The invention of color television standards was an important part of the history and technology of television.

Ceefax was the world's first teletext information service and a forerunner to the current BBC Red Button service. Ceefax was started by the BBC in 1974 and ended, after 38 years of broadcasting, at 23:32:19 BST on 23 October 2012, in line with the digital switchover completion in Northern Ireland.
Multichannel Television Sound (MTS) is the method of encoding three additional audio channels into analog 4.5 MHz audio carriers on System M and System N. It was developed by the Broadcast Television Systems Committee, an industry group, and sometimes known as BTSC as a result.
Antiope was a French teletext standard in the 1980s. It also formed the basis for the display standard used in the French videotex service Minitel. The term allegedly stood for Acquisition Numérique et Télévisualisation d’Images Organisées en Pages d’Écriture, which could be loosely translated as Digital Acquisition and Remote Visualization of Images Organized into Written Pages.

EIA-608, also known as "Line 21 captions" and "CEA-608", is a standard for closed captioning for NTSC TV broadcasts in the United States, Canada and Mexico. It was developed by the Electronic Industries Alliance and required by law to be implemented in most television receivers made in the United States.
NABTS, the North American Broadcast Teletext Specification, is a protocol used for encoding NAPLPS-encoded teletext pages, as well as other types of digital data, within the vertical blanking interval (VBI) of an analog video signal. It is standardized under standard EIA-516, and has a rate of 15.6 kbit/s per line of video. It was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System C.

Teletext, or broadcast teletext, is a standard for displaying text and rudimentary graphics on suitably equipped television sets. Teletext sends data in the broadcast signal, hidden in the invisible vertical blanking interval area at the top and bottom of the screen. The teletext decoder in the television buffers this information as a series of "pages", each given a number. The user can display chosen pages using their remote control. In broad terms, it can be considered as Videotex, a system for the delivery of information to a user in a computer-like format, typically displayed on a television or a dumb terminal, but that designation is usually reserved for systems that provide bi-directional communication, such as Prestel or Minitel.
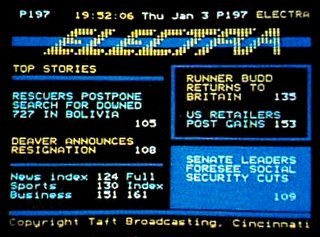
Electra was a teletext service in the United States that was in operation from 1982 up until 1993, when it was shut down due to a lack of funding, and discontinuation of teletext-capable television sets by the only US television manufacturer offering teletext capability at the time, Zenith. It was owned, operated and maintained by Cincinnati-based Taft Broadcasting and Tulsa, Oklahoma-based Satellite Syndicated Systems (SSS), later known as Tempo Enterprises, in cooperation with cable/satellite TV station Superstation WTBS, who carried Electra's data on their vertical blanking interval. SSS's own TV network, the Satellite Program Network, carried the service before it was shut down in 1989. The service was also available to C-band satellite dish users via the Galaxy 1 and Satcom 3R satellites.

ExtraVision was a teletext service created and operated by the American television network CBS in the early to mid-1980s. It was carried in the vertical blanking interval of the video from local affiliate stations of the CBS network. It featured CBS program information, news, sports, weather, even subtitling for CBS programming. ExtraVision could also have its pages customized by the local affiliate station carrying it, for such things as program schedules, local community announcements, and station promotions. WGBH Boston, a pioneer in assisting the deaf and hard-of-hearing with closed captioning, also provided content for those audiences to ExtraVision and assisted in providing captioning for CBS programming via ExtraVision.

World System Teletext (WST) is the name of a standard for encoding and displaying teletext information, which is used as the standard for teletext throughout Europe today. It was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System B.

ON TV was an American subscription television (STV) service that operated in eight markets between 1977 and 1985. Originally established by National Subscription Television, a joint venture of Oak Industries and Chartwell Communications, ON TV was part of a new breed of STV operations that broadcast premium programming—including movies, sporting events, and concerts—over an encrypted signal on a UHF television station and leased decoders to subscribing customers. At its peak in 1982, ON TV boasted more than 700,000 customers—more than half of them in Los Angeles, its most successful market. However, the rapidly expanding availability of cable television, coupled with a recession, caused the business to quickly lose subscribers at the same time that Oak Industries was experiencing severe financial difficulties. Between March 1983 and June 1985, all eight operations closed.

The National Captioning Institute, Inc. (NCI) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that provides real-time and off-line closed captioning, subtitling and translation, described video, web captioning, and Spanish captioning for television and films. Created in 1979 and headquartered in Chantilly, Virginia, the organization was the first to caption live TV and home video, and holds the trademark on the display icon featuring a simple geometric rendering of a television set merged with a speech balloon to indicate that a program is captioned by National Captioning Institute. National Captioning Institute also has an office in Santa Clarita, California.

WSNS-TV is a television station in Chicago, Illinois, United States, serving as the local outlet for the Spanish-language network Telemundo. It is owned and operated by NBCUniversal's Telemundo Station Group alongside NBC outlet WMAQ-TV. The two stations share studios at the NBC Tower on North Columbus Drive in the city's Streeterville neighborhood and broadcast from the same transmitter atop the Willis Tower in the Chicago Loop.
This is a timeline of the history of teletext on television in the UK..

JTES, the Japanese Teletext Specification, is a protocol used for encoding teletext pages, as well as other types of digital data, within the vertical blanking interval (VBI) of an analog video signal in Japan. It was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System D.

343-line is the number of scan lines in some early electronic monochrome analog television systems. Systems with this number of lines were used with 30 interlaced frames per second by the United States from 1935 to 1938, and with 25 interlaced frames per second in the Soviet Union from 1937 onwards. A similar system was under development in Poland in 1939.
References
- 1 2 "Portfolio 1981-89: Teletext". The Communication Studio. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ Ellers, Ed. "TELETEXT GALLERY - TELETEXT AROUND THE WORLD - UNITED STATES OF AMERICA". The Teletext Museum. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ Graziplene, Leonard R. (2000). Teletext: Its Promise and Demise. Lehigh University Press. ISBN 978-0-934223-64-5.
- ↑ Technology, United States Congress House Committee on Science and Technology Subcommittee on Science, Research, and (1984). Developing Technologies for Television Captioning: Benefits for the Hearing Impaired : Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Science, Research, and Technology of the Committee on Science and Technology, U.S. House of Representatives, Ninety-eighth Congress, First Session, November 9, 1983. U.S. Government Printing Office.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Gingras, Richard. "Broadcast Teletext, 1980". www.richardgingras.com. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- 1 2 Watson, Barbara (September 1983). "NBC offers teletext" (PDF). RCA Engineer. p. 18.
- ↑ Renner-Smith, Susan (September 1984). "Teletext decoder for network-TV "magazine"". Popular Science. p. 40.
- ↑ Hoard, Bruce (April 25, 1983). "FCC Authorizes Teletext Broadcasting". Computerworld. p. 71.
- 1 2 3 Astle, B. (September 1983). "Teletext standards in North America" (PDF). RCA Engineer. pp. 15–25.
- ↑ Carlson, David (2009). "ExtraVision". David Carlson's Virtual World. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- 1 2 3 SHAW, SYDNEY (May 2, 1984). "Teletext, a new service that displays 'pages' of information..." United Press International, Inc.
- ↑ Vaughan, John (2019-01-13). "TV In-Channel Magazine NBC Teletext". John Vaughan - my Portfolio. Retrieved 2022-12-16.
- ↑ Dixon, Douglas (July 1989). "Life before the chips: simulating digital video interactive technology". Communications of the ACM. 32 (7): 824–831. doi: 10.1145/65445.65449 . ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 17999029.
- ↑ Gillies, Donald (1989). Technological Determinism In Canadian Telecommunications: Telidon Technology, Industry and Government. Ryerson Polytechnical Institute. p. 6. doi:10.22230/cjc.1990v15n2a549 (inactive 1 November 2024).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ↑ Downey, Gregory J. (2008-02-25). Closed Captioning: Subtitling, Stenography, and the Digital Convergence of Text with Television. JHU Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-8018-8710-9.
