Related Research Articles

In computing, a northbridge is one of two chips comprising the core logic chipset architecture on a PC motherboard. A northbridge is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB) to handle high-performance tasks, and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. Since the 2010s, die shrink and improved transistor density have allowed for increasing chipset integration, and the functions performed by northbridges are now often incorporated into other components. As of 2019, Intel and AMD had both released chipsets in which all northbridge functions had been integrated into the CPU. Modern Intel Core processors have the northbridge integrated on the CPU die, where it is known as the uncore or system agent.

The GeForce 6 series is Nvidia's sixth generation of GeForce graphic processing units. Launched on April 14, 2004, the GeForce 6 family introduced PureVideo post-processing for video, SLI technology, and Shader Model 3.0 support.

The nForce4 is a motherboard chipset released by Nvidia in October 2004. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors and Intel Pentium 4 LGA 775 processors.

Scalable Link Interface (SLI) is the brand name for a now discontinued multi-GPU technology developed by Nvidia for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output. SLI is a parallel processing algorithm for computer graphics, meant to increase the available processing power.

AMD CrossFire is a brand name for the multi-GPU technology by Advanced Micro Devices, originally developed by ATI Technologies. The technology allows up to four GPUs to be used in a single computer to improve graphics performance.

The GeForce 7 series is the seventh generation of Nvidia's GeForce graphics processing units. This was the last series available on AGP cards.
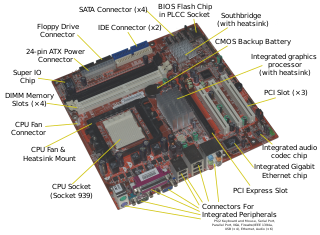
The Radeon Xpress 200 is a computer chipset released by ATI. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors as well as supporting Intel Pentium 4, Pentium D and Celeron processors. Additionally, it includes support for DDR400 RAM and DDR-2 667 RAM on the Intel Edition.
The GeForce 8 series is the eighth generation of Nvidia's GeForce line of graphics processing units. The third major GPU architecture developed by Nvidia, Tesla represents the company's first unified shader architecture.
The nForce 500 is a motherboard chipset series and the successor to the nForce4 series. It was revealed by NVIDIA on 2006-03-07 and released on May 23, 2006. The nForce 500 series supports AMD's Socket AM2 and support for Intel's LGA 775 has also been added.
The Xpress 3200 is a revision of the Xpress 200 computer chipset released by ATI. The chipset supports AMD64 processors for Socket 939 and Socket AM2.
AMD 580 chipset series is a computer chipset series designed by the AMD Graphics Product Group, for the AMD processors. It was designed for usage with ATI's CrossFire Multi GPU Technology, with both PCI Express slots running at x16 lanes each.
NVIDIA System Tools is a discontinued collection of utilities for accessing, monitoring, and adjusting system components, including temperature and voltages with a graphical user interface within Windows, rather than through the BIOS.
The nForce 600 chipset was released in the first half of November 2006, coinciding with the GeForce 8 series launch on November 8, 2006. The nForce 600 supports Intel's LGA 775 socket and AMD's Quad FX platform and replaces the nForce 500 series.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.

The GeForce 9 series is the ninth generation of Nvidia's GeForce series of graphics processing units, the first of which was released on February 21, 2008. Products are based on a slightly repolished Tesla microarchitecture, adding PCIe 2.0 support, improved color and z-compression, and built on a 65 nm process, later using 55 nm process to reduce power consumption and die size.
GeForce 8000 series is a series of Nvidia motherboard chipsets aimed at home theater PC and gaming pc solutions using CPUs by AMD. The chipsets are capable of full 1080p Blu-ray and HD DVD playback with most processing being done by the integrated chipset from the motherboard and not requiring an additional video card.

The Intel X58 is an Intel chip designed to connect Intel processors with Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) interface to peripheral devices. Supported processors implement the Nehalem microarchitecture and therefore have an integrated memory controller (IMC), so the X58 does not have a memory interface. Initially supported processors were the Core i7, but the chip also supported Nehalem and Westmere-based Xeon processors.
Nvidia Ion was a product line of Nvidia Corporation intended for motherboards of low-cost portable computers. It used graphics processing units and chipsets intended for small products.
GPU switching is a mechanism used on computers with multiple graphic controllers. This mechanism allows the user to either maximize the graphic performance or prolong battery life by switching between the graphic cards. It is mostly used on gaming laptops which usually have an integrated graphic device and a discrete video card.

The AMD 900 chipset series is identical to the AMD 800 chipset series except for the fact that it is only found on Socket AM3+ mainboards, whereas its predecessor is only found on Socket AM3 mainboards. It was released in 2011.
References
- ↑ (in Chinese) ExpReview report, retrieved October 12, 2007
- ↑ Fudzilla report, retrieved February 13, 2008
- 1 2 Fudzilla report, retrieved January 31, 2008
- ↑ "EVGA nForce 790i Ultra SLI Motherboard | Hardware Secrets". Archived from the original on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 2011-01-15.
- ↑ NVIDIA 790i Reference Board
- ↑ The Inquirer report, retrieved October 15, 2007
- ↑ "The Inquirer report". The Inquirer . Archived from the original on 2007-10-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)