
The Group of Eight (G8) was an inter-governmental political forum from 1997 until 2014. It had formed from incorporating the country of Russia into the Group of Seven, or G7, and returned to its previous name after Russia was disinvited in 2014.
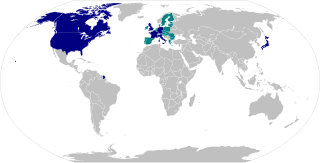
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental organization consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. The heads of government of the member states, as well as the representatives of the European Union, meet at the annual G7 Summit.

The NatureServe conservation status system, maintained and presented by NatureServe in cooperation with the Natural Heritage Network, was developed in the United States in the 1980s by The Nature Conservancy (TNC) as a means for ranking or categorizing the relative imperilment of species of plants, animals, or other organisms, as well as natural ecological communities, on the global, national or subnational levels. These designations are also referred to as NatureServe ranks, NatureServe statuses, or Natural Heritage ranks. While the Nature Conservancy is no longer substantially involved in the maintenance of these ranks, the name TNC ranks is still sometimes encountered for them.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one.

Asterophora is a genus of fungi that grow as parasites on mushrooms. The genus contains four species, which have a widespread distribution, especially in temperate areas. The most recently described species, A. salvaterrensis, was found in Pinus pinaster forests in Galicia. Asterophora species are characterized by the massive production of chlamydospores in their fruit bodies and by the production of carminophilous lysosomes in their basidia. A frequently used but synonymous genus name is Nyctalis. The chlamydospores have been classified in the genus Ugola, which is an anamorphic name.
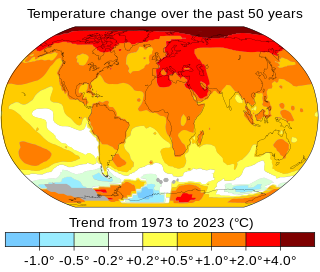
Climate change includes both the global warming driven by human emissions of greenhouse gases, and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century, humans have had unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale.
Ugola is a genus of fungi in the Lyophyllaceae family. The genus was first described scientifically by the French naturalist Michel Adanson in his 1763 Familles des Plantes. The three fungi in the genus are anamorphs of species of Asterophora, a genus of fungi that are parasitic on other mushrooms.

Asterophora mirabilis is a species of fungus that grows as a parasite on mushrooms. It was originally described as Nyctalis mirabilis by Australian mycologist Tom May in 1995, and later transferred to the genus Asterophora in 2001. The fungus grows in temperate rainforests of Australia on decaying fruit bodies of species in the genera Russula and Lactarius.

Tricholoma myomyces is a mushroom of the agaric genus Tricholoma, usually considered to be a synonym of Tricholoma terreum. The species was first described scientifically by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794 as Agaricus myomyces, and later transferred to the genus Tricholoma by Danish mycologist Jakob Emanuel Lange in 1933. It is found in Europe and northern North America.
Nachaba auritalis is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It is found in Brazil.
Nachaba congrualis is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859, and is known from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Nachaba diplagialis is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It is found in South America.
Nachaba funerea is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It was described by Cajetan Felder, Rudolf Felder and Alois Friedrich Rogenhofer in 1875, and is known from Amazonas, Brazil.
Nachaba oppositalis is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859, and is known from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Nachaba reconditana is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It was described by Francis Walker in 1864, and is known from Brazil.
Nachaba tryphaenalis is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It was described by Cajetan Felder, Rudolf Felder and Alois Friedrich Rogenhofer in 1875, and is known from Amazonas, Brazil.
Nachaba fluella is a species of snout moth in the genus Nachaba. It is found in South America.

Gerris is a bug genus in the family Gerridae.
Acalypta nyctalis is a species of lace bug in the family Tingidae. It is found in North America.








