Related Research Articles

The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Shield or the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton, the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the continental United States.
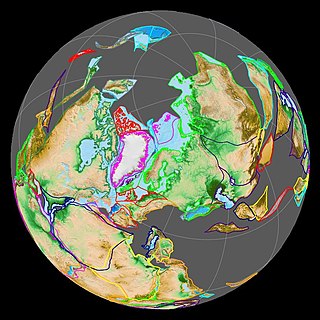
Laurasia was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around 335 to 175 million years ago (Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana 215 to 175 Mya during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean c. 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Eurasia.

Columbia, also known as Nuna or Hudsonland, is a hypothetical ancient supercontinent. It was first proposed by John J.W. Rogers and M. Santosh in 2002 and is thought to have existed approximately 2,500 to 1,500 million years ago (Ma), in the Paleoproterozoic era. The assembly of the supercontinent was likely completed during global-scale collisional events from 2,100 to 1,800 Ma.

Arctica, or Arctida is a hypothetical ancient continent which formed approximately 2.565 billion years ago in the Neoarchean era. It was made of Archaean cratons, including the Siberian Craton, with its Anabar/Aldan shields in Siberia, and the Slave, Wyoming, Superior, and North Atlantic cratons in North America. Arctica was named by Rogers 1996 because the Arctic Ocean formed by the separation of the North American and Siberian cratons. Russian geologists writing in English call the continent "Arctida" since it was given that name in 1987, alternatively the Hyperborean craton, in reference to the hyperboreans in Greek mythology.

The Moine Thrust Belt or Moine Thrust Zone is a linear tectonic feature in the Scottish Highlands which runs from Loch Eriboll on the north coast 190 kilometres (120 mi) southwest to the Sleat peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The thrust belt consists of a series of thrust faults that branch off the Moine Thrust itself. Topographically, the belt marks a change from rugged, terraced mountains with steep sides sculptured from weathered igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in the west to an extensive landscape of rolling hills over a metamorphic rock base to the east. Mountains within the belt display complexly folded and faulted layers and the width of the main part of the zone varies up to ten kilometres, although it is significantly wider on Skye.

The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, from Labrador to Mexico, as well as to Scotland.
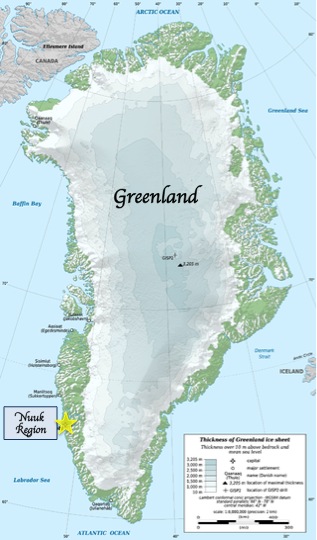
The Isua Greenstone Belt is an Archean greenstone belt in southwestern Greenland, aged between 3.7 and 3.8 billion years. The belt contains variably metamorphosed mafic volcanic and sedimentary rocks, and is the largest exposure of Eoarchaean supracrustal rocks on Earth. Due to its age and low metamorphic grade relative to many Eoarchaean rocks, the Isua Greenstone Belt has become a focus for investigations on the emergence of life and the style of tectonics that operated on the early Earth.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.
The High Arctic Large Igneous Province (HALIP) is a Cretaceous large igneous province in the Arctic. The region is divided into several smaller magmatic provinces. Svalbard, Franz Josef Land, Sverdrup Basin, Amerasian Basin, and northern Greenland are some of the larger divisions. Today, HALIP covers an area greater than 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi), making it one of the largest and most intense magmatic complexes on the planet. However, eroded volcanic sediments in sedimentary strata in Svalbard and Franz Josef Land suggest that an extremely large portion of HALIP volcanics have already been eroded away.
The Orcadian Basin is a sedimentary basin of Devonian age that formed mainly as a result of extensional tectonics in northeastern Scotland after the end of the Caledonian orogeny. During part of its history, the basin was filled by a lake now known as Lake Orcadie. In that lacustrine environment, a sequence of finely bedded sedimentary rocks was deposited, containing well-preserved fish fossils, with alternating layers of mudstone and coarse siltstone to very fine sandstone. These flagstones split easily along the bedding and have been used as building material for thousands of years. The deposits of the Orcadian Basin form part of the Old Red Sandstone (ORS). The lithostratigraphic terms lower, middle and upper ORS, however, do not necessarily match exactly with sediments of lower, middle and upper Devonian age, as the base of the ORS is now known to be in the Silurian and the top in the Carboniferous.
The Kangaamiut dike swarm is a 2.04 billion year old dike swarm located in the Qeqqata region of western Greenland. The dikes cut Archean orthogneisses and are exposed along approximately 150 km (93 mi) of the coast and a similar distance up to the inland ice to the east, covering an area of about 18,000 km2 (6,900 sq mi). To the north it is bounded by the paleoproterozoic Ikertooq shear zone while to the south the boundary is gradational with a gradual reduction in the density of dikes. The dike swarm was intruded during a phase of extensional tectonics. They were later deformed during the Nagssugtoqidian orogeny, with the amount of strain increasing towards the Iqertooq shear zone.

The North Atlantic Igneous Province (NAIP) is a large igneous province in the North Atlantic, centered on Iceland. In the Paleogene, the province formed the Thulean Plateau, a large basaltic lava plain, which extended over at least 1.3 million km2 (500 thousand sq mi) in area and 6.6 million km3 (1.6 million cu mi) in volume. The plateau was broken up during the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean leaving remnants preserved in north Ireland, west Scotland, the Faroe Islands, northwest Iceland, east Greenland, western Norway and many of the islands located in the north eastern portion of the North Atlantic Ocean. The igneous province is the origin of the Giant's Causeway and Fingal's Cave. The province is also known as Brito–Arctic province and the portion of the province in the British Isles is also called the British Tertiary Volcanic Province or British Tertiary Igneous Province.

Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and the Hebridean Terrane in northwest Scotland. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today.
The Greenland plate is a tectonic microplate bounded to the west by Nares Strait, a probable transform fault; on the southwest by the Ungava transform underlying Davis Strait; on the southeast by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; and the northeast by the Gakkel Ridge, with its northwest border still being explored. The Greenland craton is made up of some of the oldest rocks on Earth. The Isua greenstone belt in southwestern Greenland contains the oldest known rocks on Earth dated at 3.7–3.8 billion years old.
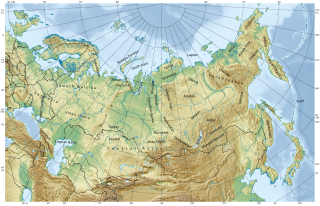
The geology of Russia, the world's largest country, which extends over much of northern Eurasia, consists of several stable cratons and sedimentary platforms bounded by orogenic (mountain) belts.

The geological deformation of Iceland is the way that the rocks of the island of Iceland are changing due to tectonic forces. The geological deformation help to explain the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, fissures, and the shape of the island. Iceland is the largest landmass situated on an oceanic ridge. It is an elevated plateau of the sea floor, situated at the crossing of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Greenland-Iceland-Scotland ridge. It lies along the oceanic divergent plate boundary of North American Plate and Eurasian Plate. The western part of Iceland sits on the North American Plate and the eastern part sits on the Eurasian Plate. The Reykjanes Ridge of the Mid-Atlantic ridge system in this region crosses the island from southwest and connects to the Kolbeinsey Ridge in the northeast.
The North Atlantic Craton (NAC) is an Archaean craton exposed in southern West Greenland, the Nain Province in Labrador, and the Lewisian complex in northwestern Scotland. The NAC is bounded by the Nagssugtoqidian orogen to the north and the 1.8–1.87 Ga Ketilidan–Makkovik mobile belt to the south. The latter can be linked to the Lewisian-Malin boundary in Scotland, which in turn can be linked to the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt in Baltica.
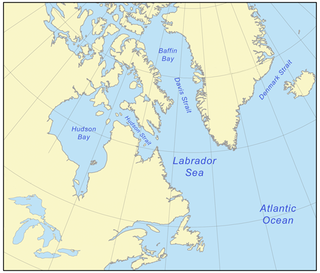
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.
The Ketilidian orogeny was a late Paleoproterozoic mountain-building event that affected southern Greenland during the period 1.85 to 1.72 Ga. The orogenic belt formed during this event, sometimes known as the Ketilidian mobile belt, forms the southern boundary to the mainly Archaean North Atlantic Craton. The belt is 250–350 km wide, much of it covered by ice. It is correlated with the Makkovik Province in Labrador, Canada, which has a similar history.
The Laxfordian orogeny was an orogenic event between 1.9 and 1 billion years ago. It primarily affected the North Atlantic Craton, in particular a section that cleaved off during the Mesozoic as the Scottish Shield Fragment, part of the Lewisian complex within the Hebridean Terrane.
References
- ↑ Mayborn, K.R.; Lesher, C.E. (2006). "Origin and evolution of the Kangâmiut mafic dyke swarm, West Greenland" (PDF). In Garde, A.A.; Kalsbeek, F. (eds.). Precambrian crustal evolution and Cretaceous-Palaeogene faulting in West Greenland. Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin. Vol. 11. pp. 61–86. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-12-02. Retrieved 2019-09-09.
- ↑ Garde, A.A.; Hollis, J.A. (2010). "A buried Palaeoproterozoic spreading ridge in the northern Nagssugtoqidian orogen, West Greenland". In Kusky, T. M; Zhai, M.-G.; Xiao, W. (eds.). The Evolving Continents: Understanding Processes of Continental Growth. Special Publications. Vol. 338. Geological Society, London. p. 213–234. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.980.1494 . doi:10.1144/SP338.11. ISBN 9781862393035.