
Arunachal Pradesh is a state in Northeast India. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region.

Northeast India is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) with several neighbouring countries – 1,395 kilometres (867 mi) with Tibet Autonomous Region, China in the north, 1,640 kilometres (1,020 mi) with Myanmar in the east, 1,596 kilometres (992 mi) with Bangladesh in the south-west, 97 kilometres (60 mi) with Nepal in the west, and 455 kilometres (283 mi) with Bhutan in the north-west. It comprises an area of 262,230 square kilometres (101,250 sq mi), almost 8 percent of that of India.
The leaf muntjac, leaf deer or Putao muntjac is a small species of muntjac. It was documented in 1997 by biologist Alan Rabinowitz during his field study in the isolated Naungmung Township in Myanmar. Rabinowitz discovered the species by examining the small carcass of a deer that he initially believed was the juvenile of another species; however, it proved to be the carcass of an adult female. He managed to obtain specimens, from which DNA analysis revealed a new cervid species. Local hunters knew of the species and called it the leaf deer because its body could be completely wrapped by a single large leaf. It is found in Myanmar and India.

India has some of the world's most biodiverse regions. The political boundaries of India encompass a wide range of biomes–desert, high mountains, highlands, tropical and temperate forests, swamplands, plains, grasslands, areas surrounding rivers, as well as island archipelago. It hosts 4 biodiversity hotspots: the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, the Indo-Burma region and the Sundaland. These hotspots have numerous endemic species.

The Namdapha flying squirrel is an arboreal, nocturnal flying squirrel endemic to Arunachal Pradesh in northeast India, where it is known from a single specimen collected in Namdapha National Park in 1981. No population estimate is available for B. biswasi, but the known habitat is tall Mesua ferrea jungles, often on hill slopes in the catchment area of Dihing River in northeastern India.
Nanorana is a genus of dicroglossid frogs. They are found in Asia, from the Himalayan region of northern Pakistan and northern India, Nepal, and western China east to montane southern China and southeast to Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, and northern Vietnam. Common names of these frogs reflect the complex taxonomic history of the genus and include Yunnan slow frogs and High Himalaya frogs.

The crab-eating mongoose is a mongoose species ranging from the northeastern Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia to southern China and Taiwan. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

Sclater's monal, Lophophorus sclateri, also known as the crestless monal, is a large, approximately 68 centimetres (27 in) long, pheasant of the east Himalayan region. As other monals, the male is a colorful bird. It has a highly iridescent purplish-green upperparts plumage, short and curly metallic green crown feathers, copper neck, purplish-black throat, white back, blue orbital skin, yellowish-orange bill and brown iris. In the nominate subspecies, the tail is white with a broad chestnut band, while the tail is entirely white in L. s. arunachalensis from western Arunachal Pradesh in India. The crestless female is mostly a dark brown bird with a white throat and tail-tip, dull bluish orbital skin and a pale yellow bill.
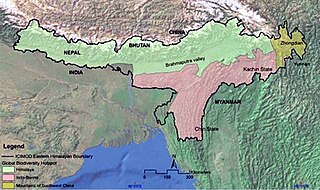
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.
Liurana medogensis, commonly known as Medog papilla-tongued frog or Medog eastern frog, is a species of frog in the family Ceratobatrachidae. It is found in Mêdog County, Tibet (China) and in Arunachal Pradesh, northeastern India. However, the records from India might represent another species, and the IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2020) does not include them in the range of this species.
Nanorana annandalii is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is found in northeastern India and eastern Nepal. Nanorana gammii(Anderson, 1871) was until quite recently (2006) considered a synonym of Nanorana annandalii but is now treated as a separate species; this change confounds older records of Nanorana annandalii. This species lives in rocky streams and brooks in montane forests. It can also be found near pools in forest clearings. It is threatened by habitat loss (deforestation).

Odorrana chloronota, commonly known as the chloronate huia frog or copper-cheeked frog, is a species of frog in the family Ranidae that is found in Cambodia, China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and possibly Bangladesh and Nepal.
Mamang Dai is an Indian poet, novelist and journalist based in Itanagar, Arunachal Pradesh. She received Sahitya Akademi Award in 2017 for her novel The Black Hill.
Biermannia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to eastern India, China and Southeast Asia.
Creteuchiloglanis is a genus of sisorid catfishes native to Asia.
Musa arunachalensis is a new species in the genus Musa. It was described by botanists from the University of Calicut in Kerala.
Trimeresurus arunachalensis, the Arunachal pitviper, is a species of venomous pit viper endemic to the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is only known from the village of Ramda in the West Kameng district, where a single specimen was discovered during biodiversity surveys. It can physically be distinguished by its scalation, its acutely pointed snout reminiscent of the hump-nosed viper, and its brownish dorsal coloration with glossy orange-reddish-brown sides and belly. The last new species of (green) pit viper was described from India 70 years before the discovery of T. arunachalensis. Genetic analysis indicates that the closest relative of this species is the Tibetan bamboo pit viper. The single specimen known of this species makes it one of the rarest known pit vipers in the world, though further surveys of the forest habitat will likely reveal more individuals.
Smithophis is a genus of snakes in the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae; the one species that was known prior to 2019 had been classified under the genus Rhabdops, but was removed in the process of erecting the new genus Smithophis. The genus is endemic to Asia.
Larsenianthus arunachalensis is a species of the genus Larsenianthus in the ginger family (Zingiberaceae).. It was first described in 2010 and is native to northeastern India.








