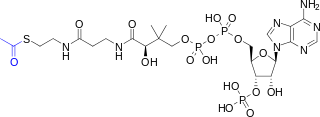
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.

Dehydroalanine is a dehydroamino acid. It does not exist in its free form, but it occurs naturally as a residue found in peptides of microbial origin. As an amino acid residue, it is unusual because it has an unsaturated backbone.

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein.
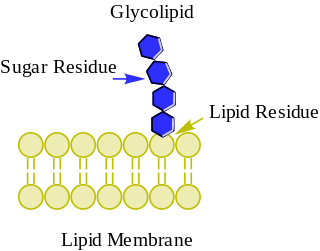
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds. The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body.

Histone deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.98, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on both histone and non-histone proteins. HDACs allow histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. HDAC's action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins. In general, they suppress gene expression.

N-acetyltransferase (NAT) is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of acetyl groups from acetyl-CoA to arylamines, arylhydroxylamines and arylhydrazines. They have wide specificity for aromatic amines, particularly serotonin, and can also catalyze acetyl transfer between arylamines without CoA. N-acetyltransferases are cytosolic enzymes found in the liver and many tissues of most mammalian species, except the dog and fox, which cannot acetylate xenobiotics.
In molecular biology and genetics, transcription coregulators are proteins that interact with transcription factors to either activate or repress the transcription of specific genes. Transcription coregulators that activate gene transcription are referred to as coactivators while those that repress are known as corepressors. The mechanism of action of transcription coregulators is to modify chromatin structure and thereby make the associated DNA more or less accessible to transcription. In humans several dozen to several hundred coregulators are known, depending on the level of confidence with which the characterisation of a protein as a coregulator can be made. One class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second ATP dependent class modifies the conformation of chromatin.

Modified starch, also called starch derivatives, is prepared by physically, enzymatically, or chemically treating native starch to change its properties. Modified starches are used in practically all starch applications, such as in food products as a thickening agent, stabilizer or emulsifier; in pharmaceuticals as a disintegrant; or as binder in coated paper. They are also used in many other applications.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.

Histone acetylation and deacetylation are the processes by which the lysine residues within the N-terminal tail protruding from the histone core of the nucleosome are acetylated and deacetylated as part of gene regulation.

Thiolases, also known as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferases (ACAT), are enzymes which convert two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway.
In enzymology, a 2-ethylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-tubulin N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme which is encoded by the ATAT1 gene.
ATP citrate synthase (also ATP citrate lyase (ACLY)) is an enzyme that in animals catalyzes an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis. By converting citrate to acetyl-CoA, the enzyme links carbohydrate metabolism, which yields citrate as an intermediate, with fatty acid biosynthesis, which consumes acetyl-CoA. In plants, ATP citrate lyase generates cytosolic acetyl-CoA precursors of thousands of specialized metabolites, including waxes, sterols, and polyketides.
In enzymology, a peptide alpha-N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polysialic-acid O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Acylamino-acid-releasing enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the APEH gene.
Protein acetylation are acetylation reactions that occur within living cells as drug metabolism, by enzymes in the liver and other organs. Pharmaceuticals frequently employ acetylation to enable such esters to cross the blood–brain barrier, where they are deacetylated by enzymes (carboxylesterases) in a manner similar to acetylcholine. Examples of acetylated pharmaceuticals are diacetylmorphine (heroin), acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), THC-O-acetate, and diacerein. Conversely, drugs such as isoniazid are acetylated within the liver during drug metabolism. A drug that depends on such metabolic transformations in order to act is termed a prodrug.











