
The 1848 United States presidential election was the 16th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1848. In the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.

The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott. A third party candidate from the Free Soil party, John P. Hale, also ran and came in third place, but got no electoral votes.
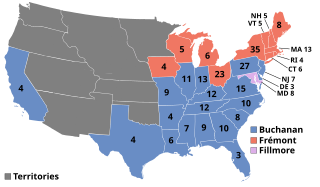
The 1856 United States presidential election was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a threeway election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and Know Nothing/Whig nominee Millard Fillmore. The main issue was the expansion of slavery as facilitated by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. Buchanan defeated President Franklin Pierce at the 1856 Democratic National Convention for the nomination. Pierce had become widely unpopular in the North because of his support for the pro-slavery faction in the ongoing civil war in territorial Kansas, and Buchanan, a former Secretary of State, had avoided the divisive debates over the Kansas–Nebraska Act by being in Europe as the Ambassador to the United Kingdom.
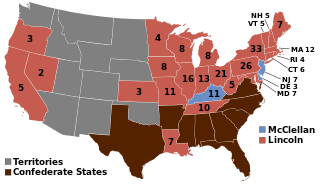
The 1864 United States presidential election was the 20th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. Near the end of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

The 1872 United States presidential election was the 22nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1872. Despite a split in the Republican Party, incumbent President Ulysses S. Grant defeated Democratic-endorsed Liberal Republican nominee Horace Greeley.

The 1932 United States presidential election was the 37th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. The incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the governor of New York and the vice presidential nominee of the 1920 presidential election. Roosevelt was the first Democrat in 80 years to simultaneously win an outright majority of the electoral college and popular vote, a feat last accomplished by Franklin Pierce in 1852, as well as the first Democrat in 56 years to win a majority of the popular vote, which was last achieved by Samuel J. Tilden in 1876. Roosevelt was the last sitting governor to be elected president until Bill Clinton in 1992. Hoover became the first incumbent president to lose an election to another term since William Howard Taft in 1912, the last to do so until Gerald Ford lost 44 years later, and the last elected incumbent president to do so until Jimmy Carter lost 48 years later. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans. It was the first time since 1916 that a Democrat was elected president.

The States' Rights Democratic Party, also colloquially referred to as the Dixiecrat Party was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition to the national Democratic Party. After President Harry S. Truman, the leader of the Democratic Party, ordered integration of the military in 1948 and other actions to address civil rights of African Americans, including the first presidential proposal for comprehensive civil and voting rights, many Southern white politicians who objected to this course organized themselves as a breakaway faction. They wished to protect the ability of states to maintain racial segregation. Its members were referred to as "Dixiecrats", a portmanteau of "Dixie", referring to the Southern United States, and "Democrat".

A United States presidential nominating convention is a political convention held every four years in the United States by most of the political parties who will be fielding nominees in the upcoming U.S. presidential election. The formal purpose of such a convention is to select the party's nominees for popular election as President and Vice President, as well as to adopt a statement of party principles and goals known as the party platform and adopt the rules for the party's activities, including the presidential nominating process for the next election cycle. Presidential nominating conventions are generally held in a different city every four years. With 26, Chicago has hosted the most major party conventions, beginning with Abraham Lincoln's nomination in 1860.

The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the Republican Party in the United States. They are administered by the Republican National Committee. The goal of the Republican National Convention is to officially nominate and confirm a candidate for president and vice president, adopt a comprehensive party platform and unify the party, as well as publicize and launch the fall campaign.

The Democratic Party of Hawaiʻi is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the state of Hawaii.

The 1944 United States Senate elections coincided with the re-election of Franklin D. Roosevelt to his fourth term as president. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1984 Democratic National Convention was held at the Moscone Center in San Francisco, California from July 16 to July 19, 1984, to select candidates for the 1984 United States presidential election. Former Vice President Walter Mondale was nominated for president and Representative Geraldine Ferraro of New York was nominated for vice president. Ferraro became the first woman to be nominated by either major party for the presidency or vice presidency. In another first, the 1984 Democratic Convention was chaired by the female governor of Kentucky, Martha Layne Collins. The Democratic National Committee Chairman at the time, Charles T. Manatt, led the convention.

The Michigan Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the state of Michigan. It is based in Lansing. Lavora Barnes is the party's current chair. She was previously the party's Chief Operating Officer. It is currently the state's dominant party, controlling the majority of Michigan's U.S. House seats, both U.S. Senate seats, both houses of the state legislature, and the governorship.
The Utah Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Utah. The party describes itself as a big tent party.

The National Union Party, commonly the Union Party or Unionists, was a wartime coalition of Republicans, War Democrats, and border state Unconditional Unionists that supported the Lincoln Administration during the American Civil War. It held the 1864 National Union Convention that nominated Abraham Lincoln for president and Andrew Johnson for vice president in the 1864 United States presidential election. Following Lincoln's successful re-election and assassination, Johnson tried and failed to sustain the Union Party as a vehicle for his presidential ambitions. The coalition did not contest the 1868 elections, but the Republican Party continued to use the "Union Republican" label throughout the period of Reconstruction.
The Texas Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Texas and one of the two major political parties in the state. The party's headquarters are in Austin, Texas.

The 2008 Washington Democratic presidential caucuses were a series of events held by the Washington State Democratic Party to determine the delegates that the Party sent to the 2008 Democratic National Convention. Delegates were selected in a four-tier process that began with precinct caucuses, was further refined in legislative district caucuses and/or county conventions, concluded for some delegates in the congressional district caucuses, and finally concluded for the remaining delegates at the state convention.

The Democratic Party of Puerto Rico is the local affiliate of the U.S. National Democratic Party in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. Party membership consists of supporters of both the current Commonwealth status and those who favor statehood for Puerto Rico.

The 2008 United States presidential election in Washington took place on November 4, 2008, and was part of the 2008 United States presidential election. Voters chose 11 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1855 New York state election was held on November 6, 1855, to elect the Secretary of State, the State Comptroller, the Attorney General, the State Treasurer, the State Engineer, two judges of the New York Court of Appeals, a Canal Commissioner and an Inspector of State Prisons, as well as members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.


















