
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida.

Project Stormfury was an attempt to weaken tropical cyclones by flying aircraft into them and seeding with silver iodide. The project was run by the United States Government from 1962 to 1983. The hypothesis was that the silver iodide would cause supercooled water in the storm to freeze, disrupting the inner structure of the hurricane, and this led to seeding several Atlantic hurricanes. However, it was later shown that this hypothesis was incorrect. It was determined that most hurricanes do not contain enough supercooled water for cloud seeding to be effective. Additionally, researchers found that unseeded hurricanes often undergo the same structural changes that were expected from seeded hurricanes. This finding called Stormfury's successes into question, as the changes reported now had a natural explanation.

The Lockheed WC-130 is a high-wing, medium-range aircraft used for weather reconnaissance missions by the United States Air Force. The aircraft is a modified version of the C-130 Hercules transport configured with specialized weather instrumentation including a dropsonde deployment/receiver system and crewed by a meteorologist for penetration of tropical cyclones and winter storms to obtain data on movement, size and intensity.

Hurricane hunters, typhoon hunters, or cyclone hunters are aircrews that fly into tropical cyclones to gather weather data. In the United States, the organizations that fly these missions are the United States Air Force Reserve's 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Hurricane Hunters. Such missions have also been flown by Navy units and other Air Force and NOAA units. Other organizations also fly these missions, such as Government Flying Service Hong Kong.

The 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron, also known by its nickname, Hurricane Hunters, is a flying unit of the United States Air Force, and "the only Department of Defense organization still flying into tropical storms and hurricanes." Aligned under the 403rd Wing of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC) and based at Keesler Air Force Base, Mississippi, with ten aircraft, it flies into tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and the Central Pacific Ocean for the specific purpose of directly measuring weather data in and around those storms. The 53rd WRS currently operates the Lockheed WC-130J aircraft as its weather data collection platform.

The Joint typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean for all branches of the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies. Their warnings are intended for the protection of primarily military ships and aircraft as well as military installations jointly operated with other countries around the world.

The 1947 Fort Lauderdale hurricane was a long-lived and an intense tropical cyclone that affected the Bahamas, southernmost Florida, and the Gulf Coast of the United States in September 1947. The fourth Atlantic tropical cyclone of the year, it formed in the eastern Atlantic Ocean on September 4, becoming a hurricane, the third of the 1947 Atlantic hurricane season, less than a day later. After moving south by west for the next four days, it turned to the northwest and rapidly attained strength beginning on September 9. It reached a peak intensity of 145 mph (233 km/h) on September 15 while approaching the Bahamas. In spite of contemporaneous forecasts that predicted a strike farther north, the storm then turned to the west and poised to strike South Florida, crossing first the northern Bahamas at peak intensity. In the Bahamas, the storm produced a large storm surge and heavy damage, but with no reported fatalities.

Hurricane Carrie was the strongest tropical cyclone of the 1957 Atlantic hurricane season. The third named storm and second hurricane of the year, Carrie formed from an easterly tropical wave off the western coast of Africa on September 2, a type of tropical cyclogenesis typical of Cape Verde-type hurricanes. Moving to the west, the storm gradually intensified, reaching hurricane strength on September 5. Carrie intensified further, before reaching peak intensity on September 8 as a Category 4 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) in the open Atlantic Ocean. The hurricane curved northwards and fluctuated in intensity as it neared Bermuda on September 14. However, Carrie passed well north of the island and turned to the northeast towards Europe. Weakening as it reached higher latitudes, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on September 23, prior to affecting areas of the British Isles, and subsequently dissipated on September 28.

A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorological data to forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputers with sophisticated mathematical modeling software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions. Statistical models forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computers. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track, intensity, storm surge, and rainfall. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem.

James Louis Franklin is a former weather forecaster encompassing a 35-year career with National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). He served as the first branch chief of the newly formed Hurricane Specialist Unit (HSU) before his retirement in 2017.

Robert Homer Simpson was an American meteorologist, hurricane specialist, first director of the National Hurricane Research Project (NHRP) from 1955 to 1959, and a former director (1967–1974) of the National Hurricane Center (NHC). He was the co-developer of the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale with Herbert Saffir. His wife was Joanne Simpson.

Tropical cyclone forecasting is the science of forecasting where a tropical cyclone's center, and its effects, are expected to be at some point in the future. There are several elements to tropical cyclone forecasting: track forecasting, intensity forecasting, rainfall forecasting, storm surge, tornado, and seasonal forecasting. While skill is increasing in regard to track forecasting, intensity forecasting skill remains unchanged over the past several years. Seasonal forecasting began in the 1980s in the Atlantic basin and has spread into other basins in the years since.
The National Hurricane Research Laboratory (NHRL) is the hurricane research arm of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It was formed in December 1964 out of the National Hurricane Research Project, the U. S. Weather Bureau's effort to scientifically examine tropical cyclones in order to make better predictions. Laboratory status signified that this effort was now a permanent part of the Weather Bureau's activities.
The Hurricane Research Division (HRD) is a section of the Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) in Miami, Florida, and is the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) focus for tropical cyclone research. The thirty member division is not a part of the National Hurricane Center but cooperates closely with them in carrying out its annual field program and in transitioning research results into operational tools for hurricane forecasters. HRD was formed from the National Hurricane Research Laboratory in 1984, when it was transferred to AOML and unified with the oceanographic laboratories.

The NOAA Hurricane Hunters are a group of aircraft used for hurricane reconnaissance by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). They fly through hurricanes to help forecasters and scientists gather operational and research data. The crews also conduct other research projects including ocean wind studies, winter storm research, thunderstorm research, coastal erosion, and air chemistry flights.

Hurricane Greta was an extremely large late-season Atlantic hurricane in the 1956 Atlantic hurricane season. Originating from a tropical depression near Jamaica on October 30, the system initially featured non-tropical characteristics as it tracked northward. By November 2, the system began producing gale-force winds around the low-pressure area; however, winds near the center of circulation were calm. By November 3, the system intensified into a tropical storm and was named Greta. Steadily strengthening, Greta attained hurricane intensity on November 4, eventually reaching a peak intensity with 100 mph (160 km/h) winds. Shortly after, Greta began to gradually weaken as it tracked over cooler waters. The storm eventually became extratropical on November 7 over the central Atlantic. Although Greta did not directly impact land as a tropical storm or hurricane, it generated large swells that impacted numerous areas. One person was killed in Puerto Rico and coastal damages from the waves amounted to roughly $3.6 million.

Hurricane Debbie was an intense and long-lived hurricane that formed during August 1969. The fifth tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, third hurricane and second major hurricane of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season, Debbie formed on August 14 in the southern Atlantic Ocean and took a general northwesterly path until turning northward into the central Atlantic. The storm was characterized by numerous fluctuations in intensity, but it still reached winds corresponding to Category 3 status on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The hurricane bypassed the island of Bermuda to the southeast on August 22, before ultimately brushing southeastern Newfoundland with strong winds. It dissipated over the cold waters east of Greenland. Although Debbie had little effect on land, it was extensively researched and was subject to a weather modification experiment by Project Stormfury, in which it was seeded with silver iodide.

The history of Atlantic tropical cyclone warnings details the progress of tropical cyclone warnings in the North Atlantic Ocean. The first service was set up in the 1870s from Cuba with the work of Father Benito Viñes. After his death, hurricane warning services were assumed by the US Army Signal Corps and United States Weather Bureau over the next few decades, first based in Jamaica and Cuba before shifting to Washington, D.C. The central office in Washington, which would evolve into the National Meteorological Center and the Weather Prediction Center, assumed the responsibilities by the early 20th century. This responsibility passed to regional hurricane offices in 1935, and the concept of the Atlantic hurricane season was established to keep a vigilant lookout for tropical cyclones during certain times of the year. Hurricane advisories issued every 12 hours by the regional hurricane offices began at this time.

The Automated Tropical Cyclone Forecasting System (ATCF) is a piece of software originally developed to run on a personal computer for the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) in 1988, and the National Hurricane Center (NHC) in 1990. ATCF remains the main piece of forecasting software used for the United States Government, including the JTWC, NHC, and Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Other tropical cyclone centers in Australia and Canada developed similar software in the 1990s. The data files with ATCF lie within three decks, known as the a-, b-, and f-decks. The a-decks include forecast information, the b-decks contain a history of center fixes at synoptic hours, and the f-decks include the various fixes made by various analysis center at various times. In the years since its introduction, it has been adapted to Unix and Linux platforms.
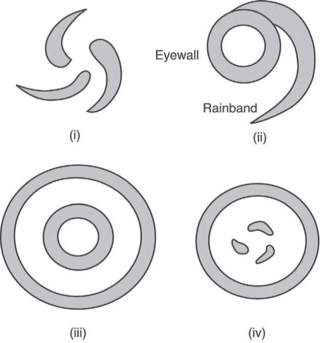
The Hurricane Rainband and Intensity Change Experiment (RAINEX) is a project to improve hurricane intensity forecasting via measuring interactions between rainbands and the eyewalls of tropical cyclones. The experiment was planned for the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. This coincidence of RAINEX with the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season led to the study and exploration of infamous hurricanes Katrina, Ophelia, and Rita. Where Hurricane Katrina and Hurricane Rita would go on to cause major damage to the US Gulf coast, Hurricane Ophelia provided an interesting contrast to these powerful cyclones as it never developed greater than a category 1.

















