A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies.

The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy and is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way, where the Solar System resides. It was originally named the Andromeda Nebula and is cataloged as Messier 31, M31, and NGC 224. Andromeda has a diameter of about 46.56 kiloparsecs and is approximately 765 kpc from Earth. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology.

Hoag's Object is an unusual ring galaxy in the constellation of Serpens Caput. It is named after Arthur Hoag, who discovered it in 1950 and identified it as either a planetary nebula or a peculiar galaxy. The galaxy has approximately eight billion stars, and is roughly 120,000 light years across.

The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy 2.73 million light-years (ly) from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC (New General Catalogue) 598. With the D25 isophotal diameter of 18.74 kiloparsecs (61,100 light-years), the Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, behind the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way.

Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge. These are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars, many of which reside in globular clusters.

The Galactic Center is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately 8 kiloparsecs (26,000 ly) away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula.

The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy (Sgr dSph), also known as the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters in its main body, with the brightest of them—NGC 6715 (M54)—being known well before the discovery of the galaxy itself in 1994. Sgr dSph is roughly 10,000 light-years in diameter, and is currently about 70,000 light-years from Earth, travelling in a polar orbit at a distance of about 50,000 light-years from the core of the Milky Way. In its looping, spiraling path, it has passed through the plane of the Milky Way several times in the past. In 2018 the Gaia project of the European Space Agency showed that Sgr dSph had caused perturbations in a set of stars near the Milky Way's core, causing unexpected rippling movements of the stars triggered when it moved past the Milky Way between 300 and 900 million years ago.

Dwingeloo 1 is a barred spiral galaxy about 10 million light-years away from the Earth, in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies in the Zone of Avoidance and is heavily obscured by the Milky Way. The size and mass of Dwingeloo 1 are comparable to those of Triangulum Galaxy.

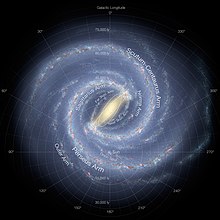
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is 3,500 light-years across and approximately 10,000 light-years in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion Bridge, and formerly, the Local Spur and Orion Spur.

The Norma Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way extending from and around its central hub region. The inner portion of the Arm is called the Norma Arm in narrow meaning. The outer end of it is identified either with the Cygnus Arm, which lies outside the Perseus Arm, or the Outer Arm, which is located farther away from the center of the Galaxy than the Cygnus Arm. The Norma Arm begins 2.2 kpc from the Galactic Center, and extends outward to a radius of 15.5±2.8 kpc. It is named for the Norma constellation, through which the Arm as seen from Earth passes.

The 1.2 meter Millimeter-Wave Telescope at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and its twin instrument at CTIO in Chile have been studying the distribution and properties of molecular clouds in our galaxy and its nearest neighbours since the 1970s. The telescope is nicknamed "The Mini" because of its unusually small size. At the time it was built, it was the smallest radio telescope in the world. Together, "The Mini" and its twin in Chile have obtained what is by far the most extensive, uniform, and widely used galactic survey of interstellar carbon monoxide. "The Mini" is currently in operation from October to May each year.

The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικὸς κύκλος, meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Doust Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies.

The Cartwheel Galaxy (also known as ESO 350-40 or PGC 2248) is a lenticular ring galaxy about 500 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. It has a D25 isophotal diameter of 44.23 kiloparsecs (144,300 light-years), and a mass of about 2.9–4.8 × 109 solar masses; its outer ring has a circular velocity of 217 km/s.

Sagittarius A is a complex radio source at the center of the Milky Way, which contains a supermassive black hole. It is located in the constellation Sagittarius, and is hidden from view at optical wavelengths by large clouds of cosmic dust in the spiral arms of the Milky Way. The dust lane that obscures the Galactic Center from a vantage point around the Sun causes the Great Rift through the bright bulge of the galaxy.

Leo IV is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy situated in the Leo constellation, discovered in 2006 in the data obtained by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The galaxy is located at the distance of about 160 kpc from the Sun and moves away from the Sun with the velocity of about 130 km/s. It is classified as a dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) meaning that it has an approximately round shape with the half-light radius of about 130 pc.

The thick disk is one of the structural components of about 2/3 of all disk galaxies, including the Milky Way. It was discovered first in external edge-on galaxies. Soon after, it was proposed as a distinct galactic structure in the Milky Way, different from the thin disk and the halo in the 1983 article by Gilmore & Reid. It is supposed to dominate the stellar number density between 1 and 5 kiloparsecs above the galactic plane and, in the solar neighborhood, is composed almost exclusively of older stars. Its stellar chemistry and stellar kinematics are also said to set it apart from the thin disk. Compared to the thin disk, thick disk stars typically have significantly lower levels of metals—that is, the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium.

The Far 3 kpc Arm was discovered in 2008 by astronomer Tom Dame, while preparing a talk on the galaxy's spiral arms for a meeting of the 212th American Astronomical Society. It is one of Milky Way's spiral arms and it is located in the first galactic quadrant at a distance of 3 kiloparsecs from the Galactic Center. Along with the Near 3 kpc Arm, the existence of which has been known since the mid-1950s, the counterpart inner arms establish our Galaxy's simple symmetry.
High-velocity clouds (HVCs) are large collections of gas found throughout the galactic halo of the Milky Way. Their bulk motions in the local standard of rest have velocities which are measured in excess of 70–90 km s−1. These clouds of gas can be massive in size, some on the order of millions of times the mass of the Sun, and cover large portions of the sky. They have been observed in the Milky Way's halo and within other nearby galaxies.

In astrobiology and planetary astrophysics, the galactic habitable zone is the region of a galaxy in which life might most likely develop. The concept of a galactic habitable zone analyzes various factors, such as metallicity and the rate and density of major catastrophes such as supernovae, and uses these to calculate which regions of a galaxy are more likely to form terrestrial planets, initially develop simple life, and provide a suitable environment for this life to evolve and advance. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may favor the birth and development of habitable planets more than smaller galaxies such as the Milky Way. In the case of the Milky Way, its galactic habitable zone is commonly believed to be an annulus with an outer radius of about 10 kiloparsecs (33,000 ly) and an inner radius close to the Galactic Center.
Thomas M. Dame is Director of the Radio Telescope Data Center at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, a Senior Radio Astronomer at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and a Lecturer on Astronomy at Harvard University. He is best known for mapping the Milky Way galaxy in Carbon Monoxide and for the discovery of both the Far 3 kpc Arm and the Outer Scutum–Centaurus Arm of the Milky Way.