Map with clickable regions
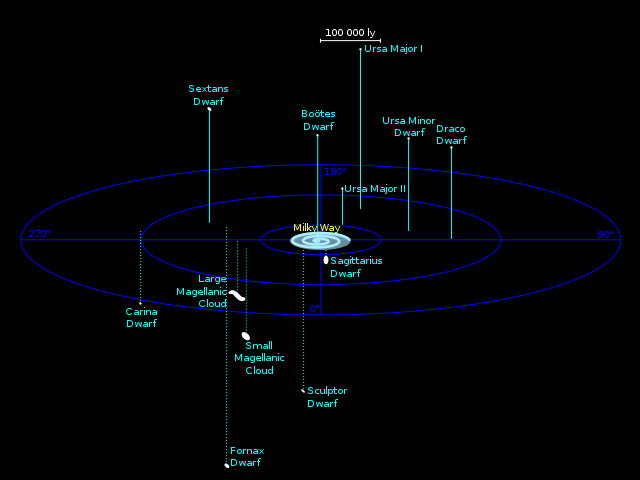
The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group. [1]
There are 61 small galaxies confirmed to be within 420 kiloparsecs (1.4 million light-years ) of the Milky Way, [2] but not all of them are necessarily in orbit, and some may themselves be in orbit of other satellite galaxies. The only ones visible to the naked eye are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, which have been observed since prehistory. Measurements with the Hubble Space Telescope in 2006 suggest the Magellanic Clouds may be moving too fast to be orbiting the Milky Way. [3] Of the galaxies confirmed to be in orbit, the largest is the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, which has a diameter of 2.6 kiloparsecs (8,500 ly) [4] or roughly a twentieth that of the Milky Way.
Satellite galaxies that orbit from 1,000 ly (310 pc ) of the edge of the disc of the Milky Way Galaxy to the edge of the dark matter halo of the Milky Way at 980,000 ly (300 kpc) from the center of the galaxy, [a] are generally depleted in hydrogen gas compared to those that orbit more distantly. This is because of their interactions with the dense hot gas halo of the Milky Way that strip cold gas from the satellites. Satellites beyond that region still retain copious quantities of gas. [5] [6]
The Milky Way's satellite galaxies include the following: [7] [2]
| Name | Diameter (kpc) | Distance (kpc) | Absolute visual magnitude | Type | Discovered |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Magellanic Cloud | 4 | 48.5 | −18.1 | SBm | prehistoric |
| Antlia 2 | 2.9 | 130 | −8.5 | Irr? | 2018 |
| Sagittarius Dwarf | 2.6 | 20 | −13.5 | E | 1994 |
| Crater II | 2.2 | 117.5 | −8.2 | dSph | 2016 [8] |
| Small Magellanic Cloud | 2 | 61 | −16.8 | Irr | prehistoric |
| Canes Venatici I | 1.1 | 220 | −8.6 | dSph | 2006 |
| Canis Major Dwarf | 1.5 | 8 | −14.4 | Irr | 2003 |
| Boötes III | 1.0 | 46 | −5.75 | dSph? | 2009 |
| Sculptor Dwarf | 0.8 | 90 | −11.1 | dE3 | 1937 |
| Draco Dwarf | 0.7 | 80 | −8.8 | dE0 | 1954 |
| Hercules | 0.7 | 135 | −6.6 | dSph | 2006 |
| Leo II | 0.7 | 210 | −9.8 | dE0 | 1950 |
| Fornax Dwarf | 0.6 | 140 | −13.4 | dE2 | 1938 |
| Eridanus II [9] | 0.55 | 366 | −7.1 | dSph | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Sextans Dwarf Spheroidal | 0.5 | 90 | −9.3 | dE3 | 1990 |
| Carina Dwarf Spheroidal | 0.5 | 100 | −9.1 | dE3 | 1977 |
| Leo I | 0.5 | 250 | −12.0 | dE3 | 1950 |
| Ursa Minor Dwarf | 0.4 | 60 | −8.8 | dE4 | 1954 |
| Leo T | 0.34 | 420 | −8.0 | dSph/dIrr | 2006 |
| Aquarius II | 0.32 | 108 | −4.2 | dSph | 2016 [12] |
| Boötes I | 0.30 | 60 | −6.3 | dSph | 2006 |
| Canes Venatici II | 0.30 | 155 | −4.9 | dSph | 2006 |
| Leo IV | 0.30 | 160 | −5.8 | dSph | 2006 |
| Tucana IV | 0.25 | 48 | −3.5 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Columba I | 0.21 | 182 | −4.5 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Ursa Major II Dwarf | 0.20 | 30 | −4.25 | dG D | 2006 |
| Grus II | 0.19 | 53 | −3.9 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Cetus III | 0.18 | 251 | −2.4 | dSph? | 2017 [14] |
| Coma Berenices | 0.14 | 42 | −4.1 | dG D | 2006 |
| Hydra II | 0.14 | 128 | −4.8 | dSph | 2015 [15] |
| Reticulum III | 0.13 | 92 | −3.3 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Pisces II | 0.12 | 180 | −5.0 | Sph | 2010 |
| Pegasus III | 0.11 | 215 | −3.4 | dSph | 2015 [16] [17] |
| Hydrus I | 0.10 | 28 | −4.7 | dSph | 2018 [18] |
| Boötes II | 0.10 | 42 | −2.7 | dSph | 2007 |
| Tucana III | 0.09 | 25 | −2.4 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Virgo I | 0.09 | 91 | −0.3 | dSph | 2016 [14] |
| Horologium II | 0.09 | 78 | −2.6 | dSph | 2015 [19] |
| Sagittarius II | 0.08 | 67 | −5.2 | dSph | 2015 [20] |
| Leo V | 0.08 | 180 | −5.2 | dSph | 2007 |
| Triangulum II | 0.07 | 30 | −1.8 | dSph | 2015 |
| Segue 2 | 0.07 | 35 | −2.5 | dSph | 2007 |
| Segue 1 | 0.06 | 23 | −1.5 | dSph | 2007 |
| Draco II | 0.04 | 20 | −2.9 | dSph | 2015 [20] |
| Tucana V | 0.03 | 55 | −1.6 | dSph | 2015 [13] |
| Cetus II | 0.03 | 30 | 0.0 | dSph? | 2015 [13] |
| Reticulum II | 0.064 | 30 | −3.6 | dSph | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Tucana II | 0.33 | 70 | −3.9 | dSph | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Pisces Overdensity | 1.5 | 80 | −13 | dSph? | 2009 |
| DES 1 | 0.02 | 82 | −3.05 | dSph? | 2016 [21] |
| Eridanus III | 0.028 | 90 | −2.4 | dSph? [b] | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Horologium I | 0.06 | 100 | −3.5 | dSph? [b] | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Kim 2/Indus I | 0.074 | 100 | −3.5 | GC/dSph | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Phoenix II | 0.0521 | 100 | −3.7 | dSph? [b] | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Ursa Major I Dwarf | 0.64 | 100 | −5.5 | dG Sph | 2005 |
| Pictoris I | 0.058 | 115 | −3.7 | dSph? [b] | 2015 [10] [11] |
| Grus I | 0.12 | 120 | −3.4 | dSph | 2015 [10] |
| Pegasus IV | 0.082 | 90 | −4.25 | dSph | 2022 [22] |
| Carina II | 0.182 | 36 | −4.5 | dSph | 2018 [23] |
| Carina III | 0.06 | 28 | −2.4 | GC? | 2018 [23] |
| Boötes IV | 0.28 | 209 | −4.53 | dSph | 2019 [24] |
| Centaurus I | 0.076 | 116 | −5.55 | dSph | 2020 [25] |
| Pictor II | 0.046 | 46 | −3.2 | dSph | 2016 [26] |
| Boötes V | 0.0194 | 102 | −3.2 | dSph? | 2022 [27] |
| Leo Minor I | 0.0896594412 | 82 | −2.4 | dSph | 2022 [27] |
| Virgo II | 0.07 | 72 | −1.6 | dSph | 2022 [27] |
| Willman 1 | 0.02 | 38 | −2.53 | dSph | 2018 [28] |
| Ursa Major III | 0.003 | 10 | +2.2 | dSph | 2023 |
| Leo K | 0.0087 | 434 | −4.86 | dSph | 2024 [29] |
| Leo M | 0.009 | 459 | −5.77 | dSph | 2024 [29] |
| Sextans II | 0.024? | – | – | dSph | 2024 [30] |
| Virgo III | 0.015 | 154 [31] | – | dSph | 2024 [30] |
| Pegasus W | 0.01 | 227 | +1 | dSph | 2020 |
| Eridanus IV | 0.034 | 59.7 | +0.2 | dSph? | 2021 |
| Laevens 1 (Crater 1) | 0.09 | 26.8 | +0.8 | dG D | 2014 |
| Leo VI | 0.28 | 111 | −3.56 | dSph | 2024 [32] |
| Aquarius III | 0.102 | 85 | −2.5 | dSph | 2024 [33] |

The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy is currently in the process of being consumed by the Milky Way and is expected to pass through it within the next 100 million years. The Sagittarius Stream is a stream of stars in polar orbit around the Milky Way leeched from the Sagittarius Dwarf. The Virgo Stellar Stream is a stream of stars that is believed to have once been an orbiting dwarf galaxy that has been completely distended by the Milky Way's gravity.