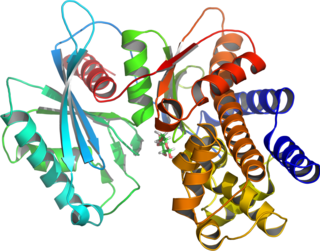
Glucokinase is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia.

Zinc finger protein GLI2 also known as GLI family zinc finger 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor.

Growth differentiation factor 10 (GDF10) also known as bone morphogenetic protein 3B (BMP-3B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDF10 gene.

Transcription factor 7-like 2 , also known as TCF7L2 or TCF4, is a protein acting as a transcription factor that, in humans, is encoded by the TCF7L2 gene. The TCF7L2 gene is located on chromosome 10q25.2–q25.3, contains 19 exons. As a member of the TCF family, TCF7L2 can form a bipartite transcription factor and influence several biological pathways, including the Wnt signalling pathway.

Homeobox protein Hox-A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXA5 gene.

ID4 is a protein coding gene. In humans, it encodes for the protein known as DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-4. This protein is known to be involved in the regulation of many cellular processes during both prenatal development and tumorigenesis. This is inclusive of embryonic cellular growth, senescence, cellular differentiation, apoptosis, and as an oncogene in angiogenesis.

Transcription factor HES-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HES5 gene.

Homeobox protein Nkx-2.2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKX2-2 gene.

Copine-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPNE1 gene.

Homeobox protein GBX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GBX2 gene.

Transcription factor AP-2 beta also known as AP2-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2B gene.

SOX1 is a gene that encodes a transcription factor with a HMG-box DNA-binding domain and functions primarily in neurogenesis. SOX1, SOX2 and SOX3, members of the SOX gene family, contain transcription factors related to SRY, the testis-determining factor.

Neurogenin-3 (NGN3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the Neurog3 gene.

Homeobox protein Nkx-6.1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKX6-1 gene.

Homeobox protein Nkx-6.2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKX6-2 gene.

Homeobox protein DBX2, also known as developing brain homeobox protein 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DBX2 gene. DBX2 plays an important role in the development of the central nervous system, specifically in the development of the neural tube and brain. DBX2 is located on chromosome 12 and is approximately 36,000 base pairs long. DBX2 is predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription activity as well as being involved in the regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II.

Forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2), also known as hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-beta (HNF-3B), is a transcription factor that plays an important role during development, in mature tissues and, when dysregulated or mutated, also in cancer.

Regulatory factor X, 6 also known as DNA-binding protein RFX6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFX6 gene.

Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase A is a type II membrane protein and an enzyme – particularly a glycosyltransferase – that, in addition to the related isoenzyme B (MGAT4B), takes part in the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to the core mannose residues of N-linked glycans in Golgi apparatus. Therefore, it is essential for the formation of tri- and tetra-antennary sugar chains. Furthermore, it is involved in glucose transport by mediating SLC2A2/GLUT2 glycosylation with controlling cell-surface expression of SLC2A2 in pancreatic beta cells and, as it is suggested, in regulating the availability of serum glycoproteins, oncogenesis, and differentiation.

FAM71E1, also known as Family With Sequence Similarity 71 Member E1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM71E1 gene. It is thought to be ubiquitously expressed at low levels throughout the body, and it is conserved in vertebrates, particularly mammals and some reptiles. The protein is localized to the nucleus and can be exported to the cytoplasm.















