
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse generator, or stimulator, is connected to a magnetic coil connected to the scalp. The stimulator generates a changing electric current within the coil which creates a varying magnetic field, inducing a current within a region in the brain itself.

Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression is not sufficient to justify it.
Neurotechnology encompasses any method or electronic device which interfaces with the nervous system to monitor or modulate neural activity.
Neurohacking is a subclass of biohacking, focused specifically on the brain. Neurohackers seek to better themselves or others by “hacking the brain” to improve reflexes, learn faster, or treat psychological disorders. The modern neurohacking movement has been around since the 1980s. However, herbal supplements have been used to increase brain function for hundreds of years. After a brief period marked by a lack of research in the area, neurohacking started regaining interest in the early 2000s. Currently, most neurohacking is performed via do-it-yourself (DIY) methods by in-home users.

Brodmann area 25 (BA25) is the subgenual area, area subgenualis or subgenual cingulate area in the cerebral cortex of the brain and delineated based on its cytoarchitectonic characteristics.
Bioelectromagnetics, also known as bioelectromagnetism, is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological entities. Areas of study include electromagnetic fields produced by living cells, tissues or organisms, the effects of man-made sources of electromagnetic fields like mobile phones, and the application of electromagnetic radiation toward therapies for the treatment of various conditions.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is major depressive disorder in which an affected person does not respond adequately to at least two different antidepressant medications at an adequate dose and for an adequate duration. Inadequate response has most commonly been defined as less than 25% reduction in depressive symptoms following treatment with an antidepressant. Many clinicians and researchers question the construct validity and clinical utility of treatment-resistant depression as currently conceptualized.

Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. It was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation.
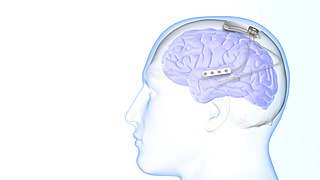
Responsive neurostimulation device is a medical device that senses changes in a person's body and uses neurostimulation to respond in the treatment of disease. The FDA has approved devices for use in the United States in the treatment of epileptic seizures and chronic pain conditions. Devices are being studied for use in the treatment of essential tremor, Parkinson's disease, Tourette's syndrome, depression, obesity, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Management of depression is the treatment of depression that may involve a number of different therapies: medications, behavior therapy, psychotherapy, and medical devices.

Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy, also known as low field magnetic stimulation (LFMS) is the use of electromagnetic fields in an attempt to heal non-union fractures and depression. By 2007 the FDA had cleared several such stimulation devices.
Magnetic seizure therapy (MST) is a proposed form of electrotherapy and electrical brain stimulation. It is currently being investigated for the treatment of major depressive disorder, treatment-resistant depression (TRD), bipolar depression, schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder. MST is stated to work by inducing seizures via magnetic fields, in contrast to ECT which does so using alternating electric currents. Additionally, MST works in a more concentrated fashion than ECT, thus able to create a seizure with less of a total electric charge. In contrast to (r)TMS, the stimulation rates are higher resulting in more energy transfer. Currently it is thought that MST works in patients with major depressive disorder by activating the connection between the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex and the parietal cortex.

Mark S. George is a Distinguished University Professor of psychiatry, radiology and neurosciences and is the director of the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Center for Advanced Imaging Research as well as the Brain Stimulation Laboratory. As of June 2020, his research has been cited over 47,000 times, with an h-index of 113 and i-10 index of 404.
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive or non-invasive means. Neurostimulation usually refers to the electromagnetic approaches to neuromodulation.

BrainsWay Ltd. is an international company that is engaged in the development of a medical device that uses H-coil for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation as a non-invasive treatment for depression, OCD, and smoking addiction. The company was founded in 2003 and has offices in the US and Jerusalem.
Neuromodulation is "the alteration of nerve activity through targeted delivery of a stimulus, such as electrical stimulation or chemical agents, to specific neurological sites in the body". It is carried out to normalize – or modulate – nervous tissue function. Neuromodulation is an evolving therapy that can involve a range of electromagnetic stimuli such as a magnetic field (rTMS), an electric current, or a drug instilled directly in the subdural space. Emerging applications involve targeted introduction of genes or gene regulators and light (optogenetics), and by 2014, these had been at minimum demonstrated in mammalian models, or first-in-human data had been acquired. The most clinical experience has been with electrical stimulation.

Reid Robison is an American board-certified psychiatrist known primarily for his work with psychedelic medicines. As an early adopter and researcher of the use of ketamine in psychiatry, Robison has made significant contributions to ketamine-assisted psychotherapy (KAP) and other treatment modalities using ketamine for mental health conditions. He previously served as coordinating investigator for a study on MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for eating disorders, sponsored by the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), and he continues to lead research and psychiatric clinical trials involving psychedelics. To date, Robison has guided thousands of ketamine-assisted therapy sessions and Spravato dosing sessions. He currently serves as Medical Director of Center for Change, an eating disorder treatment center in Utah, and Chief Clinical Officer of Numinus, a Vancouver-based mental health company focused on psychedelic research and treatments. Robison is an adjunct professor at both the University of Utah and Brigham Young University.

Abraham Zangen is an Israeli professor of neuroscience, head of the brain stimulation and behavior lab and chair of the psychobiology brain program at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU).
Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation is the application of non-invasive neurostimulation techniques on the cerebellum to modify its electrical activity. Techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can be used. The cerebellum is a high potential target for neuromodulation of neurological and psychiatric disorders due to the high density of neurons in its superficial layer, its electrical properties, and its participation in numerous closed-loop circuits involved in motor, cognitive, and emotional functions.
Todd M. Hutton is an American psychiatrist specializing in transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). He is Associate Clinical Professor of Psychiatry at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California. Hutton is also currently President of the Clinical TMS Society, as well as the founder and medical director of the Southern California TMS Center.










