Related Research Articles

A people mover or automated people mover (APM) is a type of small scale automated guideway transit system. The term is generally used only to describe systems serving relatively small areas such as airports, downtown districts or theme parks.

Transrapid is a German-developed high-speed monorail train using magnetic levitation. Planning for the system started in the late 1960s, with a test facility in Emsland, Germany inaugurated in 1983. In 1991, technical readiness for application was approved by the Deutsche Bundesbahn in cooperation with renowned universities.
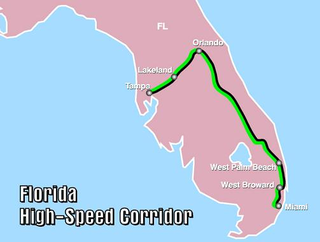
The Florida High-Speed Corridor is a canceled high-speed rail project in the U.S. state of Florida. Initial service would have run between the cities of Tampa and Orlando, with plans to then extend service to South Florida, terminating in Miami. Trains with a top speed of 168 mph (270 km/h) to 186 mph (300 km/h) would run on dedicated rail lines alongside the state's existing highway network.

California High-Speed Rail (CAHSR) is a publicly funded high-speed rail system being developed in California by the California High-Speed Rail Authority. Phase 1, about 494 miles (795 km) long, is planned to run from San Francisco to Los Angeles and Anaheim via the Central Valley, and is partially funded and under construction. A proposed Phase 2 would extend the system north to Sacramento and south to San Diego, for a total of 776 miles (1,249 km). The project was authorized by a 2008 statewide ballot to connect the state's major urban areas and reduce intercity travel times. Phase 1 targets a nonstop travel time of 2 hours and 40 minutes from San Francisco to Los Angeles, compared to about nine hours on the existing Amtrak San Joaquins.

The Las Vegas Monorail is a 3.9-mile (6.3 km) automated monorail mass transit system located adjacent to the Las Vegas Strip in Clark County, Nevada, United States. It connects several large casinos in the unincorporated communities of Paradise and Winchester, but does not enter the city of Las Vegas proper. Built at a cost of $650 million, it was privately owned and operated by the Las Vegas Monorail Company until their 2020 bankruptcy when it was sold to the Las Vegas Convention and Visitors Authority, a local government agency. In 2022, total annual ridership was roughly 4.3 million, down from a pre-Great Recession peak of 7.9 million in 2007. The monorail is a registered not-for-profit corporation, allowed under Nevada law since the monorail provides a public service. The State of Nevada assisted in bond financing, but no public money was used in construction.

The Desert Wind was an Amtrak long-distance passenger train that ran from 1979 to 1997. It operated from Chicago to Los Angeles as a section of the California Zephyr, serving Los Angeles via Salt Lake City; Ogden, Utah; and Las Vegas.

Plans for high-speed rail in the United States date back to the High-Speed Ground Transportation Act of 1965. Various state and federal proposals have followed. Despite being one of the world's first countries to get high-speed trains, it failed to spread. Definitions of what constitutes high-speed rail vary, including a range of speeds over 110 mph (180 km/h) and dedicated rail lines. Inter-city rail with top speeds between 90 and 125 mph is sometimes referred to in the United States as higher-speed rail.
The California–Nevada Interstate Maglev project was a proposed 269 mi (433 km) Maglev train line from Las Vegas, Nevada, to Anaheim, California. One segment would run from Las Vegas to Primm, Nevada, with proposed service to the Las Vegas area's forthcoming Ivanpah Valley Airport. The top speed would be 310 mph (500 km/h). Though $45 million was appropriated in 2005 for the planning phase for the first 40 mi (64 km) segment, the money was never spent, and was finally reallocated to a highway project in a Las Vegas Airport in June 2010. The maglev project was not in the 2012 transportation plan under consideration by the Southern California Association of Governments. Removing it from the plan means that the project cannot receive federal funds, even for studies. The Southern California Association of Governments did leave a small portion of the route – from Anaheim to Ontario – in their 2012 transportation plan.
Brightline West is a privately run high-speed rail route, currently under construction, to link the Las Vegas Valley and Rancho Cucamonga in the Greater Los Angeles area through the California high desert. The line will connect with existing rail at Rancho Cucamonga station of Metrolink's San Bernardino Line, a commuter rail line in Southern California. The project is intended to provide an alternative to air and automobile travel between Southern California and Las Vegas, a popular leisure destination. In December 2023, the United States Department of Transportation awarded Brightline West a $3 billion grant as part of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. Construction, initially expected to begin shortly after the grant was announced in 2023, began on April 22, 2024. Revenue service is planned to start in 2028.

Interstate 15 (I-15) is an Interstate Highway in the U.S. state of Nevada that begins in Primm, continues through Las Vegas and it crosses the border with Arizona in Mesquite. Within the state, the freeway runs entirely in Clark County. The highway was built along the corridor of the older U.S. Route 91 (US 91) and Arrowhead Trail, eventually replacing both of these roads.

Proposition 1A is a law that was approved by California voters in the November 2008 state elections. It was a ballot proposition and bond measure that allocated funds for the California High-Speed Rail Authority. It is now contained within Chapter 20 of Division 3 of the California Streets and Highways Code.
Transportation in the Las Vegas Valley including the Nevada cities of Las Vegas, North Las Vegas and Henderson is a multi-faceted system. The street system is mostly laid out in a north–south/east–west system of roads. While most residents rely on cars, there is a network of bus routes reaching some areas of the county. The Las Vegas Valley, being the one of the largest tourist destinations in the world, has a mass transportation system which favors the Las Vegas Strip.

Brightline is an intercity rail route in the United States that runs between Miami and Orlando, Florida. Part of the route runs on track owned and shared by the Florida East Coast Railway.
Justin Christopher Jones is an American attorney and politician. He is currently the Clark County Commissioner for District F since 2019 and served as a member of the Nevada Senate for the 9th district from 2012 to 2014. He is a member of the Democratic Party.

The construction of the California High-Speed Rail system is an undertaking by the California High-Speed Rail Authority. The project is expected to span about 800 miles (1,300 km) and will be completed in two phases:

The California High-Speed Rail Authority was established in 1996 after decades of advocacy for building a high speed rail system in California. The passage of Proposition 1A in 2008, followed by the awarding of federal stimulus funds in 2010, established the initial funding for the California High-Speed Rail system. Construction contracts began to be awarded in 2013, and the groundbreaking ceremony for initial construction was held on January 6, 2015.

The Boring Company (TBC) is an American infrastructure, tunnel construction services, and equipment company founded by Elon Musk. TBC was founded as a subsidiary of SpaceX in 2017, and was spun off as a separate corporation in 2018. TBC has completed one tunneling project that is open to the public, as well as multiple test tunnels.
The Pacheco Pass Tunnels are a planned set of tunnels to carry California High-Speed Rail across the Diablo Range in the vicinity of Pacheco Pass east of Gilroy, California. The tunnels will constitute the first mountain crossing constructed as part of California High-Speed Rail, connecting the San Francisco Bay Area and Central Valley portions of the system.
Victor Valley is a future high-speed rail station of Brightline West, running to Las Vegas Boulevard in the Las Vegas Valley and south to Rancho Cucamonga.
References
- ↑ Young, Allen (May 26, 2015). "Nevada joins the high-speed rail bandwagon with plans for Vegas, SoCal link" . Retrieved May 28, 2015.
- ↑ "Nevada High Speed Rail Authority" (PDF).
- ↑ "Meetings & Resources – Nevada High Speed Rail Authority" . Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ↑ "Vote on SB457". Nevada Legislature. Nevada Legislative Counsel Bureau. May 20, 2015. Retrieved May 28, 2015.
- ↑ "NRS: CHAPTER 705 - RAILROADS AND MONORAILS". www.leg.state.nv.us. Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ↑ "High-Speed Rail Project Moves Forward in Nevada". GovTech. 2015-11-19. Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ↑ "Plans to build high-speed rail between Las Vegas and California delayed again". KTNV. 2021-06-22. Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ↑ "Las Vegas-LA high-speed rail plan delayed until 2022". Las Vegas Review-Journal. 2021-06-22. Retrieved 2021-08-22.