
The Order of Preachers, commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilian priest named Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull Religiosam vitam on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters OP after their names, standing for Ordinis Praedicatorum, meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans. More recently, there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries.
Blackfriars Priory is a Dominican religious community in Oxford, England. Its primary work is the administration of two educational institutions: Blackfriars Studium, a centre of theological studies in the Roman Catholic tradition; and Blackfriars Hall, a constituent permanent private hall of the University of Oxford. The current prior of Blackfriars is Nicholas Crowe. The name Blackfriars is commonly used in Britain to denote a house of Dominican friars, a reference to their black cappa, which forms part of their habit.

Sir Michael Anthony Eardley Dummett was an English academic described as "among the most significant British philosophers of the last century and a leading campaigner for racial tolerance and equality." He was, until 1992, Wykeham Professor of Logic at the University of Oxford. He wrote on the history of analytic philosophy, notably as an interpreter of Frege, and made original contributions particularly in the philosophies of mathematics, logic, language and metaphysics.

The Monthly Review is an independent socialist magazine published monthly in New York City. Established in 1949, the publication is the longest continuously published socialist magazine in the United States.
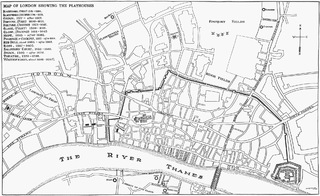
Blackfriars Theatre was the name given to two separate theatres located in the former Blackfriars Dominican priory in the City of London during the Renaissance. The first theatre began as a venue for the Children of the Chapel Royal, child actors associated with the Queen's chapel choirs, and who from 1576 to 1584 staged plays in the vast hall of the former monastery. The second theatre dates from the purchase of the upper part of the priory and another building by James Burbage in 1596, which included the Parliament Chamber on the upper floor that was converted into the playhouse. The Children of the Chapel played in the theatre beginning in the autumn of 1600 until the King's Men took over in 1608. They successfully used it as their winter playhouse until all the theatres were closed in 1642 when the English Civil War began. In 1666, the entire area was destroyed in the Great Fire of London.

Blackfriars is a restored Grade I listed 13th-century priory in Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear, England, located in the city centre, close to the city's Chinatown.

Desmond Macready Chute (1895–1962) was an English poet and artist, who became a Catholic priest in 1927.

Vincent McNabb, O.P. was an Irish Catholic scholar and Dominican priest based in London, active in evangelisation and apologetics.

Brian Evan Anthony Davies is a British philosopher, Roman Catholic priest, and friar. He is Distinguished Professor of Philosophy, Fordham University, and author of An Introduction to the Philosophy of Religion, now in its fourth English edition, which has been translated into five languages.

John Christopher "Aidan" Nichols is an English academic and Catholic priest.
Fergus Gordon Thomson Kerr is a Scottish Roman Catholic priest of the English Dominican province. He has published significantly on a wide range of subjects, but is famous particularly for his work on Ludwig Wittgenstein and Thomas Aquinas.

St Andrew's Hall and Blackfriars' Hall or The Halls are a Grade I listed complex of former Dominican priory church and convent buildings in the English city of Norwich, Norfolk, dating back to the 14th century. They are the most complete set of pre-reformation mendicant monastic structures to survive in England. The complex is made up of several flint buildings. The centrepiece is St Andrew's Hall. The halls are now used for conferences, weddings, concerts, beer festivals and meetings. The maximum capacity is 1,200 people. It is one of the Norwich 12 heritage sites.

St Ann Blackfriars was a church in the City of London, in what is now Ireland Yard in the ward of Farringdon Within. The church began as a medieval parish chapel, dedicated to St Ann, within the church of the Dominicans. The new parish church was established in the 16th century to serve the inhabitants of the precincts of the former Dominican monastery, following its dissolution under King Henry VIII. It was near the Blackfriars Theatre, a fact which displeased its congregation. It was destroyed in the Great Fire of London of 1666.
Fr Ian Anthony Ross was a Scottish born Catholic priest and member of The Order of Preachers (Dominican). He was also a noted broadcaster, writer, community activist, educator and antiquarian who served as Rector of the University of Edinburgh (1979–1982).
Victor Francis White, OP (1902–1960) was an English Dominican priest who corresponded and collaborated with Carl Gustav Jung. He was initially deeply attracted to Jung's psychology, but when Jung's Answer to Job was published in English, he gave it a very critical review. White's works include Soul and Psyche and God and the Unconscious. Jung and White enjoyed a series of correspondence, and Jung was so impressed with some of White's ideas that he invited White to his retreat house at Bollingen, where only Jung's very close friends were allowed. The correspondence between Jung and White has been published by Lammers and Cunningham (2007). While White was a great admirer of Jung, he was at times very critical of Jung. For example, he criticised Jung's essay "On the Self", and accused Jung of being too bound to a Manichaean dualism. He was also somewhat critical of Jung's Kantianism. At the same time, Jung was quite critical of White, for example, over his commitment to the doctrine of privatio boni as means of understanding the problem of evil.
The Lives of the Brethren is an early account of the first members of the Order of Preachers, also known as the Dominicans. Vitae Fratrum is potentially confusing as there are several works which are often abbreviated to that name. The book that records the early history of the Dominican order is the Vitae Fratrum Ordinis Praedicatorum. This is to be distinguished from other works such as the Vitae fratrum eremitarum Ordinis Sancti Pauli Primi Eremitae, which is a fifteenth-century account of the Pauline Hermits in Hungary, or the Liber vitasfratrum of Jordan of Quedlinburg, which recounts the early history of the Order of Saint Augustine.

Henry Vincent Pope, better known as Fr. Hugh Pope (1869–1946), was an English Dominican biblical scholar, Professor of New Testament Exegesis at the Pontificium Collegium Internationale Angelicum, the future Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, Angelicum in Rome.
Fr Austin (Liam) Flannery OP, was a Dominican priest, editor, publisher and social justice campaigner.

Blackfriars Leicester, also known as St Clement's Church, Leicester and St Clement's Priory, Leicester, is a former priory of the Order of Preachers in Leicester, England. It is also the name of a former civic parish, and a neighbourhood in the city built on and around the site of the old priory.

Bede Jarrett OP was an English Dominican friar and Catholic priest who was also a noted historian and author. Known for works including Mediæval Socialism and The Emperor Charles IV, Jarrett also founded Blackfriars Priory at the University of Oxford in 1921, formally reinstating the Dominican Order at that university for the first time since the Dissolution of the Monasteries under King Henry VIII.













