
The RWD 5 was a Polish touring and sports plane of 1931, a two-seat high-wing monoplane, constructed by the RWD team. It was made famous by its transatlantic flight, being the smallest aircraft to cross the Atlantic.

The RWD 17 was a Polish aerobatics-trainer aircraft of 1937, parasol wing monoplane, constructed by the RWD team.

The RWD-15 was a Polish touring aircraft of 1937, designed by the RWD team and built by the Doświadczalne Warsztaty Lotnicze (DWL).

The PZL-5 was a Polish two-seat touring and sports aircraft of 1930 constructed and produced by the PZL.

PZL.12 (PZL-H) was a prototype of a Polish amphibious flying boat designed and built in 1931 by Zygmunt Puławski, a pioneering Polish designer. He was killed in a crash involving this design.

The Bartel BM.4 was a Polish biplane primary trainer aircraft used from 1929 to 1939 by the Polish Air Force and Polish civilian aviation, manufactured in the Samolot factory in Poznań. It was the first plane of Polish design put into production.

The PWS-20 was a Polish single-engine high-wing 8 passenger airliner, built in the PWS factory and when it made its first flight in 1929 it became the first Polish-designed transport aircraft to fly.

The P.W.S.8 was a 1930 Polish sports plane, constructed by the Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS), that remained a prototype.

The RWD 23 was a Polish low-wing trainer aircraft of 1938, constructed by the RWD team, that remained a prototype.

The RWD-19 was a Polish two-seat low-wing sports aircraft of 1938, constructed by the RWD bureau.

The PWS-52 was a Polish sports aircraft of 1930, a single-engine high-wing monoplane, constructed by the Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów (PWS), that remained a prototype.

The P.Z.L. 27 was a prototype airliner/mail plane designed by Zbysław Ciołkosz and constructed at P.Z.L. in 1933.
The WT-1 was a 1931 high performance sports aircraft designed in Poland. It only made two flights.
The Medwecki M9 was a 1930s, Polish designed two-seat cabin tourer or trainer aircraft. Only one was completed before the outbreak of World War II.
The ITS-II was a Polish intermediate training glider. Only about five were built as it was soon outclassed by newer Polish aircraft but some were used until 1935. ITS-IIs were used in early training courses on air towing and another gave the first demonstration of glider aerobatics in Poland. It was also used to set one national record.

The Tarczyński and Stępniewki TS-1/34 Promyk was a Polish short span, high performance sailplane from the mid-1930s and was the first Polish sailplane equipped with flaps. Its construction was delayed by a financial crisis and its development terminated by World War II.
The PWS-103 was a high performance, Polish 15 m span sailplane developed from the longer-span PWS-102 just before World War II.
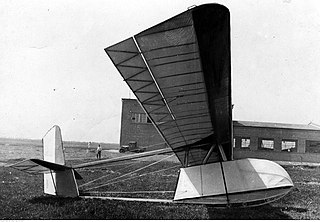
The Czajka (transl. Lapwing) or Kocjan Czajka after its designer was a Polish secondary training glider which was in continuous production from 1931 to the start of World War II. More than 160 were completed in Warsztaty Szybowcowe in Warsaw.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe Sroka, or Kocjan Sroka after its designer, was a Polish intermediate training glider. About sixty were built between 1934 and 1939.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe SG-7 was a Polish high performance, single seat sailplane. Two prototypes flew in 1937 but, outperformed by their contemporaries, no more were built.
















