
The 1960 Valdivia earthquake and tsunami or the Great Chilean earthquake on 22 May 1960 was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded. Most studies have placed it at 9.4–9.6 on the moment magnitude scale, while some studies have placed the magnitude lower than 9.4. It occurred in the afternoon, and lasted 10 minutes. The resulting tsunamis affected southern Chile, Hawaii, Japan, the Philippines, eastern New Zealand, southeast Australia, and the Aleutian Islands.

The Los Ríos Region is one of Chile's 16 regions, the country's first-order administrative divisions. Its capital is Valdivia. It began to operate as a region on October 2, 2007, having been created by subdividing the Los Lagos Region in southern Chile. It consists of two provinces: Valdivia and the newly created Ranco Province, which was formerly part of Valdivia Province.

Puyuhuapi Volcanic Group is a volcanic group of cinder cones located at the head of Puyuhuapi Channel, in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile.

Mocho-Choshuenco is a glacier covered compound stratovolcano in the Andes of Los Ríos Region, Chile. It is made of the twin volcanoes Choshuenco in the northwest and the Mocho in the southeast. The highest parts of the volcano are part of the Mocho-Choshuenco National Reserve while the eastern slopes are partly inside the Huilo-Huilo Natural Reserve.

Quetrupillán is a stratovolcano located in Los Ríos Region of Chile. It is situated between Villarrica and Lanín volcanoes, within Villarrica National Park. Geologically, Quetrupillán is located in a tectonic basement block between the main traces of Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault and Reigolil-Pirihueico Fault.

The Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault is major geological fault that runs a length of roughly 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) in a NNE-SSW orientation and exhibits current seismicity. It is located in the Chilean Northern Patagonian Andes. It is a dextral intra-arc strike-slip fault. Most large stratovolcanoes of the Southern Volcanic Zone of the Andes are aligned by the fault which allows for the movement of magma and hydrothermal fluids.

The Isthmus of Ofqui is a narrow isthmus that connects the Taitao Peninsula with the Chilean mainland. The isthmus is bounded in the south by the Gulf of Penas, in the north by the San Rafael Lagoon, in the west by the Taitao Peninsula and in the east by the Northern Patagonia Ice Field.
Mentolat is an ice-filled, 6 km (4 mi) wide caldera in the central portion of Magdalena Island, Aisén Province, Chilean Patagonia. This caldera sits on top of a stratovolcano which has generated lava flows and pyroclastic flows. The caldera is filled with a glacier.

Lago Ranco is a town and commune in southern Chile administered by the Municipality of Lago Ranco. It is located in Ranco Province in Los Ríos Region. Lago Ranco takes its name from Ranco Lake, which it shares with the commune of Futrono.
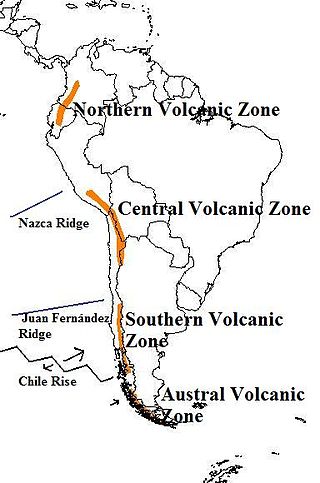
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.
Carrán-Los Venados is a volcanic group of scoria cones, maars and small stratovolcanoes in southern Chile, southeast of Ranco Lake. The highest cone is Los Guindos, which is a small stratovolcano with an elevation of 1,114 metres (3,655 ft). The volcanic group has recorded eruptions from 1955 and 1979. Located south of Maihue Lake and north Puyehue Volcano Carrán-Los Venados group is placed at the intersection of several faults on the thin crust (~30 km) of southern Chile, among them Liquiñe-Ofqui and Futrono Fault.

Chaitén is a Chilean town, commune and former capital of the Palena Province in Los Lagos Region. The town is north of the mouth of Yelcho River, on the east coast of the Gulf of Corcovado. The town is strategically close to the northern end of the Carretera Austral, where the highway goes inland. The Desertores Islands are part of the commune.
Pillanleufú River is a river in Futrono, southern Chile. It drains waters from the southern and eastern slopes of Mocho-Choshuenco volcano to Maihue Lake, which in turn flows by Calcurrupe River into Ranco Lake. The river flows in a north-south direction along the Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault.
Futrono Fault is a NWW tending geological fault in Los Ríos Region, running from the northern shore of Ranco Lake through the areas immediately south of Maihue Lake, where it intersects the large Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault, and through the east along the Hueinahue River. The volcanic group of Carrán-Los Venados is located above the fault.

Cay is a stratovolcano in the South Volcanic Zone of the Andes in Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region, Chile. The volcano is located 15 km northeast of the larger Maca Volcano and about 230 km of the Chile Trench at the intersection of NW-SE and NE-SW faults of the Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault Zone.

Puyehue and Cordón Caulle are two coalesced volcanic edifices that form a major mountain massif in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province, in the South of Chile. In volcanology this group is known as the Puyehue-Cordón Caulle Volcanic Complex (PCCVC). Four volcanoes constitute the volcanic group or complex, the Cordillera Nevada caldera, the Pliocene Mencheca volcano, Cordón Caulle fissure vents and the Puyehue stratovolcano.
Salto del Nilahue is a waterfall located in the commune of Lago Ranco in southern Chile. It lies in the lower flows of Nilahue River.
The Reigolil-Pirihueico Fault is a second-order geological fault located in the Chilean and Argentine Andes. As the name implies, it runs from Pirihueico Lake to Reigolil Valley. Reigolil-Pirihueico Fault run in north–south direction and is roughly parallel to the larger Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault, which is located 15 to 20 km west of it to which it is considered a branch of. East of Reigolil-Pirihueico Fault, close or along the Argentina-Chile boundary, are a string of volcanoes pliocene to quaternary volcanoes: Lanín, Pirihueico, Huanquihué, Quelguenco and Chihuío.
Contrafuerte River is a river in the Los Ríos Region of Chile. The river flows north from the northern slopes of Puyehue-Cordón Caulle following Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault. It flows into Nilahue River.

The 2011–2012 Puyehue-Cordón Caulle eruption was a volcanic eruption that began in the Puyehue-Cordón Caulle volcanic complex in Chile on 4 June 2011. The eruption, which occurred from the Cordón Caulle fissure after 51 years of the volcano being inactive, is one of the largest volcanic eruptions of the 21st century thus far. At least 3,500 people were evacuated from nearby areas, while the ash cloud was blown across cities all around the Southern hemisphere, including Bariloche, Buenos Aires, Montevideo, Stanley, Porto Alegre, Cape Town, Hobart, Perth, Adelaide, Sydney, Melbourne, Wellington, Auckland and Port Moresby, forcing airlines to cancel hundreds of international and domestic flights and causing travel chaos.














