
Chile officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Chile had a population of 17.5 million as of the latest census in 2017 and has a territorial area of 756,102 square kilometers (291,933 sq mi), sharing borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about 1,250,000 square kilometers (480,000 sq mi) of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish.
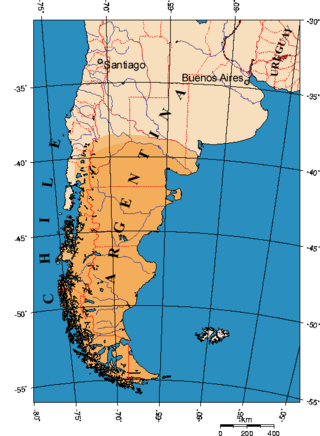
Patagonia is a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south.
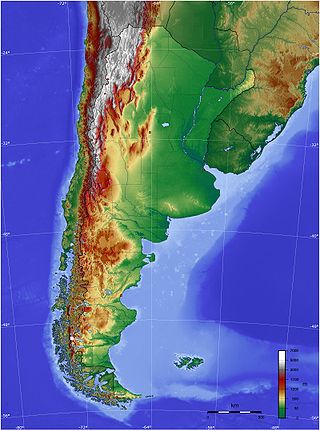
The geography of Argentina is heavily diverse, consisting of the Andes Mountains, pampas, and various rivers and lakes. Bordered by the Andes in the west and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, its neighbouring countries are Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, and Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast.

The 1960 Valdivia earthquake and tsunami or the Great Chilean earthquake on 22 May 1960 was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded. Most studies have placed it at 9.4–9.6 on the moment magnitude scale, while some studies have placed the magnitude lower than 9.4. It occurred in the afternoon, and lasted 10 minutes. The resulting tsunamis affected southern Chile, Hawaii, Japan, the Philippines, eastern New Zealand, southeast Australia, and the Aleutian Islands.

Los Lagos Region is one of Chile's 16 regions, which are first order administrative divisions, and comprises four provinces: Chiloé, Llanquihue, Osorno and Palena. The region contains the country's second-largest island, Chiloé, and the second-largest lake, Llanquihue. Its capital is Puerto Montt; other important cities include Osorno, Castro, Ancud, and Puerto Varas. Los Lagos Region is considered part of Patagonia.

The Altiplano, Collao or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north–south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile.

The Araucanía, La Araucanía Region is one of Chile's 16 first-order administrative divisions, and comprises two provinces: Malleco in the north and Cautín in the south. Its capital and largest city is Temuco; other important cities include Angol and Villarrica.

San Carlos de Bariloche, usually known as Bariloche, is a city in the province of Río Negro, Argentina, situated in the foothills of the Andes on the southern shores of Nahuel Huapi Lake. It is located within the Nahuel Huapi National Park. After development of extensive public works and Alpine-styled architecture, the city emerged in the 1930s and 1940s as a major tourism centre with skiing, trekking and mountaineering facilities. In addition, it has numerous restaurants, cafés, and chocolate shops. The city had a permanent population of 108,205 according to the 2010 census. According to the latest statistics from 2015, the population is around 122,700, and a projection for 2020 estimates 135,704.

Puerto Varas, also known as "La Ciudad De Las Rosas" or “The City Of Roses”, is a city and commune located in the southern Chilean province of Llanquihue, in the Los Lagos Region.

The Los Ríos Region is one of Chile's 16 regions, the country's first-order administrative divisions. Its capital is Valdivia. It began to operate as a region on October 2, 2007, having been created by subdividing the Los Lagos Region in southern Chile. It consists of two provinces: Valdivia and the newly created Ranco Province, which was formerly part of Valdivia Province.

General Carrera Lake or Lake Buenos Aires is a deep lake located in Patagonia and shared by Argentina and Chile. Both names are internationally accepted, while the autochthonous name of the lake is Chelenko, which means "stormy waters" in Aonikenk. Another historical name is Coluguape from Mapuche, a derivative of this name is applied to Colhué Huapí Lake after Argentine explorer Francisco Moreno reached this lake in 1876 conflating it with Coluguape.

Torres del Paine National Park is a national park encompassing mountains, glaciers, lakes, and rivers in southern Chilean Patagonia. The Cordillera del Paine is the centerpiece of the park. It lies in a transition area between the Magellanic subpolar forests and the Patagonian Steppes. The park is located 112 km (70 mi) north of Puerto Natales and 312 km (194 mi) north of Punta Arenas. The park borders Bernardo O'Higgins National Park to the west and the Los Glaciares National Park to the north in Argentine territory. Paine means "blue" in the native Tehuelche (Aonikenk) language and is pronounced PIE-neh. It was established as a National Park in 1959.

Puyehue Lake, is an Andean piedmont lake on the border of Los Lagos Region with Los Ríos Region of Chile.

Zona Sur is one of the five natural regions on which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. Its northern border is formed by the Bío-Bío River, which separates it from the Central Chile Zone. The Southern Zone borders the Pacific Ocean to the west, and to the east lies the Andean mountains and Argentina. Its southern border is the Chacao Channel, which forms the boundary with the Austral Zone. While the Chiloé Archipelago belongs geographically to the Austral Zone in terms of culture and history, it lies closer to the Southern Zone.
Los Chiles is a district of the Los Chiles canton, in the Alajuela province of Costa Rica.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Republic of Chile.

Llancahue River is a river in Panguipulli commune, southern Chile. It drains Pellaifa Lake and flows westward into Calafquén Lake of which it is the primary source.
Lake CECs is a subglacial lake in Antarctica at approximately latitude 80°S. It has an estimated area of 18 km2. The territory where the lake is located, some 160 km from Union Glacier, is claimed only by Chile.

















