
Between February 1942 and November 1943, during the Pacific War of World War II, the Australian mainland, domestic airspace, offshore islands and coastal shipping were attacked at least 111 times by aircraft from the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Force and Imperial Japanese Army Air Force. These attacks came in various forms; from large-scale raids by medium bombers, to torpedo attacks on ships, and to strafing runs by fighters.

No. 75 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter unit based at RAAF Base Tindal in the Northern Territory. The squadron was formed in 1942 and saw extensive action in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II, operating P-40 Kittyhawks. It was disbanded in 1948, but reformed the following year and operated jet aircraft throughout the Cold War. The squadron was based at Malta from 1952 to 1954, flying de Havilland Vampires, and Malaysia from 1968 to 1983, with Dassault Mirage IIIs, before returning to Australia.

No. 30 Squadron is a squadron of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Raised in 1942 as a long-range fighter unit, the squadron saw action in the Second World War, serving in the South West Pacific Area against the Japanese and operating mainly in the ground attack and anti-shipping roles from bases in New Guinea and the Netherlands East Indies. After the war, the squadron was disbanded, however, it was re-raised a short time later as a unit of the part-time Citizen Air Force, operating in the target towing and air defence role in New South Wales. In 1960s the squadron ceased flying aircraft and operated surface-to-air missiles, providing for the defence of Sydney and Darwin before disbanding in 1968. The squadron was re-raised again in 2010 and since then it has served as an airbase support squadron located at RAAF Base East Sale.

No. 76 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) flight training squadron. Established in 1942, it operated P-40 Kittyhawk fighter aircraft in the South West Pacific theatre during World War II. Following the end of hostilities it re-equipped with P-51 Mustangs and formed part of Australia's contribution to the occupation of Japan until disbanding in 1948. The squadron was re-formed in 1949 and three years later transferred to Malta, where it operated de Havilland Vampire jet fighters on garrison duty until again disbanding in 1955. It was reactivated in 1960 and operated CAC Sabre and Dassault Mirage III fighters in Australia until 1973. No. 76 Squadron was re-formed in its present incarnation in 1989 and is currently stationed at RAAF Base Williamtown, New South Wales, where it operates Hawk 127 jet training aircraft.
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) traces its history back to the Imperial Conference held in London in 1911, where it was decided aviation should be developed within the Armed Forces of the British Empire. Australia implemented this decision, the only country to do so, by approving the establishment of the Central Flying School (CFS) in 1912. The location for the proposed school was initially to be at Duntroon, Australian Capital Territory, but in July 1913 Point Cook, Victoria, was announced as the preferred location. The first flights by CFS aircraft took place there in March 1914.

No. 13 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron. The unit saw combat during World War II as a bomber and maritime patrol squadron and is currently active as a mixed regular and reserve RAAF unit located in Darwin, fulfilling both operational support and training duties.

No. 12 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) general purpose, bomber and transport squadron. The squadron was formed in 1939 and saw combat in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II. From 1941 to 1943, it mainly conducted maritime patrols off northern Australia. The squadron was based at Merauke in western New Guinea from November 1943 to July 1944, when it was withdrawn from operations. After being re-equipped, it operated as a heavy bomber unit from February 1945 until the end of the war. The squadron continued in this role until it was redesignated No. 1 Squadron RAAF in February 1948. The squadron was reformed in 1973 to operate transport helicopters but was again disbanded in 1989.

No. 60 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force fighter squadron of World War II. It was formed in January 1942 and disbanded three months later, without seeing combat.

No. 20 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) support squadron. Coming under the control of No. 96 Wing, it is responsible for the management of the airfield at RAAF Base Woomera, South Australia. The squadron originated as a maritime patrol unit during World War II. Raised in August 1941, it operated PBY Catalina and Short Empire flying boats from bases in New Guinea, Queensland and the Northern Territory, conducting search-and-rescue, mine-laying, anti-submarine and bombing missions against Japanese targets in the Pacific theatre. Following the conclusion of hostilities, the squadron was disbanded in March 1946. It was reactivated as an airfield support squadron in April 2015.

No. 93 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force fighter squadron that operated during World War II. It was formed in January 1945 and disbanded in August 1946. Due to delays in bringing operational airfields into service, the squadron saw little combat before the end of the war.

No. 21 Squadron RAAF is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) general reserve squadron. Formed in the mid-1930s as a unit of the part-time Citizen Air Force (CAF), it was mobilised for service during World War II, when it saw action against the Japanese as a fighter unit in the Malayan campaign, a dive bomber unit in the New Guinea campaign, and a heavy bomber unit in the Borneo campaign. After the war, the squadron continued to fly until 1960, when the CAF ceased flying operations. At that time, No. 21 Squadron converted to a non-flying support role, which it currently fulfils at RAAF Williams.

No. 22 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) mixed Permanent and Reserve squadron that provides support for the RAAF in the Sydney region. Formed in 1936, the squadron served in Papua New Guinea during the Second World War, and later followed the Pacific War as far as the Philippines. Following the war, the squadron was re-formed in 1948 but was converted to a non-flying support role in mid-1960. It is currently based at RAAF Base Richmond, New South Wales.

No. 457 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter squadron of World War II. Equipped with Supermarine Spitfire fighters, it was formed in England during June 1941 under Article XV of the Empire Air Training Scheme. The squadron was transferred to Australia in June 1942 and saw combat in the South West Pacific Area before being disbanded in November 1945.

No. 82 Squadron RAAF was a Royal Australian Air Force fighter squadron that operated during World War II and its immediate aftermath. It was formed in June 1943, flying Curtiss P-40 Kittyhawks and, initially, Bell P-39 Airacobras from bases in Queensland and New Guinea. The squadron became operational in September 1944, and undertook ground attack missions against Japanese targets in the Pacific theatre. Following the end of hostilities, No. 82 Squadron was re-equipped with North American P-51 Mustangs and deployed to Japan, where it formed part of the British Commonwealth Occupation Force. It remained there until October 1948, when it was disbanded.

No. 86 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter squadron of World War II. The squadron was formed in March 1943 and was deployed to Merauke in Dutch New Guinea in July that year. While No. 86 Squadron was stationed at Merauke until April 1944, it saw little combat. After being transferred back to Australia its aircraft and personnel were transferred to other units, and only a nucleus of the squadron remained. While it was re-equipped with new aircraft in June 1945, the war ended before the squadron was ready for combat and it was disbanded in December 1945.
No. 1 Wing was an Australian Flying Corps (AFC) and Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing active during World War I and World War II. The wing was established on 1 September 1917 as the 1st Training Wing and commanded the AFC's pilot training squadrons in England until April 1919, when it was disbanded. It was reformed on 7 October 1942 as a fighter unit comprising two Australian and one British flying squadrons equipped with Supermarine Spitfire aircraft, and a mobile fighter sector headquarters. The wing provided air defence to Darwin and several other key Allied bases in northern Australia until the end of the war, and was again disbanded in October 1945.

No. 77 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing of World War II. It formed part of No. 10 Operational Group at its establishment in November 1943, when it comprised three squadrons equipped with Vultee Vengeance dive bombers. No. 77 Wing commenced operations in early 1944, flying out of Nadzab, Papua New Guinea. Soon afterwards, however, the Vengeance units were withdrawn from combat and replaced with squadrons flying Douglas Bostons, Bristol Beaufighters and Bristol Beauforts. The wing saw action in the assaults on Noemfoor, Tarakan, and North Borneo, by which time it was an all-Beaufighter formation made up of Nos. 22, 30 and 31 Squadrons. It was to have taken part in the Battle of Balikpapan in June 1945, but unsuitable landing grounds meant that the Beaufighter units were withdrawn to Morotai, sitting out the remainder of the war before returning to Australia, where they disbanded, along with the wing headquarters, in 1946.

No. 72 Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing that operated during World War II. It was formed in April 1943 at Townsville, Queensland, as part of North-Eastern Area Command. Led by Group Captain Charles Eaton, the wing soon deployed to Merauke, Dutch New Guinea, where it comprised three squadrons flying CAC Boomerang and P-40 Kittyhawk fighters, and A-31 Vengeance dive bombers. Eaton was succeeded by Group Captain Allan Walters in mid-1943. No. 72 Wing took part in the defence of Torres Strait, undertaking interception, patrol and occasional ground-attack and anti-shipping duties. By July 1944, its original squadrons had all been disbanded or transferred to other operational formations. No. 120 Squadron, which had arrived in May 1944, operating Kittyhawks, remained at Merauke until February 1945. The wing headquarters returned to Australia that May, and disbanded the following month.

No. 2 Service Flying Training School was a flying training school of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) that operated during World War II. It was formed in July 1940, under the command of Wing Commander Frederick Scherger. Responsible for intermediate and advanced instruction of pilots under the Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS), the school was based at RAAF Station Forest Hill near Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, and operated CAC Wirraway and Avro Anson aircraft. The Ansons were phased out in July 1941, and the school became an all-Wirraway unit. In 1942 the RAAF divided the personnel and equipment of No. 2 SFTS between Nos. 5 and 7 Service Flying Training Schools at Uranquinty and Deniliquin, respectively. No. 2 SFTS was disbanded that April, and the base facilities taken over by No. 5 Aircraft Depot.
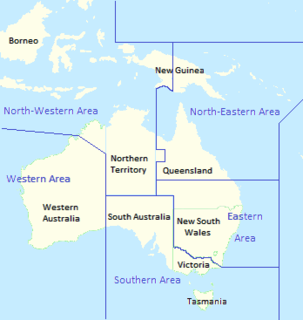
North-Western Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. Its wartime sphere of operations included the Northern Territory, adjacent portions of Queensland and Western Australia, and the Dutch East Indies. The command was formed in January 1942, following the outbreak of the Pacific War, from the western part of Northern Area Command, which had covered all of northern Australia and Papua. Headquartered at Darwin, North-Western Area Command was initially responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries.



















