Cove Pond is a shallow 287 ha wetland at the south-western end of the Caribbean island of Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory. It forms part of a larger coastal lagoon from which it is separated by a causeway constructed for access to the Cap Juluca resort.

Grey Pond is a 191 ha shallow, brackish lagoon at the eastern end of the main island of Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. Its southern and eastern shores are relatively steep-sided limestone slopes, while its north-eastern corner is separated from Savannah Bay by a belt of sand dunes. The limestone shores are covered by low, scrub vegetation.

The Mlima Combani and Mlima Mtsapéré Important Bird Area lies in the north-central part of the French island territory of Mayotte in the Comoro Islands, lying at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel between the East African country of Mozambique and Madagascar.

The Tilomar Important Bird Area, also known as Tilomar Forest, is a tract of mainly forested land in East Timor, a country occupying the eastern end of the island of Timor in the Lesser Sunda Islands of Wallacea.
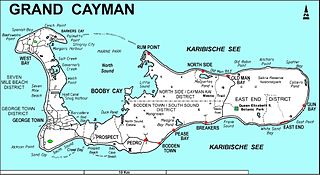
The Botanic Park and Salina Reserve Important Bird Area comprises two separate sites on Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea.
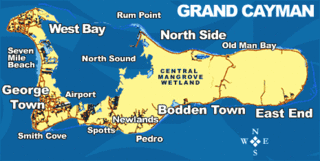
The Central Manrove Wetland is a large area of mangrove dominated wetland on Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

The Eastern Dry Forest lies at the eastern end of Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory’s Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Frank Sound Forest lies near the southern coast of the East End distinct of Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory’s Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Franklin's Forest lies near the centre of the East End distinct of Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory’s Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Mastic Reserve lies at the eastern end of the North Side of Grand Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It, with the associated Mastic Trail, is managed by the National Trust for the Cayman Islands and is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs). It is named after the yellow mastic and black mastic trees which occur in the reserve.

Sparrowhawk Hill lies in the centre of Little Cayman, one of the Cayman Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Road Salt Pond, also known as Road Bay Pond or simply Road Pond, is a wetland in Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Cauls Pond is a wetland in Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It is one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

The Merrywing Pond System is a golf course wetland system in Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It forms one of the territory’s Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Forest Bay Pond is a small wetland in Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean Sea. It forms one of the territory’s Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

South Soufriere Hills is a 35 ha patch of forest on the island of Montserrat, a British Overseas Territory in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean Sea. It forms one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

The Wades Green and Teren Hill Important Bird Area is a 226 ha tract of land on the island of North Caicos in the Turks and Caicos Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the Lucayan Archipelago of the western Atlantic Ocean. It forms one of the territory's Important Bird Areas (IBAs).

Petite Terre Islands National Nature Reserve is a reserve of the Petite Terre Islands in Guadeloupe. The reserve was established by Decree No. 98-801 of 3 September 1998 as the nature reserve for the islands of Petite Terre. It covers an area of about 990 hectares, which is demarcated by five points fixed with buoys, and includes a land area of 148.6 hectares with the balance as sea area.