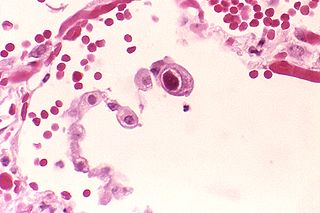
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and monkeys serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis, and pneumonia. In the medical literature, most mentions of CMV without further specification refer implicitly to human CMV. Human CMV is the most studied of all cytomegaloviruses.

Picinae containing the true woodpeckers is one of three subfamilies that make up the woodpecker family Picidae. True woodpeckers are found over much of the world, but do not occur in Madagascar or Australasia.

The American horned owls and the Old World eagle-owls make up the genus Bubo, at least as traditionally described. The genus name Bubo is Latin for the Eurasian eagle-owl.

The buntings are a group of Old World passerine birds forming the genus Emberiza, the only genus in the family Emberizidae. They are seed-eating birds with stubby, conical bills.

Mesoplodont whales are 16 species of toothed whale in the genus Mesoplodon, making it the largest genus in the cetacean order. Two species were described as recently as 1991 and 2002, and marine biologists predict the discovery of more species in the future. A new species was described in 2021. They are the most poorly known group of large mammals. The generic name "mesoplodon" comes from the Greek meso- (middle) - hopla (arms) - odon (teeth), and may be translated as 'armed with a tooth in the centre of the jaw'.

Lagenorhynchus is a genus in the infraorder Cetacea, containing only a single extant species as of 2021: the white-beaked dolphin. In addition, the extinct species Lagenorhynchus harmatuki is also classified in this genus.

The bird genus Hirundo is a group of passerines in the family Hirundinidae. The genus name is Latin for a swallow. These are the typical swallows, including the widespread barn swallow. Many of this group have blue backs, red on the face and sometimes the rump or nape, and whitish or rufous underparts. With fifteen species this genus is the largest in its family.

Gesneriaceae, the gesneriad family, is a family of flowering plants consisting of about 152 genera and ca. 3,540 species in the tropics and subtropics of the Old World and the New World, with a very small number extending to temperate areas. Many species have colorful and showy flowers and are cultivated as ornamental plants.

Myosotis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Boraginaceae. The name comes from the Ancient Greek μυοσωτίς "mouse's ear", which the foliage is thought to resemble. In the northern hemisphere they are colloquially denominated forget-me-nots or scorpion grasses. The colloquial name "forget-me-not" was calqued from the German Vergissmeinnicht and first used in English in AD 1398 through King Henry IV of England. Similar names and variations are found in many languages. Myosotis alpestris is the official flower of Alaska and Dalsland, Sweden. Plants of the genus are commonly confused with Chatham Islands' forget-me-nots which belong to the related genus Myosotidium.

The Syngnathidae is a family of fish which includes seahorses, pipefishes, and seadragons. The name is derived from Greek, σύν (syn), meaning "together", and γνάθος (gnathos), meaning "jaw". This fused jaw trait is something the entire family has in common.

Bactris is a genus of spiny palms which are native to Mexico, South and Central America and the Caribbean. Most species are small trees about 2 m tall, but some are large trees while others are shrubs with subterranean stems. They have simple or pinnately compound leaves and yellow, orange, red or purple-black fruit. The genus is most closely related to several other spiny palms—Acrocomia, Aiphanes, Astrocaryum and Desmoncus. The fruit of several species is edible, most notably B. gasipaes, while others are used medicinally or for construction.

Stenocarpus is a genus of about 22 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. They are trees or shrubs with variably-shaped leaves, zygomorphic, bisexual flowers, the floral tube opening on the lower side before separating into four parts, followed by fruit that is usually a narrow oblong or cylindrical follicle.

Enidae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks.

Terellia is a genus of tephritid or fruit flies in the family Tephritidae.

Hyotissa is a genus of large saltwater oysters, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Gryphaeidae.

Platyninae is a subfamily of ground beetles.
Speagonum is a genus of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. This genus has a single species, Speagonum mirabile. It is found on New Guinea.
Vitagonum is a genus of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. This genus has a single species, Vitagonum apterum. It is found in Fiji.
Rhabditophora is a class of flatworms. It includes all parasitic flatworms and most free-living species that were previously grouped in the now obsolete class Turbellaria. Therefore, it contains most of the species in the phylum Platyhelminthes, excluding only the catenulids, to which they appear to be the sister group.
Rosemary Margaret Smith (1933–2004) was a Scottish botanist and illustrator who specialized in the taxonomy of the Zingiberaceae, or ginger family. Many of the species she classified and identified as being placed into improper genera were found in Asian countries, especially in the isolated island of Borneo.















