
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. He was of Cappadocian Greek origin and a member of the Praetorian Guard for Roman emperor Diocletian, but was sentenced to death for refusing to recant his Christian faith. He became one of the most venerated saints and megalomartyrs in Christianity, and he has been especially venerated as a military saint since the Crusades. He is respected by Christians, Druze, as well as some Muslims as a martyr of monotheistic faith.

In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains or personal effects of a saint or other person preserved for the purpose of veneration as a tangible memorial. Relics are an important aspect of some forms of Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, shamanism, and many other religions. Relic derives from the Latin reliquiae, meaning "remains", and a form of the Latin verb relinquere, to "leave behind, or abandon". A reliquary is a shrine that houses one or more religious relics.

Petroc or Petrock was a British prince and Christian saint.
Íñigo Arista was a Vascon chieftain of the Eneko tribe, and the first king of Pamplona. He is thought to have risen to prominence after the defeat of local Frankish partisans at the Battle of Pancorbo in 816, and his rule is usually dated from shortly after the defeat of a Carolingian army in 824.

The Martyrs of Córdoba were forty-eight Christian martyrs who were executed under the rule of Muslim administration in Al-Andalus. The hagiographical treatise written by the Iberian Christian and Latinist scholar Eulogius of Córdoba describes in detail the executions of the martyrs for capital violations of Islamic law (sharīʿa), including apostasy and blasphemy. The martyrdoms recorded by Eulogius took place between 850 and 859 AD, which according to the Mālikī judges of al-Andalus broke the treaty signed between Muslims and their Christian subjects.

Saint Sunniva is the patron saint of the Norwegian Church of Norway Diocese of Bjørgvin, as well as all of Western Norway.

Columba of Spain was a virgin and nun who was born in Córdoba, Spain, and martyred around 853 by the Muslim rulers in Spain, during a persecution of Christians. She is a part of the Martyrs of Córdoba and venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church. Her feast day is September 17. Her cult was probably a combination of two virgin martyrs, Colomba of Spain and Columba of Sens, a third century French martyr.

Seaxburh, also Saint Sexburga of Ely, was a Queen as well as an abbess, and is a saint of the Christian Church. She was married to King Eorcenberht of Kent.

Pelagius of Córdoba was a Christian boy who died as a martyr in Córdoba in southern Spain around 926 AD.

The conversion of non-Islamic places of worship into mosques occurred during the life of Muhammad and continued during subsequent Islamic conquests and under historical Muslim rule. Hindu temples, Jain Temples, Christian churches, synagogues, and Zoroastrian fire temples have been converted into mosques.

The Monastery of San Salvador of Leyre is a religious complex to the south of the Sierra of Leyre, in northern Navarre, Spain, representing one of the most important historical monasteries of Spain.

Saint Eulogius of Córdoba (Spanish: San Eulogio de Córdoba was one of the Martyrs of Córdoba. He flourished during the reigns of the Cordovan emirs Abd-er-Rahman II and Muhammad I.
Rudolf of Fulda was a Benedictine monk during the Carolingian period in the 9th century. Rudolf was active at Fulda Abbey in the present-day German state of Hesse. He was one of the most distinguished scholars of his time. Many of his works have been lost. However, his Annals of Fulda and Life of St. Leoba survive.
The Chronica Prophetica is an anonymous medieval Latin chronicle written by a Christian in April 883 at or near the court of Alfonso III of Asturias in Oviedo. It uses the dating system of the Spanish Era and is essentially an interpretation of the prophecy concerning the fate of Gog found in the biblical Book of Ezekiel. To the anonymous Asturian, the destruction of the Emirate of Córdoba is closely linked with the end times. According to Kenneth Baxter Wolf in the introduction to his translation, "The fact that Asturian armies at the time were taking advantage" of the weakness of the Umayyad emirate of Córdoba and "raiding deep into Muslim territory accounts for the overly optimistic estimates of the imminent Christian domination of the peninsula" in the Chronica Prophetica.
The Battle of Torrevicente was fought on Saturday, 9 July 981 between a force loyal to the Caliphate of Córdoba under the command of Ibn Abi ‘Amir and a rebel force under Galib ibn Abd al-Rahman and his Christian allies, King Ramiro Garcés of Viguera and Count García Fernández of Castile. It was Galib's intention to continue the policy of previous caliphs, Abd ar-Rahman III and al-Hakam II, which was to maintain supremacy over the Christian principalities in peace. Ibn Abi ‘Amir was pursuing a new policy of jihad, signalled by his seven aggressive actions against the Christians in the previous three years. Both Ramiro and Galib died during the battle and Ibn Abi ‘Amir was victorious. It was the twelfth of Ibn Abi ‘Amir's military campaigns, and was called in Muslim sources the "Campaign of the Victory".

October 21 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - October 23
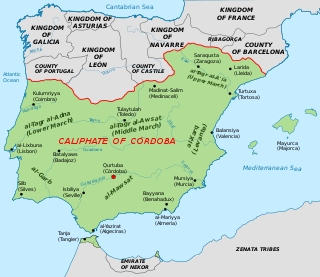
The Caliphate of Córdoba, also known as the Córdoban Caliphate, was an Arab Islamic state ruled by the Umayyad dynasty from 929 to 1031. Its territory comprised Iberia and parts of North Africa, with its capital in Córdoba. It succeeded the Emirate of Córdoba upon the self-proclamation of Umayyad emir Abd ar-Rahman III as caliph in January 929. The period was characterized by an expansion of trade and culture, and saw the construction of masterpieces of al-Andalus architecture.

The Brescia Casket, also called the lipsanotheca of Brescia or reliquary of Brescia, is an ivory box, perhaps a reliquary, from the late 4th century, which is now in the Museo di Santa Giulia at San Salvatore in Brescia, Italy. It is a virtually unique survival of a complete Early Christian ivory box in generally good condition. The 36 subjects depicted on the box represent a wide range of the images found in the evolving Christian art of the period, and their identification has generated a great deal of art-historical discussion, though the high quality of the carving has never been in question. According to one scholar: "despite an abundance of resourceful and often astute exegesis, its date, use, provenance, and meaning remain among the most formidable and enduring enigmas in the study of early Christian art."

The Leyre Casket is one of the jewels of Hispano-Arab Islamic art. It is a casket or reliquary made of elephant ivory which was made in 1004/5 in the Caliphate of Cordoba.














