| Oculofaciocardiodental syndrome | |
|---|---|
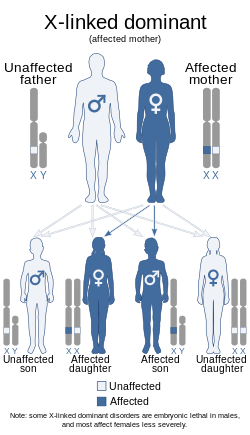 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked dominant manner. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Oculofaciocardiodental syndrome is a rare X-linked dominant genetic disorder. [1]
| Oculofaciocardiodental syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked dominant manner. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Oculofaciocardiodental syndrome is a rare X-linked dominant genetic disorder. [1]
The incidence of this condition is less than 1 per million. It is primarily only found in females. Its highly rare in males, but some males were born with it. Teeth with large roots (radiculomegaly), heart defects and small eyes (microphthalmia) are the characteristic triad found in this syndrome.
Typical features of the condition include:[ citation needed ]
This condition is caused by lesions in the BCOR gene located on the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp11.4). This protein encodes the BCL6 corepressor, but little is currently known about its function. The inheritance is X-linked dominant.[ citation needed ]
A genetically related disorder is Lenz microphthalmia syndrome. [2]
Diagnosis can be confirmed through DNA testing.
The first features of this syndrome noted were the abnormal teeth, which were described by Hayward in 1980. [3]