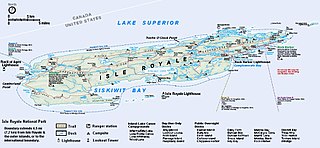
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale and more than 400 small adjacent islands, as well as the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michigan. Isle Royale is 45 mi (72 km) long and 9 mi (14 km) wide, with an area of 206.73 sq mi (535.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest lake island in the world. In addition, it is the largest natural island in Lake Superior, the second-largest island in the Great Lakes, the third-largest in the contiguous United States, and the 33rd-largest island in the United States.

Rock Harbor is the main access point for visitors landing on Isle Royale in northern Lake Superior. It sits four miles (6.4 km) from the northeastern end of the 45-mile-long (72 km) island, the whole of which is protected as Isle Royale National Park. Two structures in Rock Harbor—the Rock Harbor Light and the Edisen Fishery—are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The following is a list of Registered Historic Places in Keweenaw County, Michigan.
This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listings posted May 20, 2022.

A fire lookout tower, fire tower or lookout tower, provides housing and protection for a person known as a "fire lookout" whose duty it is to search for wildfires in the wilderness. The fire lookout tower is a small building, usually located on the summit of a mountain or other high vantage point, in order to maximize the viewing distance and range, known as view shed. From this vantage point the fire lookout can see smoke that may develop, determine the location by using a device known as an Osborne Fire Finder, and call fire suppression personnel to the fire. Lookouts also report weather changes and plot the location of lightning strikes during storms. The location of the strike is monitored for a period of days after in case of ignition.

USS Puritan, a civilian transport built by Craig Shipbuilding Company in Toledo, Ohio, was launched in 1901, and lengthened by 26 ft (7.9 m) in 1908. The ship sailed on the Great Lakes in passenger service, was purchased by the U.S. Navy at the end of the war, and returned to passenger service after the war. The ship sank in 1933 near Isle Royale in Lake Superior, and its wreck is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

SS Kamloops was a Canadian lake freighter that was part of the fleet of Canada Steamship Lines from its launching in 1924 until it sank with all hands in Lake Superior off Isle Royale, Michigan, United States, on or about 7 December 1927.

The Rock of Ages Light is a U.S. Coast Guard lighthouse on a small rock outcropping approximately 2.25 miles (3.62 km) west of Washington Island and 3.5 miles (5.6 km) west of Isle Royale, in Eagle Harbor Township, Keweenaw County, Michigan. It is an active aid to navigation.

The Rock Harbor Lighthouse is a light station located in Rock Harbor on Isle Royale National Park, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977.

The Passage Island Light Station is a lighthouse located 3.25 mi (5.23 km) NE of Isle Royale, in NW Lake Superior, Michigan on Passage Island. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2006.
The Glenlyon was a freighter built in 1893; it was sunk off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1924 and the remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

Algoma was a screw steamer built in 1883. She sank off Mott Island near Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1885 and some of her remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

America was a packet boat transporting passengers, mail, and packages between settlements along the North Shore of Lake Superior, an inland sea in central North America. Built in 1898, America sank in Washington Harbor off the shore of Isle Royale in 1928, where the hull still remains. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

The Cumberland was a wooden-hulled side paddlewheeler built in 1871; it was wrecked off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1877 and the remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

The Henry Chisholm was a wooden freighter; it was sunk off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1898 and the remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

SS Monarch was a passenger-package freighter built in 1890 that operated on the Great Lakes. She was sunk off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1906 and the remains of her wreck and cargo are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

The Minong Mine is a historic mine site located west of McCargoe Cove campground on Isle Royale National Park, Michigan, United States. The district contains both the remnants of a 19th-century copper mine and remains of pre-contact mining activity. Pre-contact archeological sited in the district include a Late Archaic copper mining pit site designated 20KE24 and a nearby site designated 20KE73. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977 and designated a National Historic Landmark in 2021.

The New Feldtmann Fire Tower is a fire tower located on Feldtmann Ridge in Isle Royale National Park. The tower was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2021.

The Ishpeming Fire Tower is a fire tower located on Greenstone Ridge in Isle Royale National Park. The tower was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2021.

SS Emperor was a steel-hulled Canadian lake freighter in service between 1911 and 1947. She was built between 1910 and April 1911 by the Collingwood Shipbuilding Company in Collingwood, Ontario, for Inland Lines, Ltd. of Midland, Ontario. She entered service on May 3, 1911. Emperor was sold to Canada Steamship Lines of Montreal, Quebec. Under the ownership of Canada Steamship Lines, she carried a wide variety of cargoes, but most frequently iron ore to Point Edward, Ontario, where it would be transported to Hamilton, Ontario, by train. After the opening of the fourth Welland Canal, Emperor carried the ore straight to Hamilton. She was involved in several accidents throughout her career.

SS Chester A. Congdon was a steel-hulled American lake freighter in service between 1907 and 1918. She was built in 1907 by the Chicago Shipbuilding Company of South Chicago, Illinois, for the Holmes Steamship Company, and was intended to be used in the grain trade on the Great Lakes. She entered service on September 19, 1907, when she made her maiden voyage. In 1911, Salt Lake City was sold to the Acme Transit Company. A year later, she was transferred to the Continental Steamship Company, and was renamed Chester A. Congdon, after lawyer and entrepreneur Chester Adgate Congdon. She was involved in several accidents throughout her career.






















