
The Ohio River is a 981-mile-long (1,579 km) river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River, which divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the sixth oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people.

The Allegheny River is a 325-mile-long (523 km) tributary of the Ohio River that is located in western Pennsylvania and New York in the United States. It runs from its headwaters just below the middle of Pennsylvania's northern border, northwesterly into New York, then in a zigzag southwesterly across the border and through Western Pennsylvania to join the Monongahela River at the Forks of the Ohio at Point State Park in Downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.

Fort Duquesne was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed as Pittsburgh in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Fort Duquesne was destroyed by the French before its British conquest during the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War on the North American front. The British replaced it, building Fort Pitt between 1759 and 1761. The site of both forts is now occupied by Point State Park, where the outlines of the two forts have been laid in brick.

New York State Route 17 (NY 17) is a major state highway that extends for 397 miles (638.91 km) through the Southern Tier and Downstate regions of New York in the United States. It begins at the Pennsylvania state line in Mina and follows the Southern Tier Expressway east through Corning to Binghamton and the Quickway from Binghamton east to Woodbury, where it turns south to follow the Orange Turnpike to the New Jersey state line near Suffern, where it connects to New Jersey Route 17. From the Pennsylvania border to the village of Waverly and from Binghamton to Windsor, NY 17 is concurrent with Interstate 86 (I-86). Eventually, the entire east–west portion of NY 17 from the Pennsylvania border to Woodbury will become I-86 as projects to upgrade the route to Interstate Highway standards are completed.

The Kittanning Path was a major east-west Native American trail that crossed the Allegheny Mountains barrier ridge connecting the Susquehanna River valleys in the center of Pennsylvania to the highlands of the Appalachian Plateau and thence to the western lands beyond drained by the Ohio River. Kittanning Village was the first major Delaware (Lenape) Indian settlement along the descent from the Allegheny Plateau.

French Creek is a tributary of the Allegheny River in northwestern Pennsylvania and western New York in the United States.

Fort Le Bœuf was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek, in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort was part of a line that included Fort Presque Isle, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne.
Pierre-Joseph Céloron de Blainville — also known as Celeron de Bienville — was a French Canadian Officer of Marine. In 1739 and '40 he led a detachment to Louisiana to fight the Chickasaw in the abortive Chickasaw Campaign of 1739. In 1749 he led the 'Lead Plate Expedition' to advance France's territorial claim on the Ohio Valley.
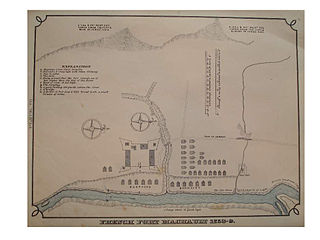
Fort Machault was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort helped the French control these waterways, part of what was known as the Venango Path from Lake Erie to the Ohio River. It was one of four forts designed to protect French access to the Ohio Country and connections between its northern and southern colonies. From north to south the forts were Fort Presque Isle, Fort Le Boeuf, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne. In January 1759 the British launched an expedition to attack Fort Machault, but had to turn back after encountering resistance from French-Allied Native Americans. The fort was abandoned by the French in August 1759, and burned so that the British could not use it. It was replaced by the British in 1760 with Fort Venango.

New York State Route 394 (NY 394) is a state highway located within Cattaraugus and Chautauqua counties in southwestern New York in the United States. Its western terminus is located on the shore of Lake Erie at an intersection with NY 5 in the Westfield hamlet of Barcelona. The eastern terminus is located at an interchange with the Southern Tier Expressway at the Coldspring hamlet of Steamburg. From Mayville to Jamestown, NY 394 follows the western edge of Chautauqua Lake. East of Jamestown, the route straddles the Southern Tier Expressway and connects to the highway in four different locations, including at its eastern terminus.

New York State Route 380 (NY 380) was a 23-mile (37 km) north–south state highway in Chautauqua County, New York, in the United States. The southern terminus of the route was at an intersection with NY 60 in the town of Gerry. Its northern terminus was at a junction with NY 5 north of the village of Brocton in the town of Portland. In actuality, most of NY 380 was maintained by Chautauqua County; the only part that was maintained by the New York State Department of Transportation was from NY 424 in Stockton to the west end of its overlap with U.S. Route 20 (US 20) in Brocton.
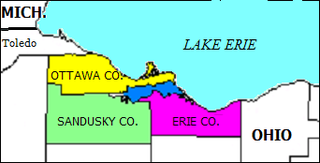
Sandusky Bay is a bay on Lake Erie in northern Ohio, formed at the mouth of the Sandusky River. It was identified as Lac Sandouské on a 1718 French map, with early variations recorded that suggest the name was derived from Native American languages. The Thomas A. Edison Memorial Bridge was constructed across it in the 20th century to connect highways in Erie and Ottawa counties.

The Great Lakes Seaway Trail, formerly named and commonly known as the Seaway Trail, is a 518-mile (834 km) National Scenic Byway in the northeastern United States, mostly contained in New York but with a small segment in Pennsylvania. The trail consists of a series of designated roads and highways that travel along the Saint Lawrence Seaway—specifically, Lake Erie, the Niagara River, Lake Ontario, and the Saint Lawrence River. It begins at the Ohio state line in rural Erie County, Pennsylvania, and travels through several cities and villages before ending at the Seaway International Bridge northeast of the village of Massena in St. Lawrence County, New York. It is maintained by the non-profit Seaway Trail, Inc.
Venango Path was a Native American trail between the Forks of the Ohio and Presque Isle, Pennsylvania, United States of America. The latter was located at Lake Erie. The trail, a portage between these important water routes, was named after the Lenape village of Venango, at the confluence of French Creek and the Allegheny River. The village site was later developed by European Americans as the small city of Franklin, Pennsylvania.

Lake Erie Basin consists of Lake Erie and surrounding watersheds, which are typically named after the river, creek, or stream that provides drainage into the lake. The watersheds are located in the states of Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, and Pennsylvania in the United States, and in the province of Ontario in Canada. The basin is part of the Great Lakes Basin and Saint Lawrence River Watershed, which feeds into the Atlantic Ocean. 80% of the lake's water flows in from the Detroit River, with only 9% coming from all of the remaining watersheds combined. A littoral zone serves as the interface between land and lake, being that portion of the basin where the lake is less than 15 feet (4.6 m) in depth.

Chautauqua Creek is a tributary of Lake Erie, approximately 15 miles (24 km) long, in the southwestern corner of New York in the United States. The headwaters of the creek rise in the town of Sherman, in Chautauqua County, and flow in a northerly direction through the town and village of Westfield where they empty into Lake Erie. For much of its length, the creek serves as the boundary line between the towns of Westfield and Chautauqua.

This article covers the water based Canadian canoe routes used by early explorers of Canada with special emphasis on the fur trade.
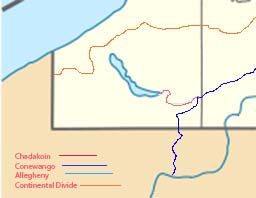
The Chadakoin River is a 7.8-mile-long (12.6 km) stream that is a tributary of the Conewango Creek. The Chadakoin lies entirely in Chautauqua County in Western New York in the United States.

The Saint Lawrence River Divide is a continental divide in central and eastern North America that separates the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Basin from the southerly Atlantic Ocean watersheds. Water, including rainfall and snowfall, lakes, rivers and streams, north and west of the divide, drains into the Gulf of St. Lawrence or the Labrador Sea; water south and east of the divide drains into the Atlantic Ocean or Gulf of Mexico. The divide is one of six continental divides in North America that demarcate several watersheds that flow to different gulfs, seas or oceans.


















