Related Research Articles

An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage, precision agriculture, forest fire monitoring, river monitoring, environmental monitoring, policing and surveillance, infrastructure inspections, smuggling, product deliveries, entertainment, and drone racing.

The Northrop Grumman MQ-4C Triton is an American high-altitude long endurance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed for and flown by the United States Navy as a surveillance aircraft. Together with its associated ground control station, it is an unmanned aircraft system (UAS). Developed under the Broad Area Maritime Surveillance (BAMS) program, the Triton is intended to provide real-time intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions (ISR) over vast ocean and coastal regions, continuous maritime surveillance, conduct search and rescue missions, and to complement the Boeing P-8 Poseidon maritime patrol aircraft.
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) project to modernize the National Airspace System (NAS). The FAA began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to finish the final implementation segment by 2030. The goals of the modernization include using new technologies and procedures to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation.
The Detroit Region Aerotropolis is a four-community, two-county public-private economic development partnership focused on driving corporate expansion and new investments around Wayne County Airport Authority's airports: Detroit Metropolitan Airport and Willow Run Airport. The Detroit Region Aerotropolis promotes greenfield expansion in Southeast Michigan, offering development-ready land centered in an expansive network of transportation infrastructure including two airports, three major interstates, five Class-A rail lines, and the American Center for Mobility.
Remote and virtual tower (RVT) is a modern concept where the air traffic service (ATS) at an airport is performed somewhere other than in the local control tower. Although it was initially developed for airports with low traffic levels, in 2021 it was implemented at a major international airport, London City Airport.

The AeroVironment RQ-20 Puma is an American unmanned aircraft system which is small, battery powered, and hand-launched. Its primary mission is surveillance and intelligence gathering using an electro-optical and infrared camera. It is produced by AeroVironment.

SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd. or Shenzhen DJI Sciences and Technologies Ltd. or DJI is a Chinese technology company headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong, backed by several state-owned entities. DJI manufactures commercial unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) for aerial photography and videography. It also designs and manufactures camera systems, gimbal stabilizers, propulsion systems, enterprise software, aerial agriculture equipment, and flight control systems.

Amazon Prime Air, or simply Prime Air, is a drone delivery service operated by Amazon. The service uses delivery drones to autonomously fly individual packages to customers, and launched in 2022. The service currently operates in two cities in the US, with plans to expand into the UK and Italy in 2024.

A delivery drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) used to transport packages that include medical supplies, food, or other goods. Given their life-saving potential, use cases for medical supplies in particular have become the most widely-tested type of drone delivery, with trials and pilot projects in dozens of countries such as Australia, Canada, Botswana, Ghana, Uganda, the UK, the US among others. Delivery drones are typically autonomous and electric, sometimes also operated as a part of a fleet.
The US Federal Aviation Administration has adopted the name small unmanned aircraft system (sUAS) to describe aircraft systems without a flight crew on board weighing less than 55 pounds. More common names include UAV, drone, remotely piloted vehicle (RPV), remotely piloted aircraft (RPA), and remotely operated aircraft (ROA). These unmanned aircraft flown in the USA's National Airspace System must operate under the rules of a Community Based Organization for recreational purposes or 14 CFR Part 107 for commercial operations. All UAVs weighing more than 250 grams flown for any purpose must be registered with the FAA.

Regulation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) involves setting safety requirements, outlining regulations for the safe flying of drones, and enforcing action against errant users.
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have been used for domestic police work in various countries around the world since the mid-2000s. Their appeal comes from their small size, lack of crew, and lower cost compared to police helicopters. UAVs may be used for search and rescue operations, aerial patrols, and other roles that are usually served by crewed police aircraft. UAVs can be powerful surveillance tools by carrying camera systems capable of license plate scanning and thermal imaging, as well as radio equipment and other sensors. While a vast majority of law enforcement UAVs are unarmed, documents obtained by digital rights group Electronic Frontier Foundation indicated the U.S. Customs and Border Protection would consider arming their UAVs with "non-lethal weapons designed to immobilize" targets.

The DJI Phantom is a series of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), typically quadcopters, developed by Chinese technology company DJI. DJI Phantom devices were released between 2013 and 2019.
PrecisionHawk was a commercial drone and data company. Founded in 2010, PrecisionHawk is headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina with another global office in Toronto, Canada and satellite offices around the world. PrecisionHawk is a manufacturer of drones (Lancaster) and has more recently focused heavily on developing software for aerial data analysis (DataMapper) and drone safety systems (LATAS). PrecisionHawk is a member of the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration Pathfinder Initiative and the NASA UTM Program. An angel investor in the company, Bob Young, founder of Red Hat, became CEO in August 2015. In August 2016, PrecisionHawk became the first U.S. company to receive an FAA exemption to commercially fly drones beyond the operator's visual line of sight.
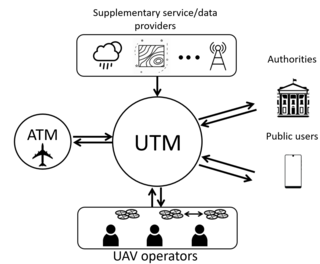
Unmanned aircraft system traffic management (UTM) is an air traffic management ecosystem under development for autonomously controlled operations of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) by the FAA, NASA, other federal partner agencies, and industry. They are collaboratively exploring concepts of operation, data exchange requirements, and a supporting framework to enable multiple UAS operations beyond visual line-of-sight at altitudes under 400 ft above ground level in airspace where FAA air traffic services are not provided.

Wing Aviation LLC, doing business as Wing, is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. that develops a drone delivery system and UTM systems. The company completed its first deliveries in 2014. The company has operations in Australia, the United States, Finland, and Ireland, with potential expansion to the United Kingdom planned. In July 2018, Project Wing graduated from Google X to become an independent Alphabet company. As of January 2019, Wing began delivering take-out food and beverages out of its test facility in Bonython, Australia, as part of a pilot program. In April 2019 Wing became the first drone delivery company to receive an Air operator's certificate from the Federal Aviation Administration to allow it to operate as an airline in the US. In the first quarter of 2022, the service made more than 50,000 deliveries.
Unifly is a European software company that provides a platform for drone telematics services for unmanned traffic management. The company provides mapping and location data to connect authorities with pilots for the safe integration of drones into the airspace and unmanned aviation. The company was a wholly owned subsidiary of VITO until a corporate spin-off in 2015. Unifly is headquartered in Antwerp, Belgium.
Cape is a California-based company that has developed a cloud-based software for Aerial Telepresence of drones. It is the first platform for full commercial drone telepresence and the first company in the U.S. to be awarded Section 333 and Part 107 waivers by the FAA. The company was founded in 2014 and operates in the US, Canada, New Zealand, Middle East, Mexico, and Australia. By May 2018, it had performed more than 100,000 successful drone flights. Chris Rittler serves as a CEO of the company and Kabe Termes is the director of operations.
Parimal Kopardekar is a senior technologist for NASA as the Air Transportation Systems and principal investigator for the Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management project at the NASA Ames Research Center. He holds a doctorate and master's in industrial engineering and bachelor's degree in production engineering. He is the recipient of the Samuel J. Heyman Service to America Medals in the promising innovation category for the UTM system in 2018.
References
- ↑ "Operation Zenith". Altitude Angel. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "UK-first as drones fly safely in controlled airspace". NATS. 2018-11-23. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "Operation Zenith - Powered By GUARDIAN UTM - November 21st 2018". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "Operation Zenith: the UK's most comprehensive drone trial – ARPAS UK" . Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "Scenario 1". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "Scenario 3". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "Scenario 5". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "Call for new technology to ensure drone safety". Financial Times. 22 November 2018.
- ↑ "About - Operation Zenith - Powered By GUARDIAN UTM". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ "Delivery Partners - Operation Zenith - Powered By GUARDIAN UTM". Operation Zenith. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "Showing a new side of Vodafone Business at CES 2019". www.vodafone.com. 28 January 2019. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "DJI Supports Major Test Of Drone Airspace Integration". DJI Official. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "FREQUENTIS technology successfully connects ATM to UTM in real-life drone integration trial at Manchester Airport". Frequentis.com. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ Press (2018-11-23). "Aviation partnership takes to the skies in UK-first to fly drones safely in controlled airspace". sUAS News - The Business of Drones. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ Wright, Mike (2019-10-05). "'Drone lanes' and new air controls needed to manage growing number of devices, report says". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235 . Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- ↑ Butterworth-Hayes, Philip (2018-11-22). "Operation Zenith provides landmark demonstration of UTM technology capabilities". Unmanned airspace. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ↑ "Airspace Q3 2019 - The meaning of success - Altitude Angel and Frequentis | CANSO". www.canso.org. 26 August 2019. Retrieved 2020-06-26.