Statistics
- Order statistics
- First-order statistics, e.g., arithmetic mean, median, quantiles
- Second-order statistics, e.g., correlation, power spectrum, variance
- Higher-order statistics, e.g., bispectrum, kurtosis, skewness
Order in mathematics may refer to:
In logic, model theory and type theory:
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and as an end to obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science.
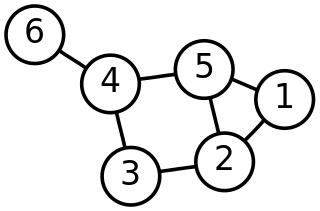
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" rather than "continuous". Objects studied in discrete mathematics include integers, graphs, and statements in logic. By contrast, discrete mathematics excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as real numbers, calculus or Euclidean geometry. Discrete objects can often be enumerated by integers; more formally, discrete mathematics has been characterized as the branch of mathematics dealing with countable sets. However, there is no exact definition of the term "discrete mathematics".

In mathematics, especially in order theory, a preorder or quasiorder is a binary relation that is reflexive and transitive. The name preorder is meant to suggest that preorders are almost partial orders, but not quite, as they are not necessarily antisymmetric.
In mathematics, a total order or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation on some set , which satisfies the following for all and in :
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limits, and related theories, such as differentiation, integration, measure, infinite sequences, series, and analytic functions.
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that are fundamentally discrete rather than continuous. In contrast to real numbers that have the property of varying "smoothly", the objects studied in discrete mathematics – such as integers, graphs, and statements in logic – do not vary smoothly in this way, but have distinct, separated values. Discrete mathematics, therefore, excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as calculus and analysis.
Order theory is a branch of mathematics that investigates the intuitive notion of order using binary relations. It provides a formal framework for describing statements such as "this is less than that" or "this precedes that". This article introduces the field and provides basic definitions. A list of order-theoretic terms can be found in the order theory glossary.

In mathematics, a cyclic order is a way to arrange a set of objects in a circle.[nb] Unlike most structures in order theory, a cyclic order is not modeled as a binary relation, such as "a < b". One does not say that east is "more clockwise" than west. Instead, a cyclic order is defined as a ternary relation [a, b, c], meaning "after a, one reaches b before c". For example, [June, October, February], but not [June, February, October], cf. picture. A ternary relation is called a cyclic order if it is cyclic, asymmetric, transitive, and connected. Dropping the "connected" requirement results in a partial cyclic order.

Lists of mathematics topics cover a variety of topics related to mathematics. Some of these lists link to hundreds of articles; some link only to a few. The template to the right includes links to alphabetical lists of all mathematical articles. This article brings together the same content organized in a manner better suited for browsing. Lists cover aspects of basic and advanced mathematics, methodology, mathematical statements, integrals, general concepts, mathematical objects, and reference tables. They also cover equations named after people, societies, mathematicians, journals, and meta-lists.
Descriptive complexity is a branch of computational complexity theory and of finite model theory that characterizes complexity classes by the type of logic needed to express the languages in them. For example, PH, the union of all complexity classes in the polynomial hierarchy, is precisely the class of languages expressible by statements of second-order logic. This connection between complexity and the logic of finite structures allows results to be transferred easily from one area to the other, facilitating new proof methods and providing additional evidence that the main complexity classes are somehow "natural" and not tied to the specific abstract machines used to define them.

Symmetry occurs not only in geometry, but also in other branches of mathematics. Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that a mathematical object remains unchanged under a set of operations or transformations.
Mathematics is a broad subject that is commonly divided in many areas or branches that may be defined by their objects of study, by the used methods, or by both. For example, analytic number theory is a subarea of number theory devoted to the use of methods of analysis for the study of natural numbers.
In mathematics, equivalent definitions are used in two somewhat different ways. First, within a particular mathematical theory, a notion may have more than one definition. These definitions are equivalent in the context of a given mathematical structure. Second, a mathematical structure may have more than one definition.